Heat treatment can change the matrix structure of nodular cast iron, eliminate the phenomenon of component segregation in the structure, improve the uniformity of structure and improve the mechanical properties of nodular cast iron. It plays an important role in the production of nodular cast iron.
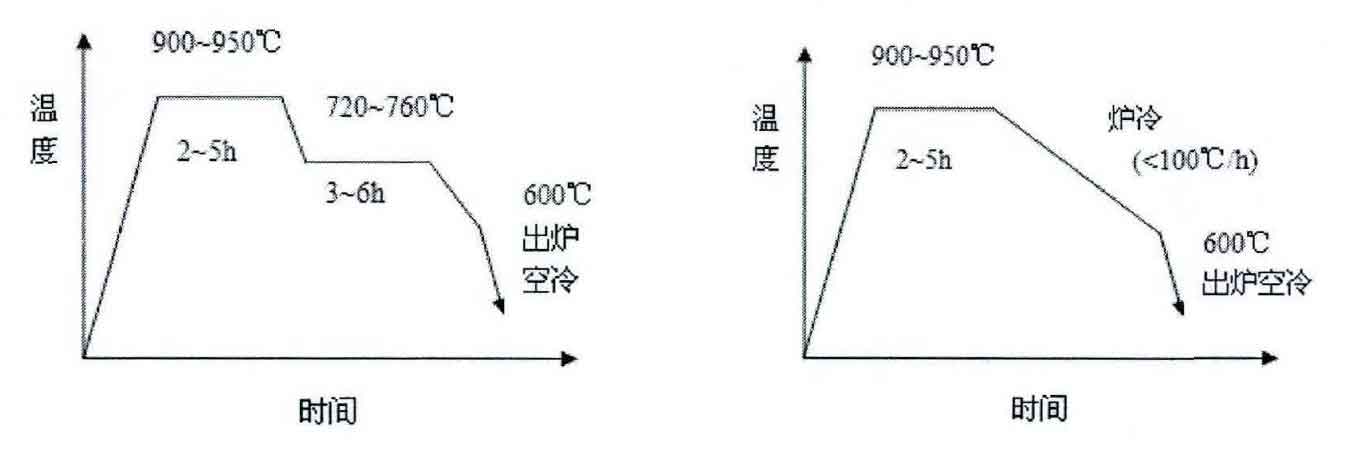
In the production of wind power nodular iron castings, graphitization annealing process is commonly used for heat treatment. The specific process is shown in the figure. Firstly, high-temperature graphitization annealing is carried out to eliminate cementite and phosphorus eutectic structure, and then low-temperature graphitization annealing is carried out to obtain ferrite matrix structure. Low temperature graphitization annealing of nodular cast iron can be divided into two processes: heat preservation and slow cooling in the furnace. Since slow cooling annealing in the furnace will produce part of pearlite structure and can not ensure the complete transformation of matrix into ferrite, high and low temperature two-stage graphitization annealing process is mostly used. The holding time at high temperature is determined according to the content and wall thickness of cementite in nodular cast iron, and the holding time at low temperature is determined according to the content and wall thickness of pearlite.