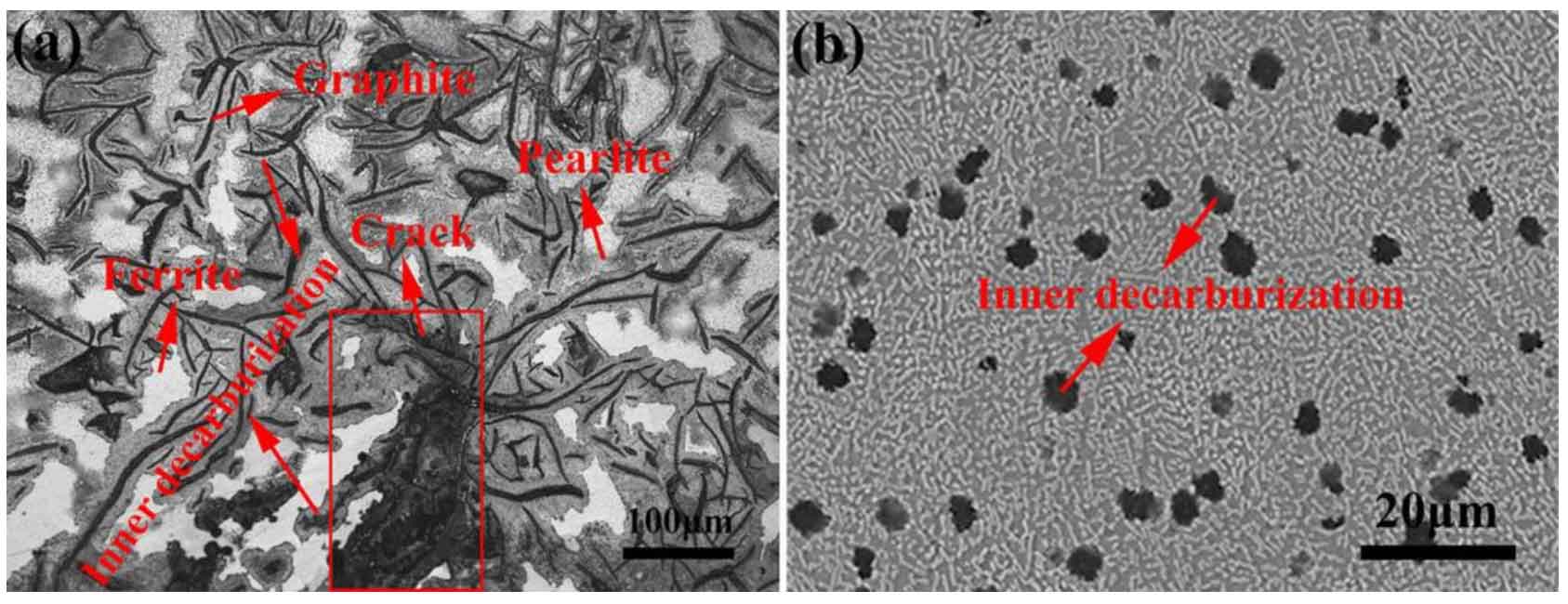
When studying the performance of gray cast iron brake drum, thermal fatigue makes the material crack, but the brake drum will also cause severe friction and wear during braking. In the service life test of brake drum, the fatigue crack length and wear thickness of brake drum are generally evaluated. Therefore, while studying thermal fatigue, it is also necessary to study its wear performance.
