Referring to the latest ductile iron standard GB / t1348-2009, the brand, mechanical properties and metallographic structure of ductile iron for wind power fittings are listed in the table. It can be seen from the table that the nodular cast iron for wind power fittings is characterized by two grades: QT350-22L and QT400-18L. The mechanical properties increase the index of low-temperature impact absorption energy of 12j, and the matrix structure is ferrite.
| Brand | Tensile strength RM / MPa | Elongation δ/% | Brinell hardness HB | Metallographic structure | Minimum impact energy of V-notch / J (low temperature – 20 ± 2 ° C) | Minimum impact energy of V-notch / J (low temperature – 40 ± 2 ° C) |
| QT350-22L | 350 | 22 | ≤160 | Ferrite | — | 12 |
| QT350-22AL | 320-350 | 15-22 | ≤160 | Ferrite | — | 12 |
| QT400-18L | 400 | 18 | ≤160 | Ferrite | 12 | — |
| QT400-18AL | 360-380 | 12-18 | 120-175 | Ferrite | 12 | — |
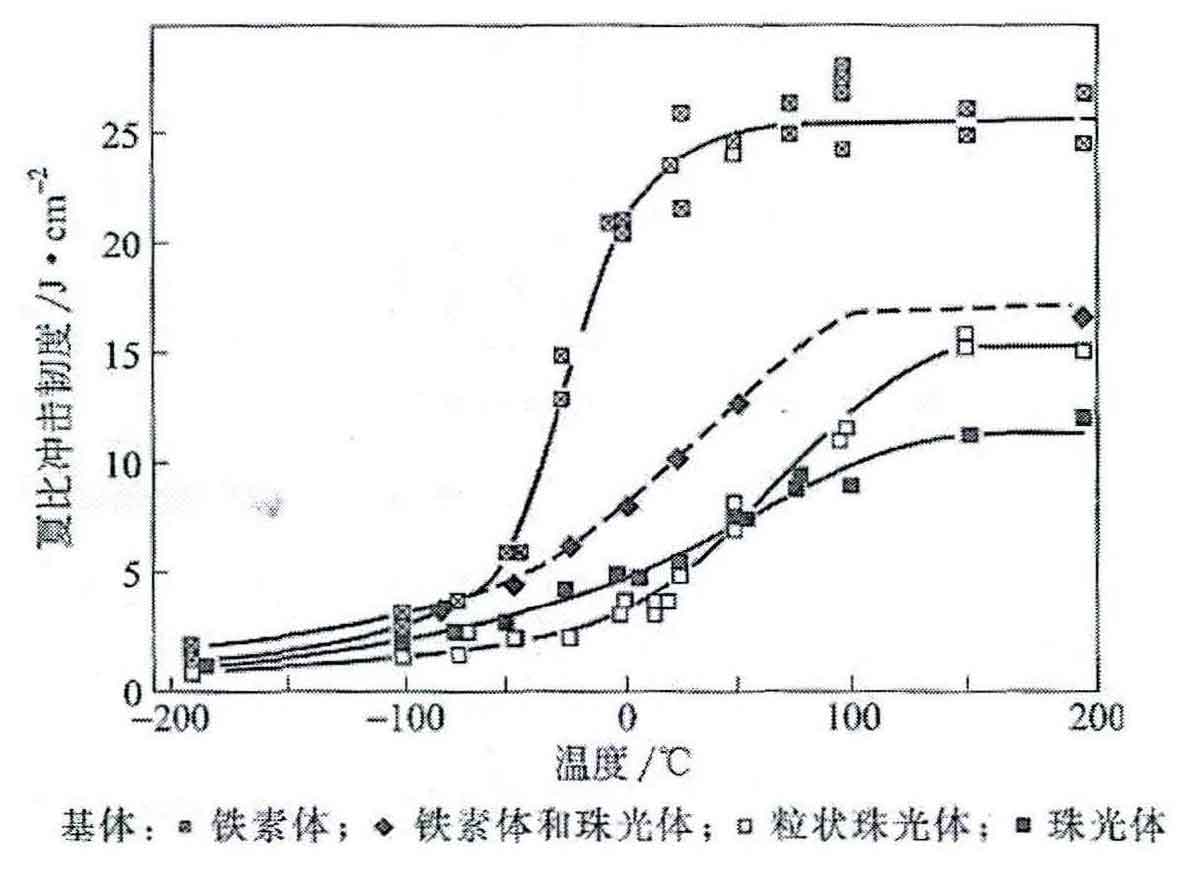
The impact toughness of nodular cast iron decreases with the decrease of temperature, and there is an obvious phenomenon of low-temperature toughness. The figure shows the phenomenon of low-temperature brittleness of nodular cast iron. As shown in the figure, when the temperature drops to the critical temperature, the impact toughness of nodular cast iron decreases significantly. Low temperature brittleness is directly related to crystal structure. Generally speaking, body centered cubic crystal structure has low temperature brittleness, while face centered cubic crystal structure has no low temperature brittleness. The ferrite in nodular cast iron is carbon soluble α- The interstitial solid solution of Fe has a body centered cubic structure, so the ductile iron for wind power fittings also has the phenomenon of low temperature brittleness.
Although ductile iron for wind power fittings also has low-temperature brittleness, its low-temperature brittleness transition temperature can be lower than – 40 ° C or lower by strengthening and toughening the structure. Thus, even at a low temperature of 40 ℃, nodular cast iron does not reach the critical temperature of low-temperature embrittlement, and still has high low-temperature impact toughness.