The figure below shows the graphite morphology of nodular cast iron prepared under different amplitude conditions. Figures (a) – (d) show the graphite morphology of nodular graphite cast iron prepared with amplitudes of 0.75, 2, 3 and 4mm respectively.
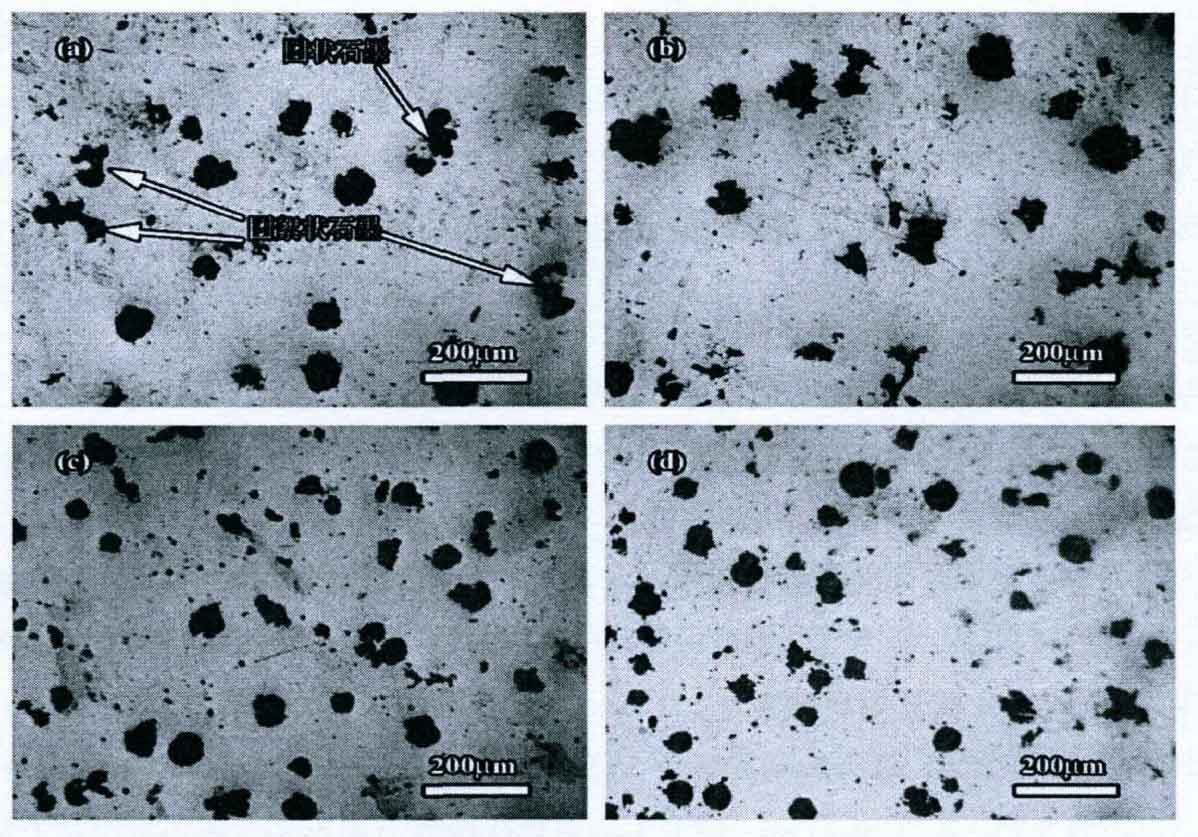
It can be seen from the figure that when the amplitude is 0.75, the number of graphite balls in the nodular graphite cast iron is small, the diameter of graphite balls is large, and there are a small amount of mass and flocculent graphite, as shown by the arrow in figure (a). When the amplitude increases from 0.75mm to 2mm, the graphite morphology becomes worse and the mass graphite increases. Continue to increase the amplitude. When the amplitude is 3mm, the number of graphite balls in nodular cast iron increases, and there are a small amount of group graphite and group flocculent graphite. When the amplitude is further increased to 4mm, the morphology of graphite balls in nodular cast iron is better, and the number of graphite balls is more. With the help of image analysis software, the graphite ball parameters of nodular graphite cast iron prepared under different amplitude conditions are statistically analyzed, and the analysis results are shown in the table.
| Amplitude /mm | Number of graphite balls per square millimeter | Diameter/ μm | Spheroidization rate |
| 0.75 | 54 | 50.0 | 0.82 |
| 2 | 50 | 62.1 | 0.74 |
| 3 | 84 | 42.3 | 0.87 |
| 4 | 105 | 40.6 | 0.91 |
It can be seen from the table that with the increase of amplitude, the number of graphite balls per unit area first decreases and then increases. In the nodular cast iron prepared under the condition of 4mm amplitude, the number of graphite balls per unit area is more. The diameter of graphite ball increases first and then decreases with the increase of amplitude. The average diameter of graphite ball of nodular cast iron prepared at the amplitude of 2mm is larger, which is 62.1 μ m; When the amplitude is 4mm, the average diameter of nodular cast iron graphite balls is the smallest, which is 40.6 μ m. However, the spheroidization rate of graphite balls in nodular cast iron shows the same trend as the number of graphite balls per unit area.
It can be seen from the formula that in the process of vibration EPC, the vibration frequency is constant, and the external force on the crystalline graphite nucleation in the metal solution is proportional to the amplitude, that is, the greater the amplitude, the greater the external force on the graphite nucleation. With the increase of the vibration force on the graphite crystal nucleus, the greater the interference of graphite in the growth process, that is, for the whole solidification process of the casting, the vibration force will promote the homogenization of the composition of the metal solution and increase the concentration difference between the metal solution and the graphite / metal solution interface. From this point of view, the application of vibration is conducive to the growth of the graphite ball. However, because the vibration can also increase the nucleation rate of graphite in the metal solution, the increase of the number of graphite nuclei in the metal solution will reduce the diameter of graphite balls. Therefore, the amplitude plays an important role in the morphology, size and distribution of graphite by affecting the nucleation and growth of graphite balls, so that the number of graphite balls per unit area and the size of graphite balls in nodular cast iron show an opposite trend, that is, the more the number of graphite balls per unit area, the smaller the average diameter of graphite balls.
From the point of view of graphite spheroidization rate of nodular cast iron, when the amplitude is 2mm, the lowest is graphite morphology, while when the amplitude is 4mm, the highest is graphite spheroidization rate and the best is graphite morphology. The change of graphite spheroidization rate should be the result of the synergistic effect of many factors. After the introduction of vibration, the closure of austenite halo around graphite ball is disturbed by vibration, which affects the growth rate of graphite along c direction and changes the spheroidization rate of graphite in nodular cast iron.
