In computer vision, the purpose of target detection is to extract the region of interest from the image or video, give the target location and output its label at the same time. The target detection algorithm based on deep learning belongs to supervised learning, that is, it needs labeled training data to train a model that can realize bucket tooth target detection. Therefore, first collect or collect the bucket data with bucket teeth, and then add labels and position information to the detection target, that is, bucket teeth, on the image by means of manual annotation. The data is divided as follows:
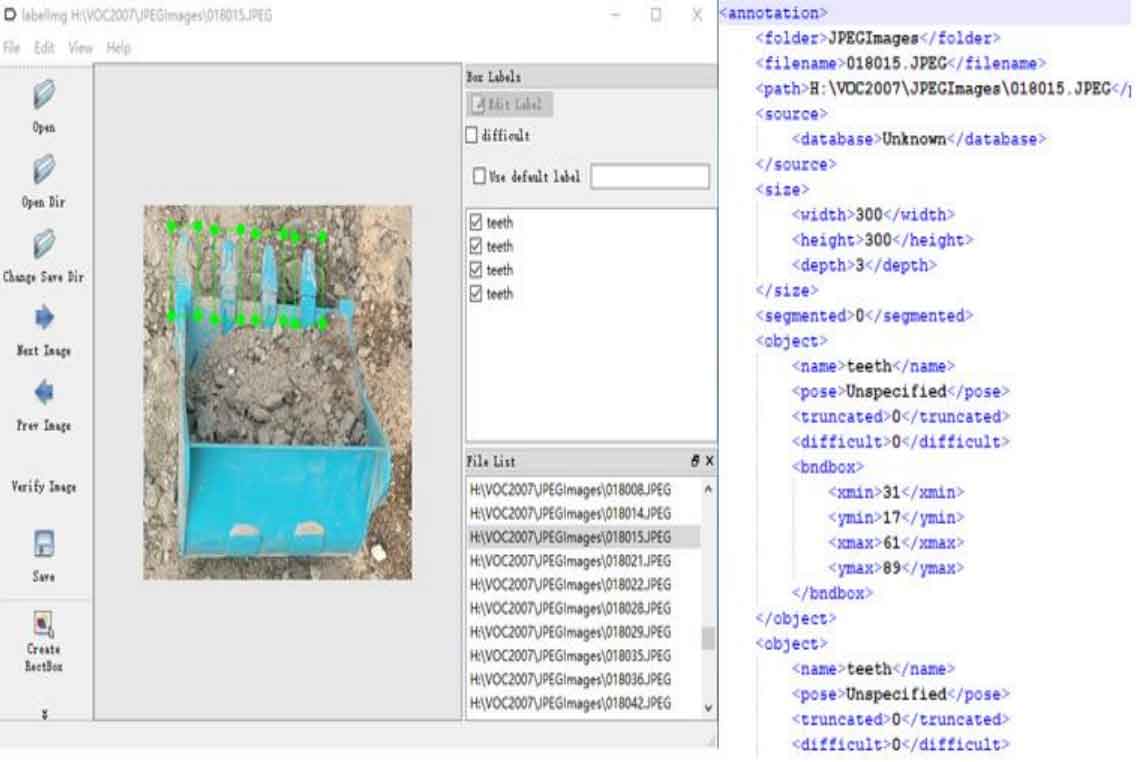
Under the condition of ensuring that the training set, verification set and test set do not intersect, 12500 images are extracted from the collected model bucket photos, including 10000 as the training set and 2500 as the verification set; In addition, of the 531 real bucket photos with bucket teeth collected and screened, 370 will be used as the training set and the rest as the verification set. For convenience, the bucket tooth data of the actual bucket used for target detection is named rstod (real shore tooth for object detection) data set, and the bucket tooth data of the model bucket is mstod (model shore tooth for object detection) data set. The labeling tool used is labelimg, which supports manually adding rectangular boxes to label the objects in the picture, specifying labels, and saving the location information of labels and interested targets in the image to an XML format file readable by fast r-cnn, as shown in the figure.
It can be seen from the figure that the established bucket tooth target detection data set only marks the normal bucket teeth and sets the label as “tooth”, and the rest are used as the background and provided to the neural network as negative samples.