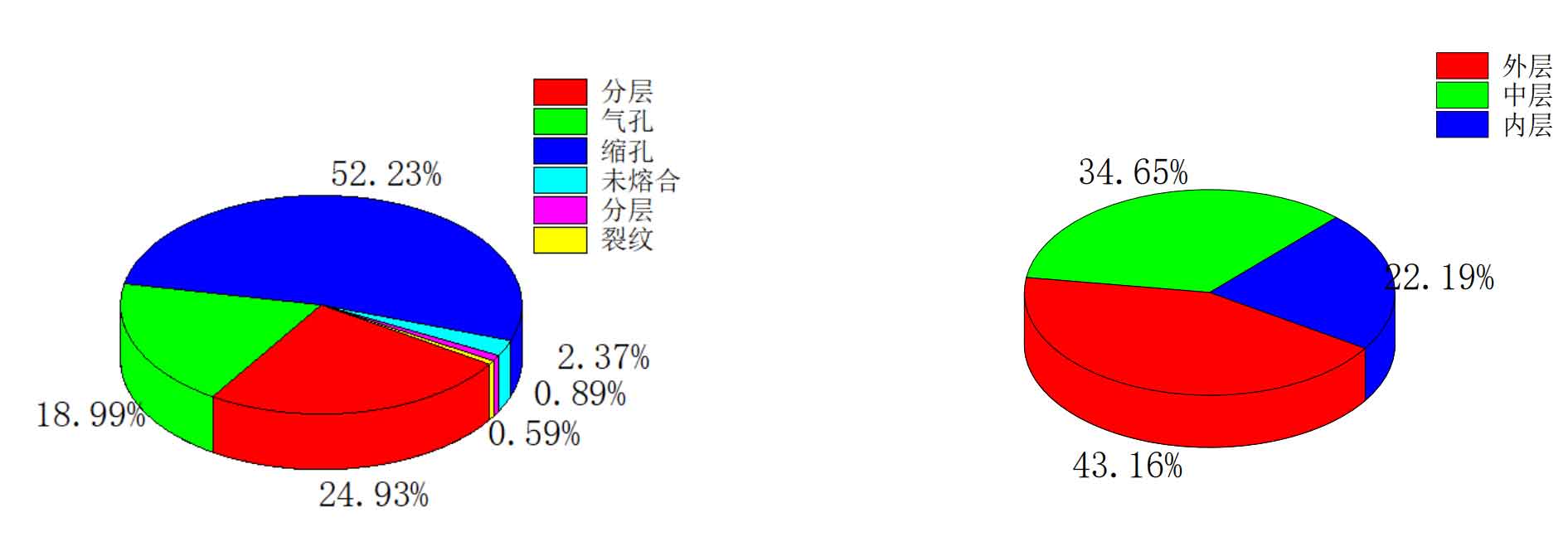
Casting defect data of 144 large and small sections of cast steel joints, including 74 sections with casting defects, accounting for 51.39% of all sections. A total of 337 visually visible casting defects were found. The casting defects are divided into 6 categories: pore defects, shrinkage defects, inclusion defects, delamination defects, crack defects and core support incomplete fusion defects. The proportion of each casting defect is shown in Figure a.
It can be seen from the figure that among the 337 visually visible casting defects, pore defects account for 18.99%, shrinkage porosity accounts for 52.23%, and inclusion defects account for 24.93%. If both shrinkage porosity defects and pore defects are regarded as holes, holes will account for 71.22%, which indicates that hole defects account for the majority. It can be considered that hole defects are the dominant casting defects in this cast steel joint. For the main section of the cast steel joint, the casting defects are mainly concentrated in the middle of the cast steel joint, there are few casting defects at both ends, and the average size of the casting defects of each section is not much different. The following will analyze the distribution of casting defects at each position, mainly from the perspective of area and thickness position.
(1) The distribution of casting defects in the overall position of cast steel joints can be divided into three categories: main pipe, intersecting line (the intersection of main pipe and branch pipe) and branch pipe position. A total of 150 casting defects were found in 120 small sections and large sections of branch pipes, including 46 near the intersection line, 63 on the main pipe and 41 on the branch pipe.
In terms of shrinkage defects, a total of 78 shrinkage defects were found, including 40 on the main pipe, 27 on the intersecting line and 11 on the branch pipe; In terms of inclusion defects, a total of 53 inclusion defects were found, including 20 on the main pipe, 11 on the intersection line and 22 on the branch pipe; In terms of pore defects, a total of 9 pore defects were found, including 7 on the main pipe and 2 near the intersection line;
Among the 41 casting defects on the branch pipe, there are 22 inclusions, accounting for 53.66%, 0 pores, accounting for 0%, 11 shrinkage porosity, accounting for 26.83%, and 8 non fusion defects, accounting for 19.51%. It can be seen that the most casting defects on the branch pipe are inclusion defects;
Among the 45 casting defects near the intersection line, there are 12 inclusions, accounting for 26.67%, 2 pores, accounting for 4.44%, 29 shrinkage porosity, accounting for 64.44%, and 2 cracks, accounting for 4.44%. It can be seen that the most casting defects near the intersection line are shrinkage cavity and porosity defects; Among the 63 casting defects in the main pipe, there are 19 inclusions, accounting for 30.16%, 7 pores, accounting for 11.11%, and 37 shrinkage and porosity, accounting for 58.73%. It can be seen that the most common casting defect in the main pipe is shrinkage and porosity.
