Common alloy elements include nickel, copper, aluminum, chromium, vanadium and other elements.
1.Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element commonly used in the production of wind power accessories abroad. Nickel can be infinitely dissolved in nodular cast iron, which has no effect on the morphology of graphite and the number of eutectic clusters, and there will be no segregation in the eutectic clusters. Nickel can stabilize austenite, reduce austenite transformation temperature, make a small amount of residual austenite appear in the matrix structure, and reduce the low-temperature brittle transformation temperature of nodular cast iron, which is conducive to the improvement of tensile strength and impact toughness of nodular cast iron. Studies have shown that adding 0.7% – 1.0% nickel can significantly improve the low-temperature impact toughness of nodular cast iron, but excessive nickel will also reduce the impact toughness of nodular cast iron.
2.Copper
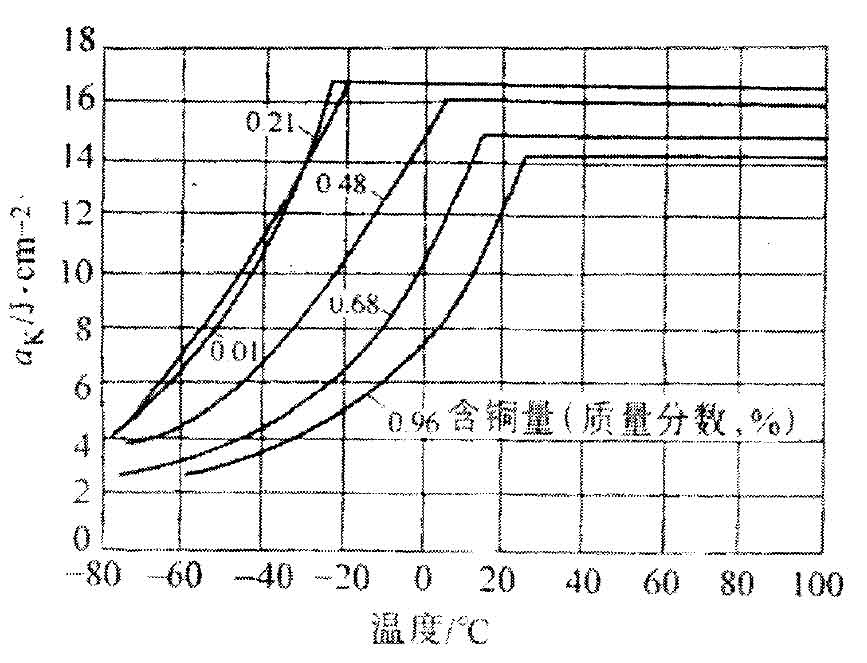
During Eutectic Transformation, copper can promote graphitization and reduce the formation of free cementite. During eutectoid transformation, it can promote the formation of pearlite, increase the tensile strength and reduce the elongation of nodular cast iron. With the increase of copper content, the low-temperature brittle transition temperature increases and the low-temperature impact toughness decreases. The figure shows the effect of copper on the impact toughness of nodular cast iron. When the copper content is 0.21%, it has little effect. When it increases to 0.48%, the low-temperature brittleness transition temperature increases significantly and the low-temperature impact toughness decreases. It is found from the figure that in order to ensure the low-temperature impact toughness, the copper content of nodular cast iron should not exceed 0.5%.
3.Aluminium
Aluminum can refine and strengthen eutectic and improve the tensile strength of nodular cast iron. Elongation and impact toughness decreased. When the silicon content exceeds or the phosphorus content exceeds, the ductile iron will appear tempering brittleness and the low-temperature brittleness transition temperature will rise sharply. Adding molybdenum can avoid this kind of tempering brittleness. The common amount is 0.1% – 0.3%.
4.Chromium
Chromium is infinitely soluble in nodular cast iron and has a strong affinity with carbon. It is easy to form network carbide in the structure, which reduces the tensile strength, elongation and impact toughness at the same time. Therefore, the chromium content should be strictly limited during production.
5.Vanadium
Vanadium is a strong anti graphitization element, which promotes the formation of carbide during eutectic and eutectoid transformation, increases the low-temperature brittle transition temperature of nodular cast iron and significantly reduces the low-temperature impact toughness. When the vanadium content is below 0.5%, pearlite increases obviously, tensile strength and hardness increase, and elongation decreases with the increase of vanadium content. When the content is too high, free cementite will appear and reduce the mechanical properties of nodular cast iron.