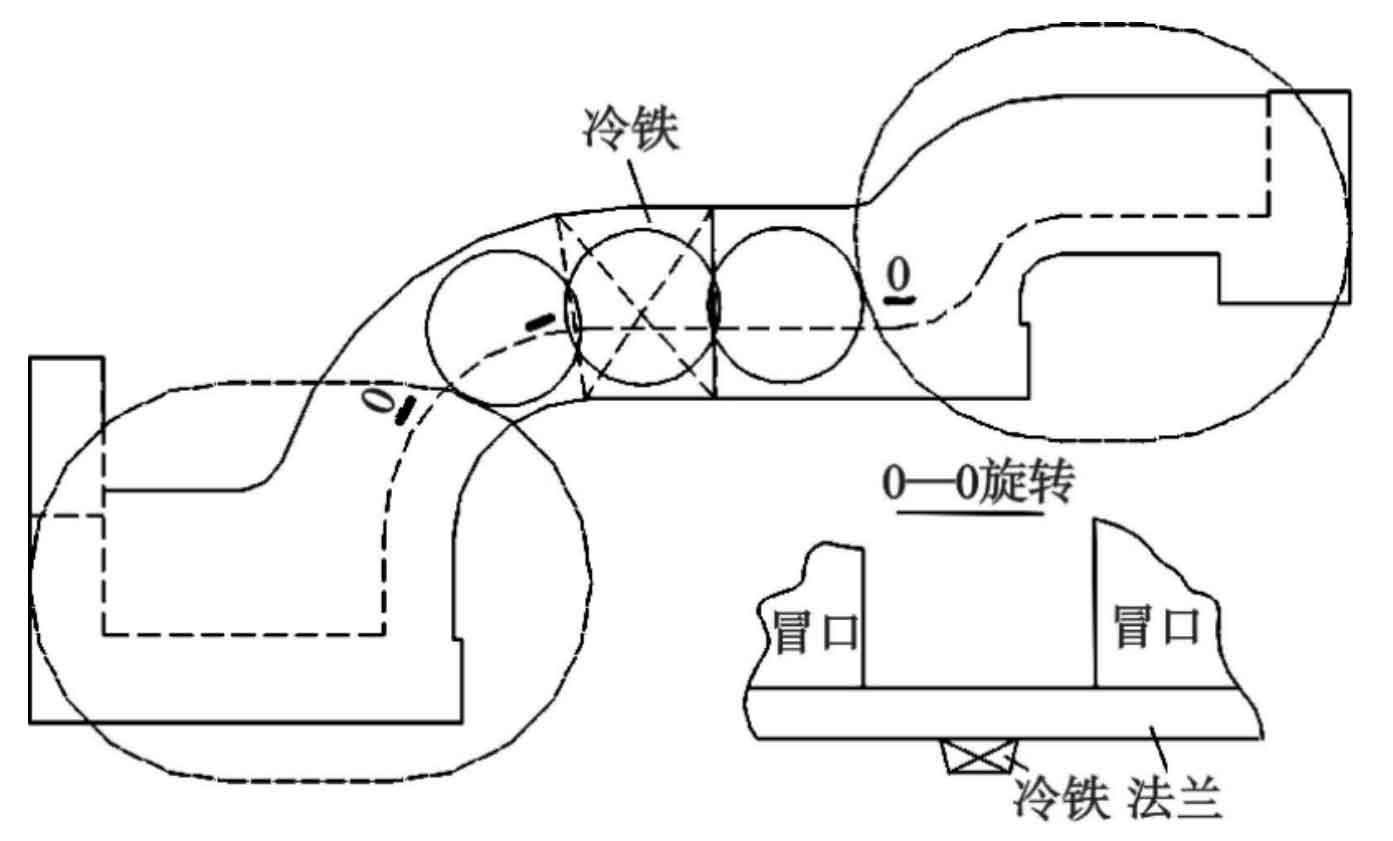
Chilled iron is the most commonly used chilling material to control the solidification of cylinder block castings. It can be used in combination with the riser. It can be formed as the end, isolate the feeding area of the riser, strengthen the sequential solidification of cylinder block castings, and prevent shrinkage cavity or porosity defects of cylinder block castings. An external cooling iron (Fig. 1) is set between the two risers. The external cooling iron with different thickness is used for process verification. Through ultrasonic flaw detection, there are still defects exceeding the standard, but the position has moved up. It can be seen that the cold iron arrangement process has local chilling effect, which can change the temperature distribution between the split flange risers, which is conducive to sequential solidification, but it does not produce a large temperature gradient on the whole. In particular, it will soon reach the thermal saturation state and stop chilling, which still can not obtain dense structure and meet the quality requirements.
The main function of the riser is to feed the cylinder block castings, as well as the functions of air outlet and slag collection. Cancel the cold iron between risers, and connect the risers as riser subsidies or integral risers (Fig. 2). The height of subsidies shall not be less than the size of hot joints at the flange of this part, so that the split can cover the risers completely, so as to facilitate the upward floating of gases and inclusions, so as to ensure the dense organization at the flange. After actual production, no defects exceeding the standard were found through flaw detection, which met the quality requirements.