Compared with gray cast iron, nodular cast iron has strict requirements for chemical composition. The raw molten iron of nodular cast iron requires high carbon content and low silicon manganese sulfur and phosphorus content. Therefore, in order to obtain high-quality castings, the furnace charge must be selected correctly. The phosphorus content of molten iron does not change during melting, but the silicon content will increase after adding inoculant and spheroidizing agent. Therefore, the silicon content of newborn iron is required to be low, generally within 0.8-1.75%, and the silicon content of newborn iron used in our laboratory is 1.2%.
The basic requirements of raw molten iron are high temperature, low sulfur and no partial oxidation. Nodular cast iron can be produced as long as the tapping temperature is above 1380 ° C and the sulfur content in the raw molten iron is less than 0.10%. In the laboratory experiment, in order to ensure that the molten iron will not solidify when ultrasonic is applied in the spheroidizing ladle, the tapping temperature is increased to 1480 ° C. At present, the furnaces used for melting molten iron in China are mainly acid cupola. Electric arc furnace and induction furnace have also been developed in recent years. In the laboratory, we use small medium frequency induction furnace to melt molten iron, as shown in Figure 1. Induction furnace has the characteristics of simple structure, low noise and low pollution. It can obtain high-quality molten iron with high temperature, low sulfur and no oxidation, and the composition is uniform.
Spheroidizing agent is a hot metal additive that can make the graphite in cast iron precipitate in a spherical shape. The development of spheroidizing agent plays an important role in promoting the production of nodular cast iron. There are many kinds of spheroidizing agents, such as industrial pure magnesium, magnesium alloy spheroidizing, rare earth magnesium alloy spheroidizing agent, etc. Among them, ferrosilicon magnesium alloy is one of the widely used spheroidizing agents. The rare earth magnesium ferrosilicon spheroidizing agent used in the experiment has a silicon content of 1%. In the production of nodular cast iron, the role of inoculation has attracted more and more attention. Inoculation treatment can not only promote graphitization and eliminate free cementite, but also effectively refine eutectic clusters, make graphite fine and round, increase the number, and reduce the dispersion of brittle phases and inclusions at the boundary of clusters. There are many kinds of inoculants, including ferrosilicon, calcium silicon, composite silicon-based inoculants, ferromanganese, aluminum, etc. the inoculant used in the experiment is fesi75 with a silicon content of 75%.
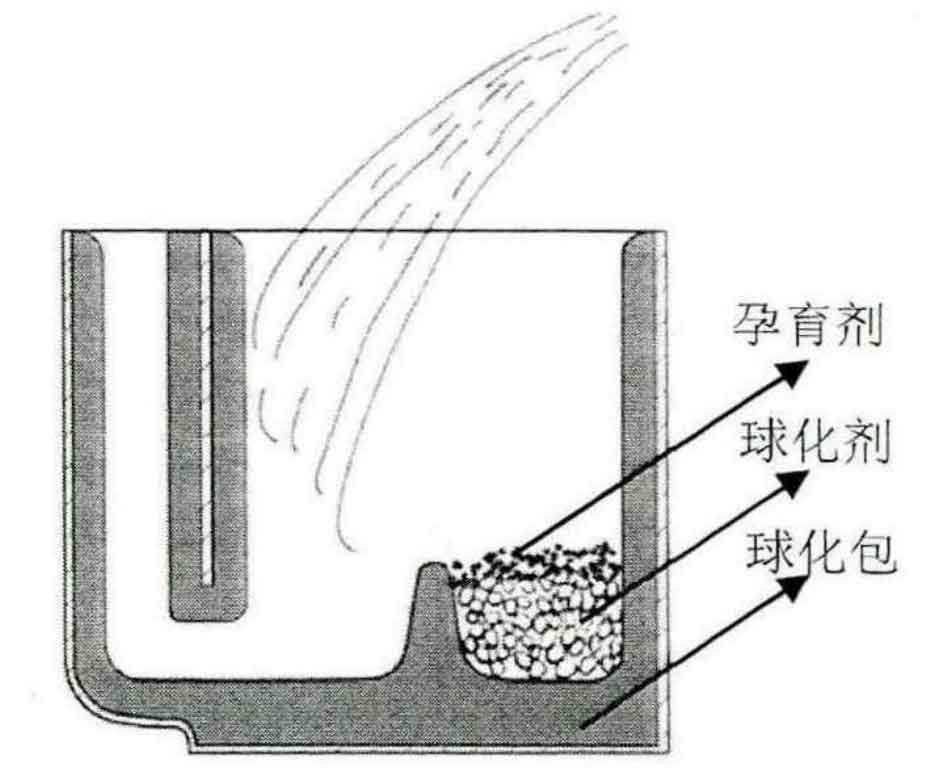
In the laboratory, the amount of spheroidizing agent and inoculant used each time is calculated according to the amount of molten iron dissolved each time and the target silicon content of nodular cast iron is 2.1%. Considering that the molten iron dissolved in the laboratory experiment is about 35kg, the spheroidizing agent and inoculant should be preheated before being put into the spheroidizing bag to prevent the local solidification of molten iron caused by chilling. For a small amount of molten iron, spheroidization and inoculation can be treated together. Using the punching method, the rare earth magnesium ferrosilicon with a block size of 15mm-25mm is stacked on one side of the preheated molten iron ladle and covered with ferrosilicon powder. When the molten iron is discharged from the furnace, the other side of the molten iron ladle is opposite to the tapping tank, as shown in Figure 2. Pouring can be carried out after the action of molten iron and nodulizing agent inoculant is basically completed and the nodulization is completed.