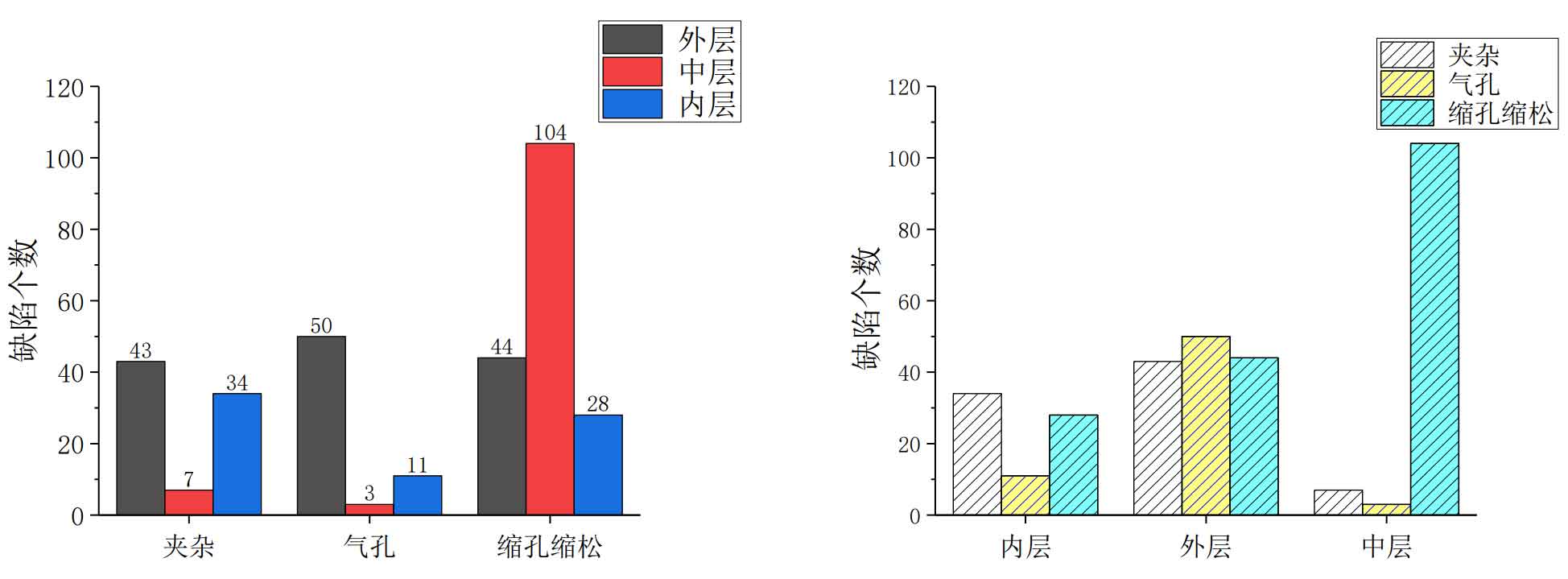
(2) The distribution of casting defects in the thickness direction of cast steel joints is divided into three positions: outer layer, middle layer and inner layer, which correspond to 1 / 3 of the outer wall thickness, 1 / 3 of the middle wall thickness and 1 / 3 of the inner wall thickness respectively. Among them, there are 142 outer casting defects, accounting for 43.16%, 114 middle casting defects, accounting for 34.65%, and 73 inner casting defects, accounting for 22.19%. There are few inner casting defects, and the casting defects are mainly concentrated in the middle and outer layers. Most casting defects are distributed in the outer and middle layers of cast steel joints, that is, the outer 2 / 3 wall thickness, and there are few casting defects in the inner side.
In terms of pore defects, a total of 64 pore defects were found, including 50 pore defects with 1 / 3 wall thickness, accounting for 78.13% of all pore defects; There are three porosity defects in the middle 1 / 3 wall thickness, accounting for 5.56%; There are 11 inner layers, accounting for 17.19%, and few. This fully shows that the distribution of pore defects has a strong regularity, and most of the pore defects are distributed on the outside of the cast steel joint.
In terms of shrinkage cavity and porosity defects, 176 shrinkage cavity and porosity defects were found, of which 44 were outside the cast steel joint, accounting for 25%; There are 104 casting defects in the middle of the wall thickness, accounting for 59.09%; There are 28 casting defects in 1 / 3 of the internal wall thickness, accounting for 15.91%; This shows that the shrinkage porosity defects of the cast steel joint are mainly concentrated in the middle of the wall thickness.
In terms of inclusion defects, a total of 84 inclusion defects were found, and 43 inclusion defects were distributed outside the cast steel joint, accounting for 51.19%; There are 7 inclusion defects in the middle of the wall thickness, accounting for 8.33%; 34 inclusions are distributed inside the cast steel joint, accounting for 40.48%; It can be seen that the probability of inclusion in the middle of the wall thickness is very low, and the inclusion basically appears in the outer and inner wall thickness.