1. Quality heat treatment welding process after welding
According to the commonly used welding specifications for steel castings, ASME IX Welding and Brazing Qualification Standards, prepare a piece with a size of 450 mm × 250 mm × 50 mm test block, using non penetrating docking method, φ 4.0 mm electrode backing φ Welding process evaluation shall be conducted using a 5.0 mm welding rod filling method, with a minimum preheating temperature of 180 ℃, interlayer temperature of 200 ℃~350 ℃, welding current of 130 A~240 A, arc voltage of 15V~30 V, and welding speed of 10 cm/min~20 cm/min To prevent welding cold cracks, 350 ℃ insulation is used for 2 hours after welding. Quality heat treatment is carried out after welding to ensure that tempering brittleness does not occur, and full quenching is required during quenching. As a medium carbon low alloy high-strength steel, it is necessary to pay attention to the slow tempering cooling rate to avoid causing internal stress.
2. Welding process for stress relieving heat treatment after quenching and tempering state welding
The carbon content of ASTM A487 Grade 4 is close to 0.3%, which belongs to low alloy high strength steel (easy quenching steel), and the structure is tempered martensite. The base metal contains Cr, Mo and other alloy elements that improve the hardenability. High carbon martensite is easily formed in the Heat-affected zone after welding, which is the main reason for the decrease of impact toughness in the Heat-affected zone.
The impact of steel castings is required to reach 42 J at – 29 ℃. In order to prevent the embrittlement of the Heat-affected zone, small heat input is adopted during welding, and preheating and post heating measures are also adopted. use φ 4.0 mm electrode backing φ The welding process qualification is carried out using a 5.0 mm welding rod filling method. The preheating temperature is 150 ℃, the interlayer temperature is 150 ℃~200 ℃, the welding current is 150 A~200 A, the arc voltage is 18 V~25 V, and the welding speed is 20 cm/min~30 cm/min In order to prevent welding cold