1. Causes
Through the collection and analysis of more than 100 casting idlers, a total of 12 casting idlers have serious ultra penetration casting defects on the riser surface, accounting for about 10%, which are mainly affected by the following two factors:
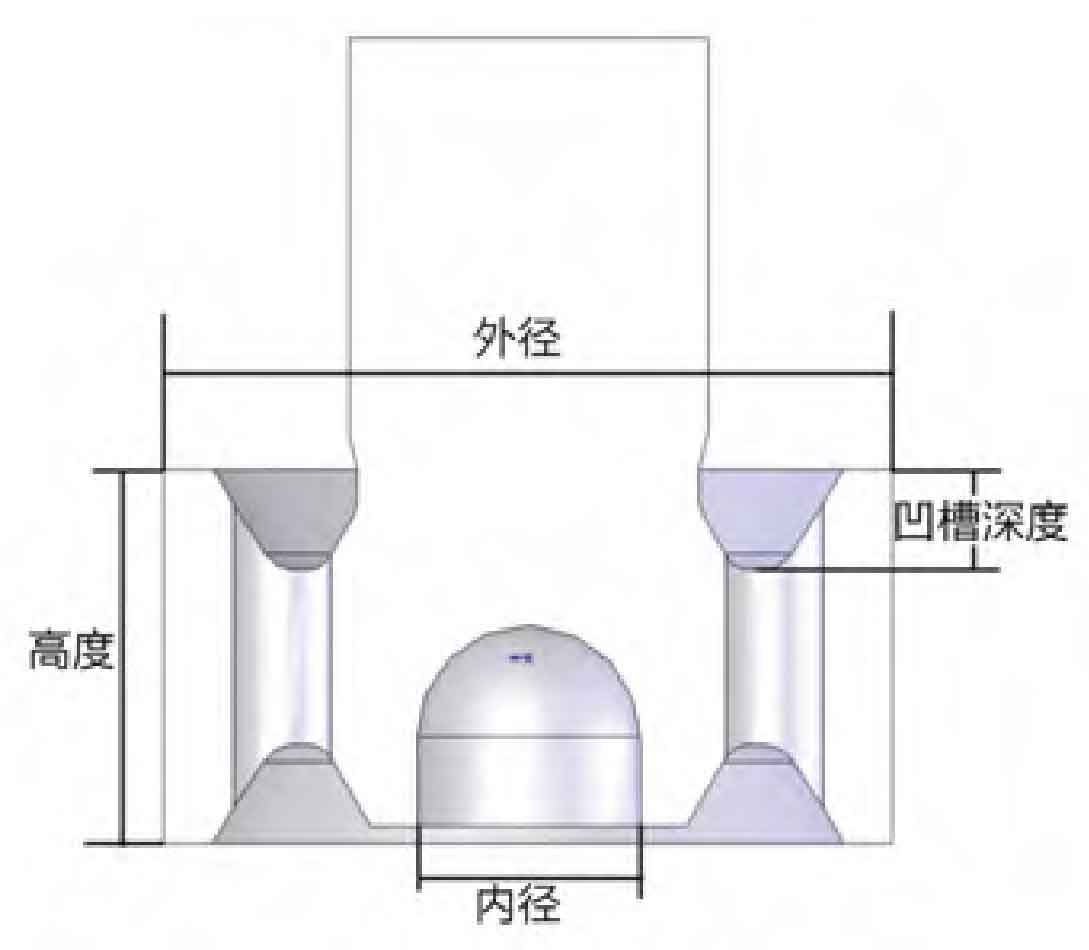
(1) Groove depth of casting idler
The groove depth of the 12 cast idlers ranges from 105 mm to 300 mm, and the groove depth of 10 cast idlers exceeds 250 mm. The steel liquid in the riser at the upper end of the outer rim of the casting supporting roller shall pass over the groove sand core, and then be fully fed upward to meet the internal quality requirements. The deeper the groove is, the greater the pressure difference that the liquid steel needs to overcome, the more difficult it is to feed upward, and the worse the feeding effect is. The more likely UT casting defects are to occur at the outer rim near the upper end face, as shown in Figure 1.
(2) Thickness of hot joint and cold iron of casting idler
Among the 12 cast idlers, 8 cast idlers with diameters greater than 2200 mm belong to large cast idlers, among which 3 cast idlers are of the same specification. Therefore, the cast idlers of this specification are taken as an example for analysis.