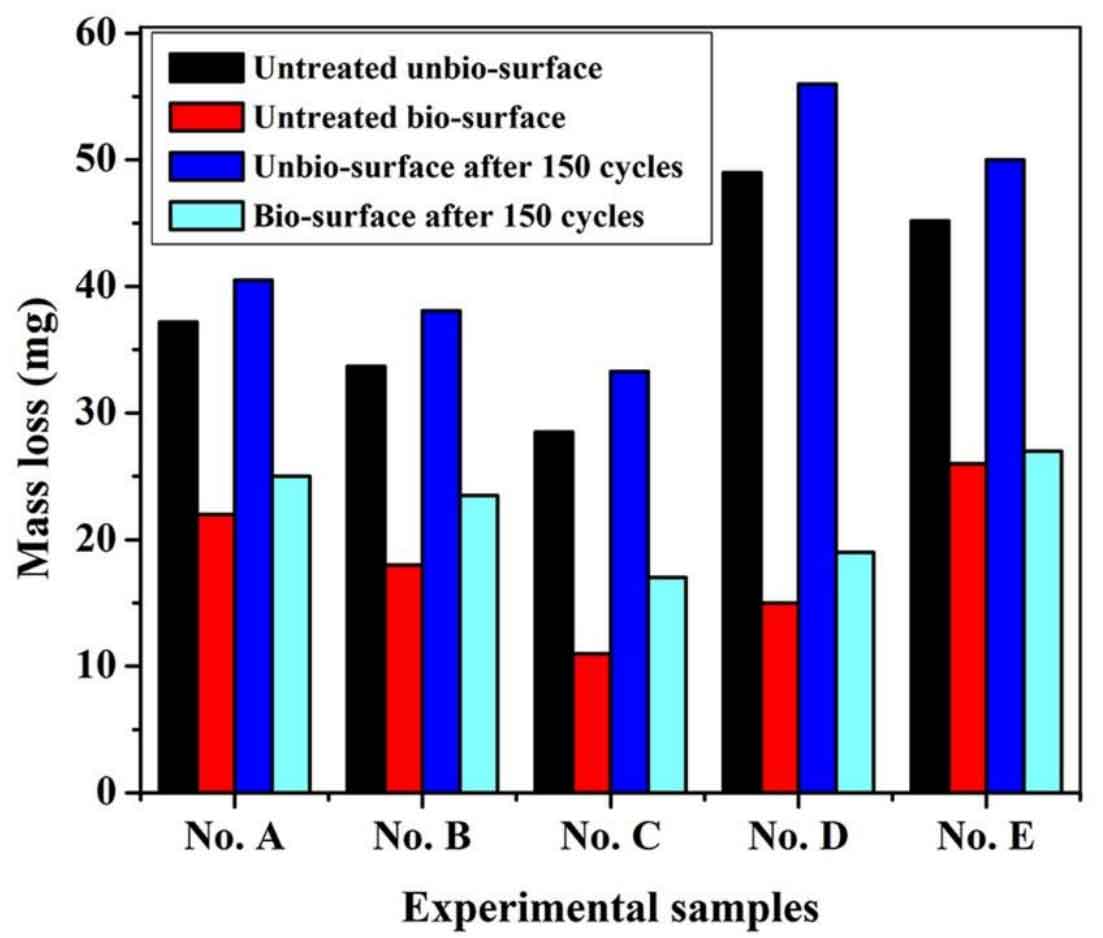
The wear weight loss of five samples with different graphite types shown in Figure 1 are the wear amount of non bionic surface without thermal fatigue treatment, bionic surface without thermal fatigue treatment, non bionic surface after 150 thermal cycles and bionic surface after 150 thermal cycles. Comparing the wear amount of friction and wear without thermal fatigue non bionic surface, we can see that the wear amount of No. C is the least, while the wear amount of No. D sample is the highest. By analyzing the microstructure and hardness of the matrix, it can be found that the matrix of No. D is ferrite with low hardness; Other types of samples are basically pearlite based, with high hardness. Compared with No. D samples, the wear resistance is improved. However, due to the high carbon content of No. C, there is coarse C-type graphite, which has a good lubrication and wear reduction effect on friction and wear, and the hardness of the matrix is the highest compared with other samples, so the wear resistance is the best. No. e because the ferrite content of the matrix is also about 20% and the graphite content is less, the wear resistance is also poor. When five types of samples are subjected to Laser Biomimetic treatment, it can be seen from the figure that their wear resistance can basically be more than doubled, about 1.69 to 3.26 times. This is closely related to the bionic unit. The bionic model has great advantages in the wear resistance of materials.