cracks, 350 ℃ heat preservation shall be adopted for 2h after welding. The welding position shall be selected for multi-layer and multi pass transverse welding process with small welding heat input. The thin electrode and low current priming shall be applied for two layers. Through the above methods, the generation of brittle structure in the Heat-affected zone can be effectively reduced. At the same time, in order to prevent the generation of cracks, preheating is required before welding, but preheating will make the cooling rate of 800 ℃~500 ℃ lower than the critical cooling rate for brittle mixed structure, which will reduce the toughness of the Heat-affected zone, so lower preheating temperature and interlayer temperature are selected. After welding, stress relieving heat treatment is carried out, heating at a heating rate of less than 60 ℃/h to 620 ℃~670 ℃ for insulation. After the insulation time exceeds 8 hours, it is cooled in the furnace to less than 200 ℃ and discharged for air cooling.
3. Inspection specifications
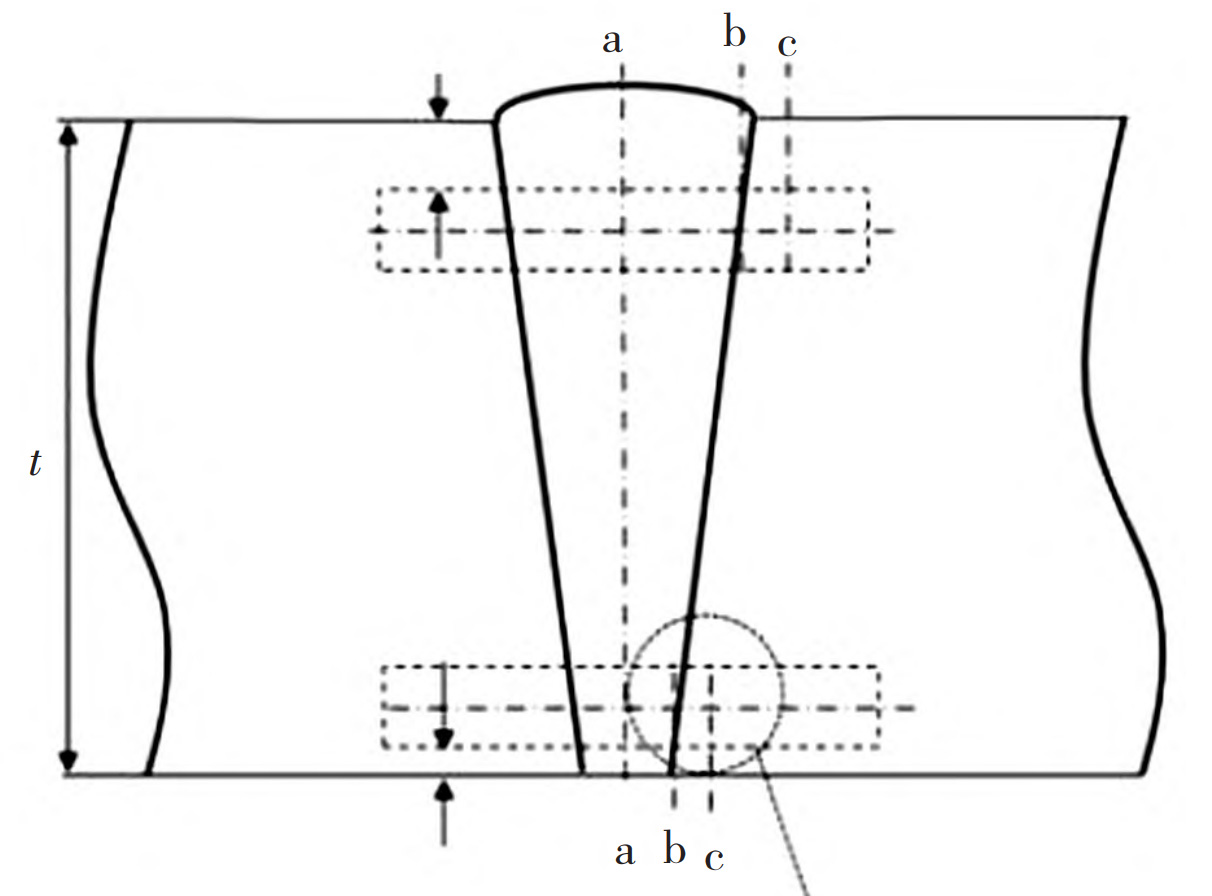
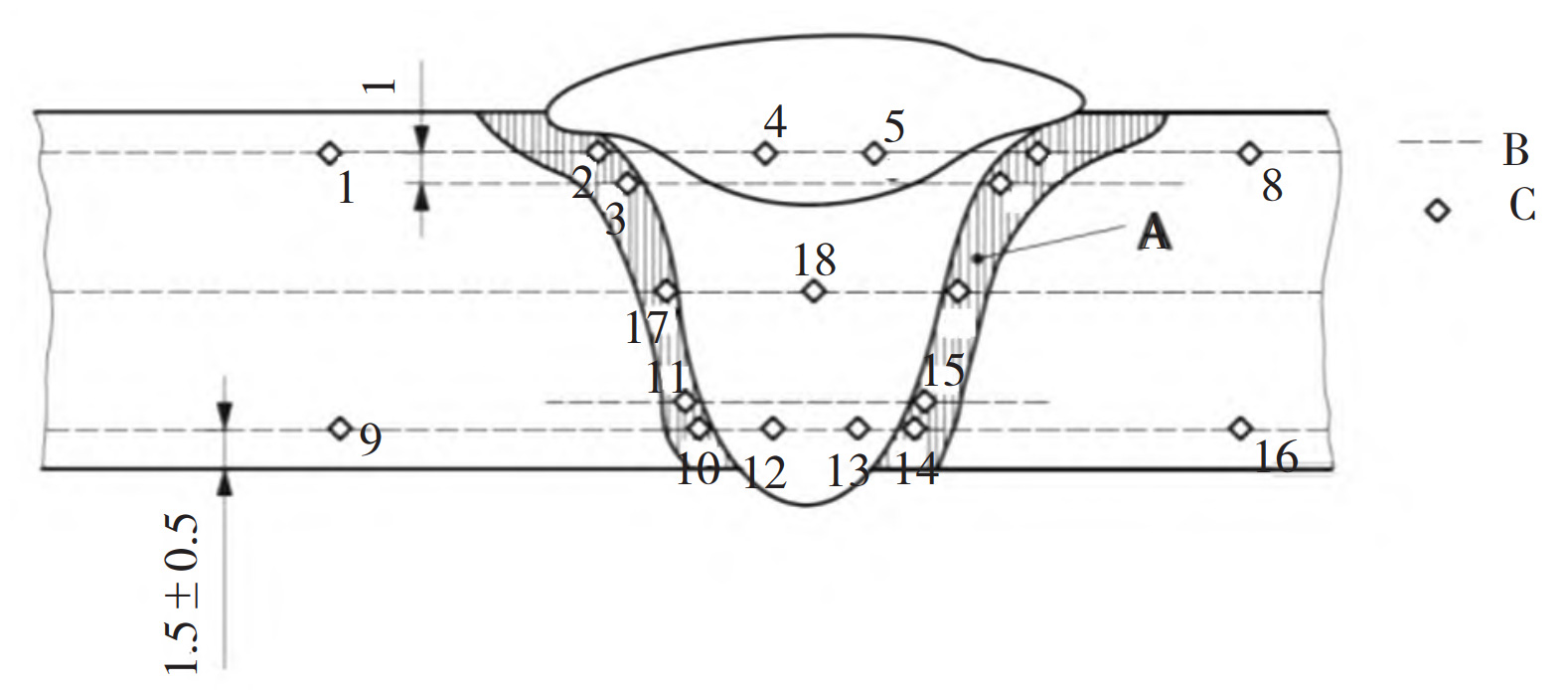
Perform non-destructive testing and mechanical property testing on welded test plates according to specifications. According to the requirements of API Spec16A “Drilling Equipment Specification”, the material performance requirements for the pressure bearing parts of the blowout preventer at 80K include tensile strength ≥ 655 MPa, yield strength ≥ 551 MPa, elongation ≥ 18%, reduction of area ≥ 35%, impact energy ≥ 42 J (-29 ℃), and the qualified range of body hardness after final heat treatment: 207 HBW~237HBW The impact test was sampled according to the requirements of API 16A Rev.2018, as shown in Figure 1 According to the requirements of NACE MRO175/ISO 15156, hardness HV10 testing was conducted. According to the latest version of the American Society for Testing and Materials’ Standard Metal Hardness Conversion Table (ASTM E140-12b), the qualified range of HV hardness for steel castings is 207 HV~248 HV. The testing method is detailed in Figure 2.