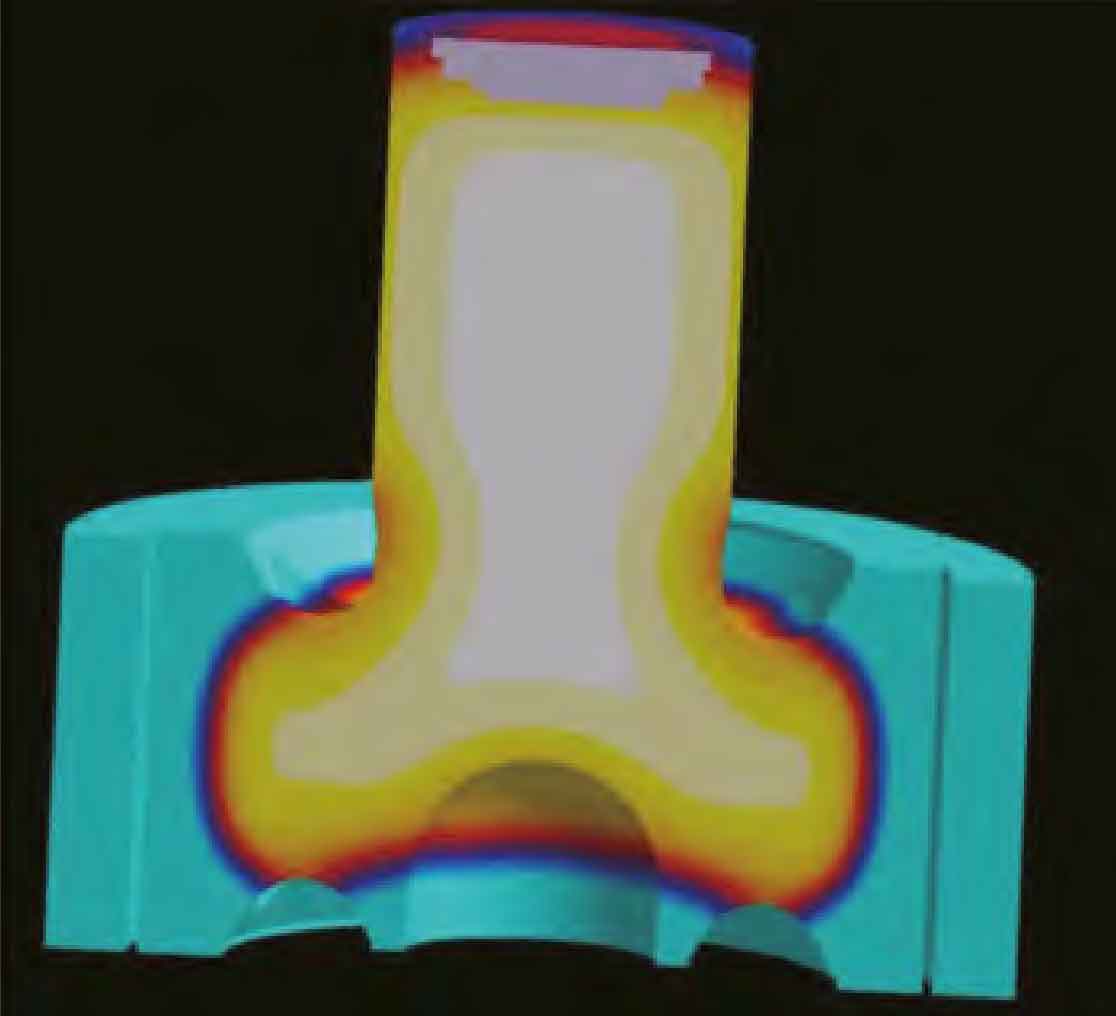
It was found that a total of 8 cast idlers of this specification were required to be produced in the same batch, and the drawing size was excircle ϕ 2 500 mm, inner circle ϕ 1 010 mm, height 1 150 mm, groove depth 300 mm. Since there is only one special cold mold ring (about 220 mm thick) on site, only one casting idler can be produced at a time. The next casting idler can be produced after the mold is demoulded at the expiration of the insulation period. Therefore, in order to ensure the production cycle, another set of model is made, and the original 300 mm thick standard cold iron molding is used for the outer round sand mold. As shown in Figure 2.
