The figure shows the fracture morphology of grey cast iron prepared under different amplitude conditions. Among them, figures (a) – (d) are the fracture morphology of grey cast iron prepared under the conditions of amplitude of 0.75, 2, 3 and 4mm respectively.
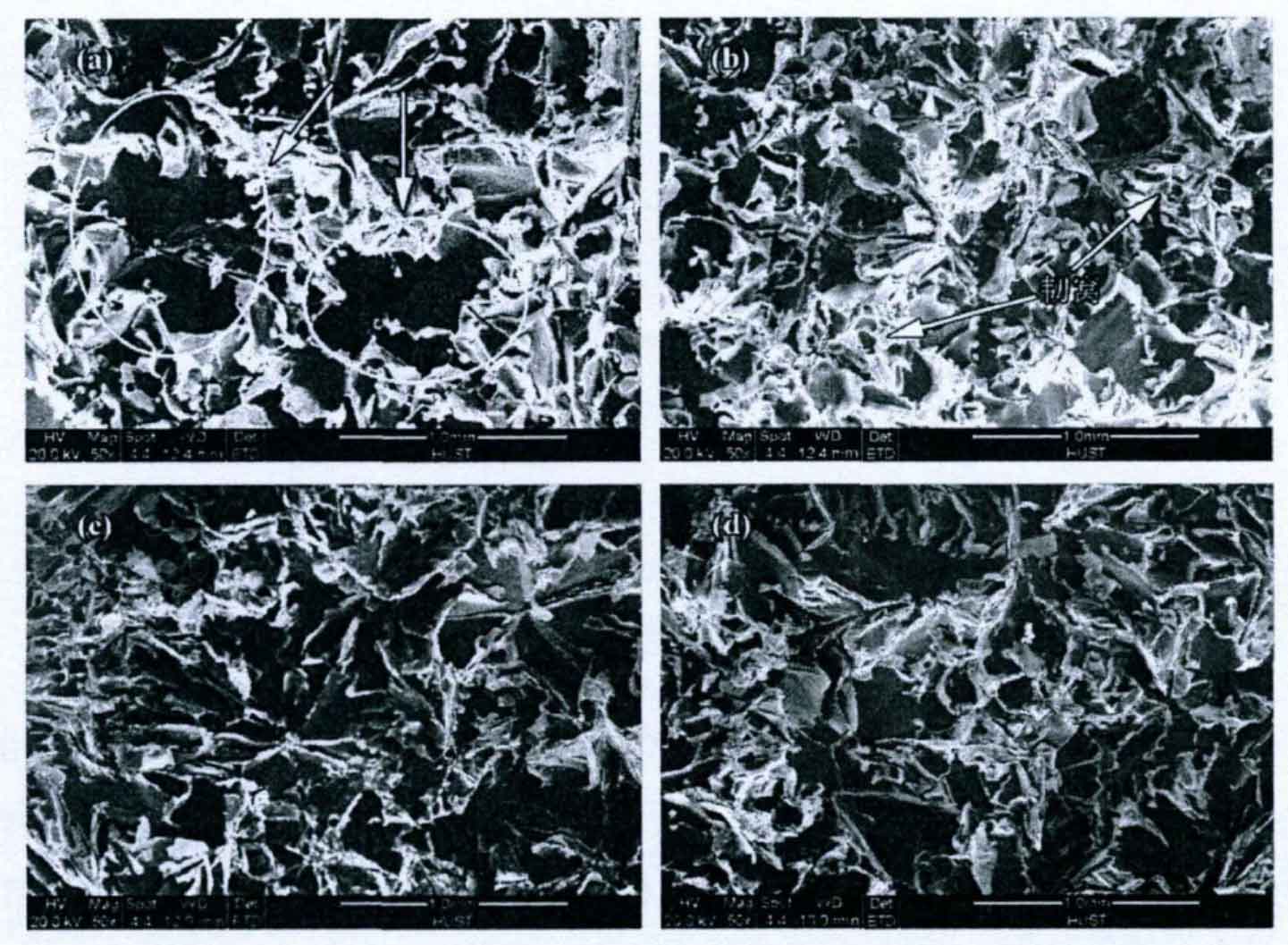
It can be seen from the figure that the fracture surface of grey cast iron is still dominated by the cleavage fracture characteristics of A-type flake graphite and matrix structure, and there are many holes on the fracture surface. The existence of these holes reduces the tensile strength of grey cast iron. In addition, the graphite on the fracture surface of gray cast iron is flower shaped, and its role in the tensile fracture process of gray cast iron has been analyzed in detail, so it will not be repeated here.
Comparing the size of holes in the fracture morphology of gray cast iron prepared under different amplitudes, it can be found that when the amplitude is 0.75mm, the size of hole defects is the largest, as shown by the arrow in figure (a), so its tensile strength is the lowest. On the fracture surface of the gray cast iron with the amplitude of 2mm, the size of eutectic is small, and there are many dimples on the fracture surface, so the tensile strength of the gray cast iron is high. When the amplitude is further increased to 4mm, large hole defects appear on the fracture surface of gray cast iron. Therefore, it can be inferred that the tensile strength of gray cast iron is low when the amplitude is 4mm.