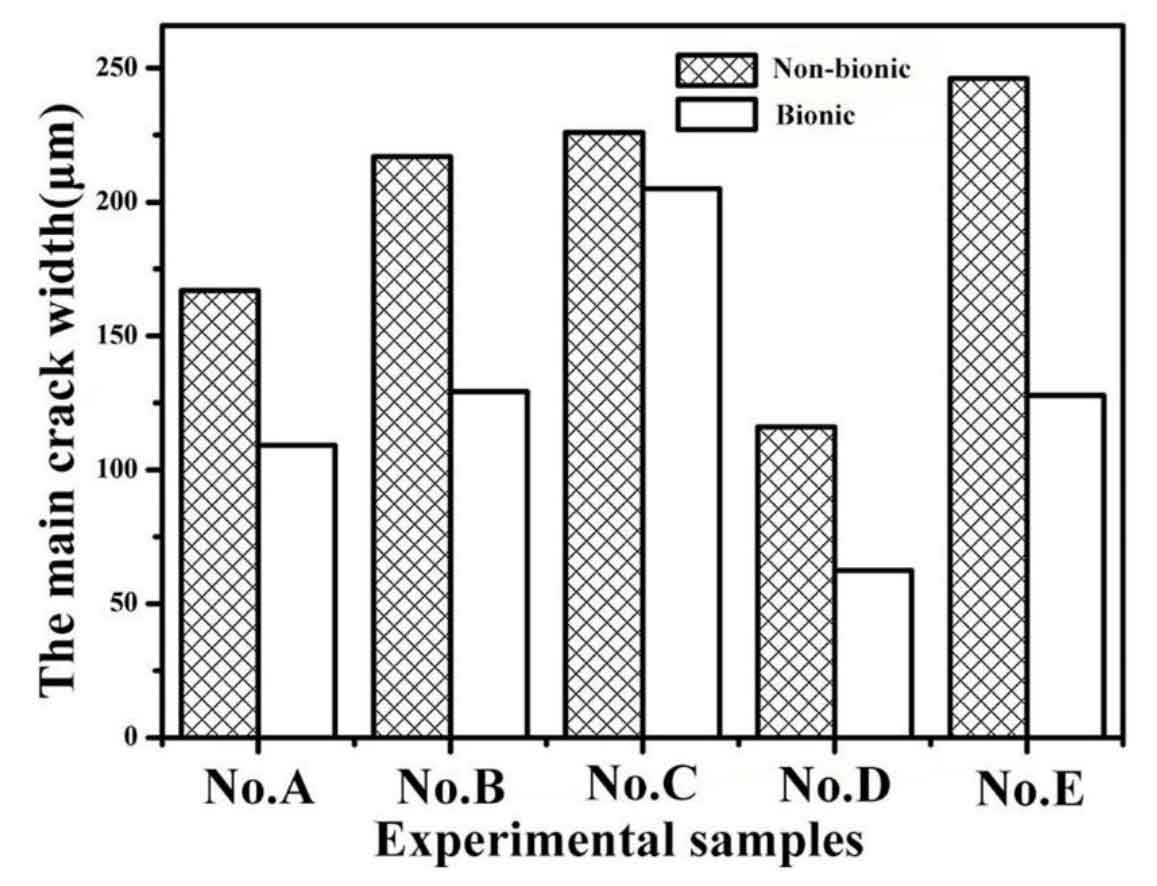
The unit body improves the overall hardness of the material and supports the friction pair, so the wear resistance of bionic gray cast iron is significantly improved. However, the improvement of wear resistance of materials containing different types of graphite is also different. The wear resistance of bionic surface of No. D is improved most obviously. The reason may be that No. D originally has high carbon content, so there are more carbon atoms dissolved in the unit and the hardness is improved the most, so it is the most wear-resistant in the wear process. Similarly, it can be seen that the wear resistance of No. C bionic surface is also greatly improved, so the wear amount of No. C bionic surface is the lowest. The bionic surface wear resistance of other samples has also been improved to a considerable extent, but the bionic surface wear resistance of No. e sample has been improved at the least, which may be related to its low carbon content. For gray cast iron brake drum, thermal fatigue and friction and wear occur simultaneously or successively. Therefore, when studying the wear resistance of gray cast iron brake drum, it is necessary to study the wear resistance after thermal fatigue. It can be seen from Figure 2 that after 150 thermal cycles of gray cast iron, the wear amount of non bionic surface and bionic surface increases in varying degrees. It can be seen from Fig. 3 that during the thermal cycle, the pearlite in the matrix decomposes and the surface decarburizes, which reduces the hardness of the sample and the lubrication of graphite; And there are many cracks on the surface of the sample, which leads to the increase of wear. However, the wear amount of bionic surface after thermal fatigue is also lower than that of non bionic surface. It shows that the bionic unit is not only conducive to improve the wear resistance of materials, but also greatly improve the wear resistance of materials after thermal fatigue.