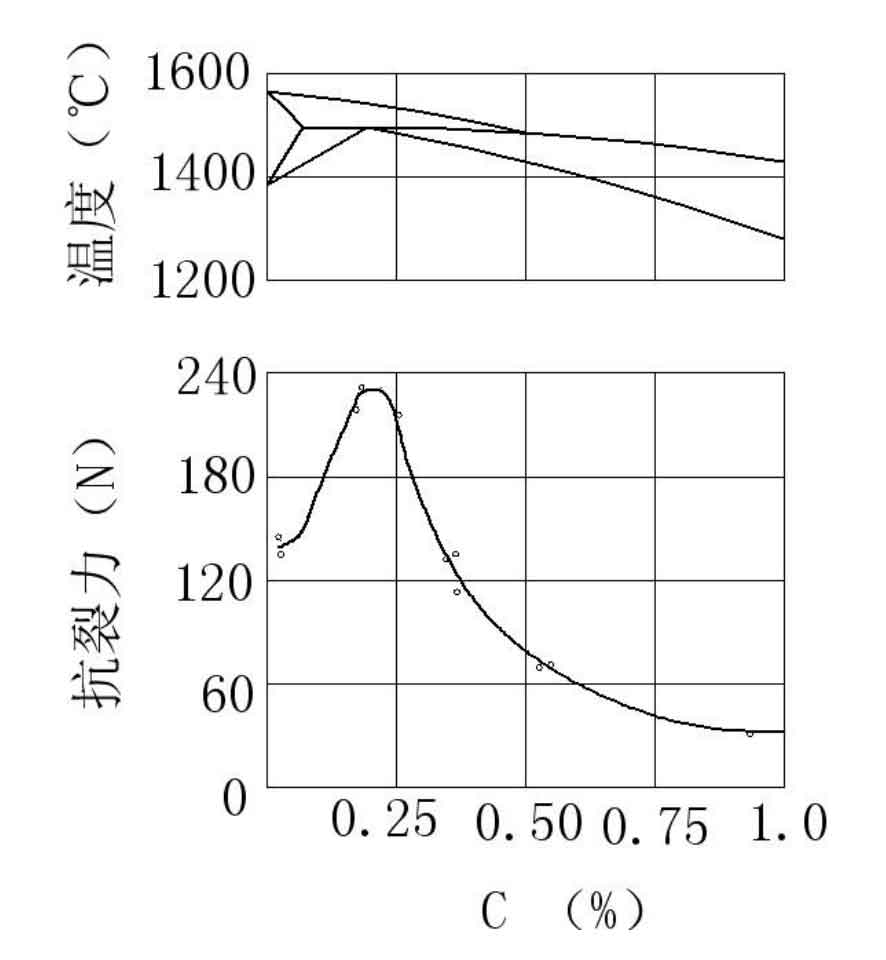
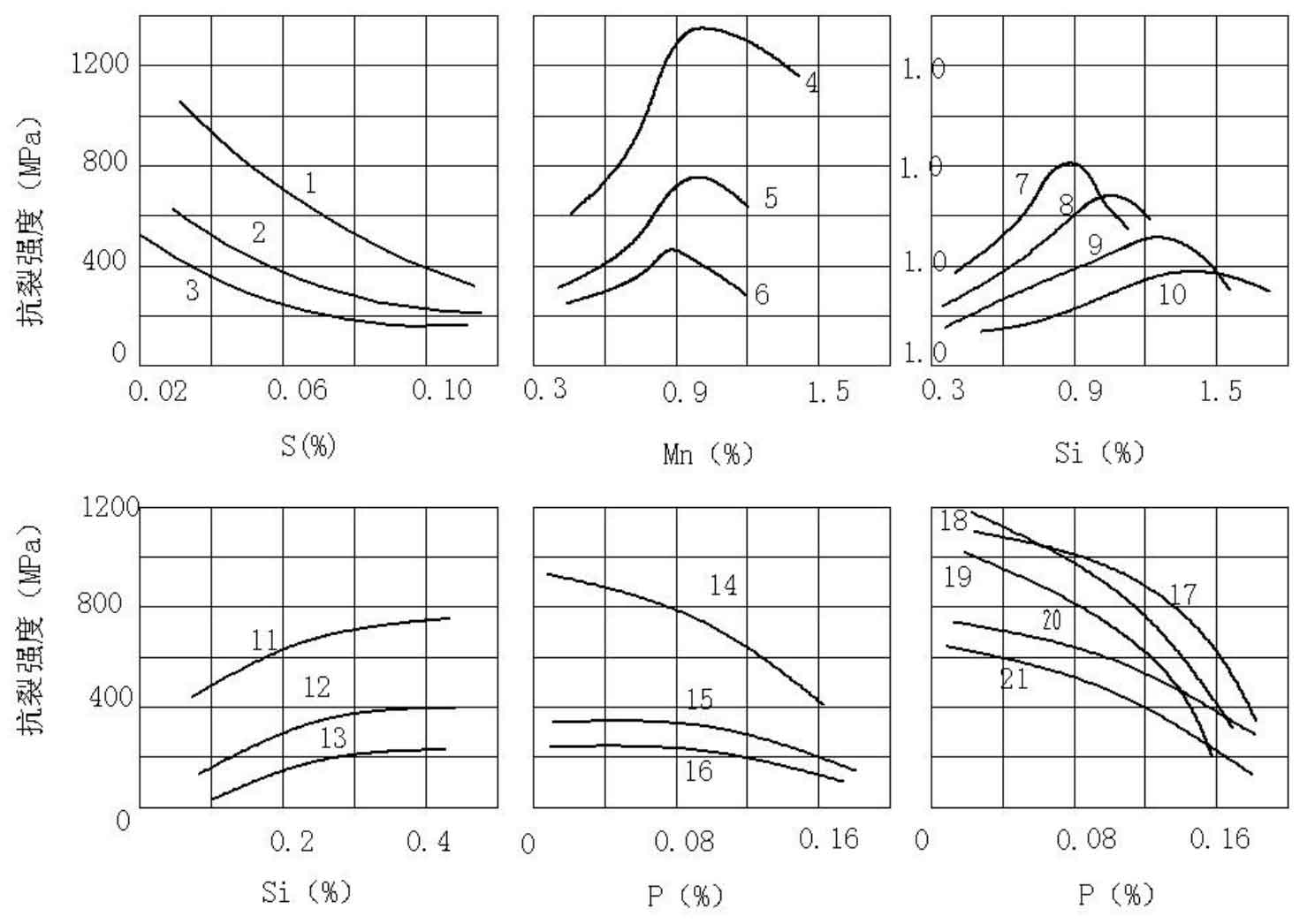
The larger the hot brittle zone of the alloy, the greater the shrinkage of the casting in this temperature range, and the greater the tendency of forming hot tears casting defects. Any element that enlarges the hot brittle zone can promote the formation of hot cracking. The effects of major elements on the hot tears resistance of carbon steel are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2. Among them, sulfur has a great influence on the formation of tears and casting defects in castings. Sulfur exists in the form of sulfide in liquid steel. These sulfides include separate FES, fes.fez. Eutectic fes.feo.fe ternary eutectic MNS or complex sulfide. These sulfides are insoluble in liquid steel, so when the molten steel solidifies, the sulfides will be pushed out at the grain boundary to form non-metallic inclusions. Sulfur forms low melting point eutectic (melting point 935 degrees) in cast steel, expands the hot brittle zone and increases hot tears casting defects. Iron oxide and iron oxide produced by oxygen in molten steel are surface active substances, which increase the tendency of hot tears casting defects in steel.
In Figure 2, 1-21 respectively shows: 1-c0 19% 2—C0. 13% 3—C0. 42%4—C0. 17% 5—C0. 12% 6—C0. 44% 7—C0. 03% 8—C0. 05% 9—C0. 08%10—C0. 1% 11—C0. 19% 12—C0. 44% 13—0.06% 14—C0. 21%15—C0. 39% 16—C0. 09% 17—C0. 40%、Mn0. 96%、S0. 05% 18—C0. 39%、Mn0. 46%、S0. 025% 19—C0. 43%、Mn0. 89%、S0. 058% 20—C0. 09%、Mn0. 40%、S0. 025% 21—C0. 08%、Mn0. 95%、S0. 058%。