The production results show that in the above two process schemes, 5 pieces of casting idlers are produced with cold iron with a thickness of 300 mm, and the quality is good. The three casting idlers produced with cold die ring all had large ultra penetration casting defects, and the casting defects were typical casting shrinkage porosity.
The larger the casting idler is, the thicker the outer rim is, the larger the hot spot is, and the longer the solidification time is. Moreover, the casting idler is made of low-alloy steel, and the paste solidification characteristics are more obvious. When the thickness of the whole ring of cold iron is limited, its chilling effect will be lower than the expected target, leading to the easy occurrence of ultra detection casting defects.
2. Countermeasures
According to the above analysis, measures should be taken to expand the feeding channel and enhance the chilling effect during the production of large casting idler.
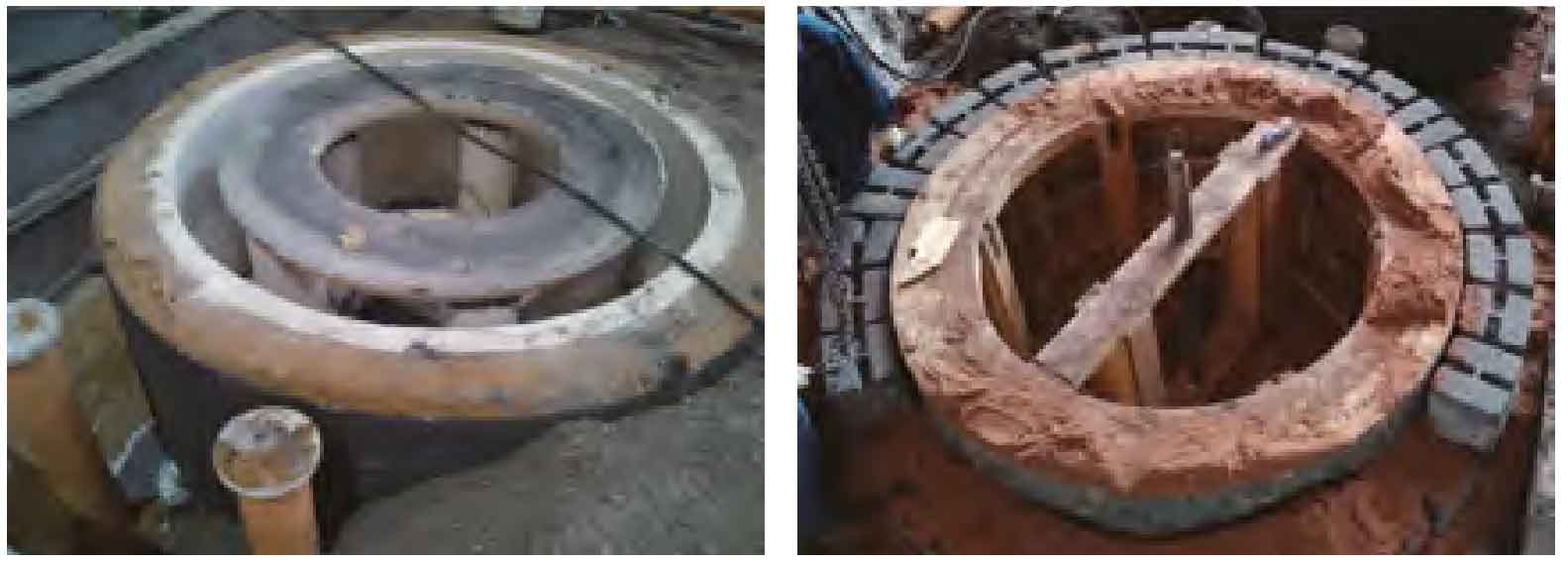

(b) 300 mm thick chilled iron production casting idler
The groove shape can be changed, the groove depth can be reduced, and the feeding channel can be expanded by optimizing the design structure or increasing the casting process filler. In addition, with the increase of casting idler size, according to the change of hot spot size, the thickness of chilled iron is increased to improve the chilling effect. At the same time, the upper end surface of the whole circle of cold iron should be aligned with the parting surface of the casting roller as much as possible, leaving enough sand hanging layer within 20 mm to improve the chilling effect of the cold iron on the upper part that is difficult to feed.