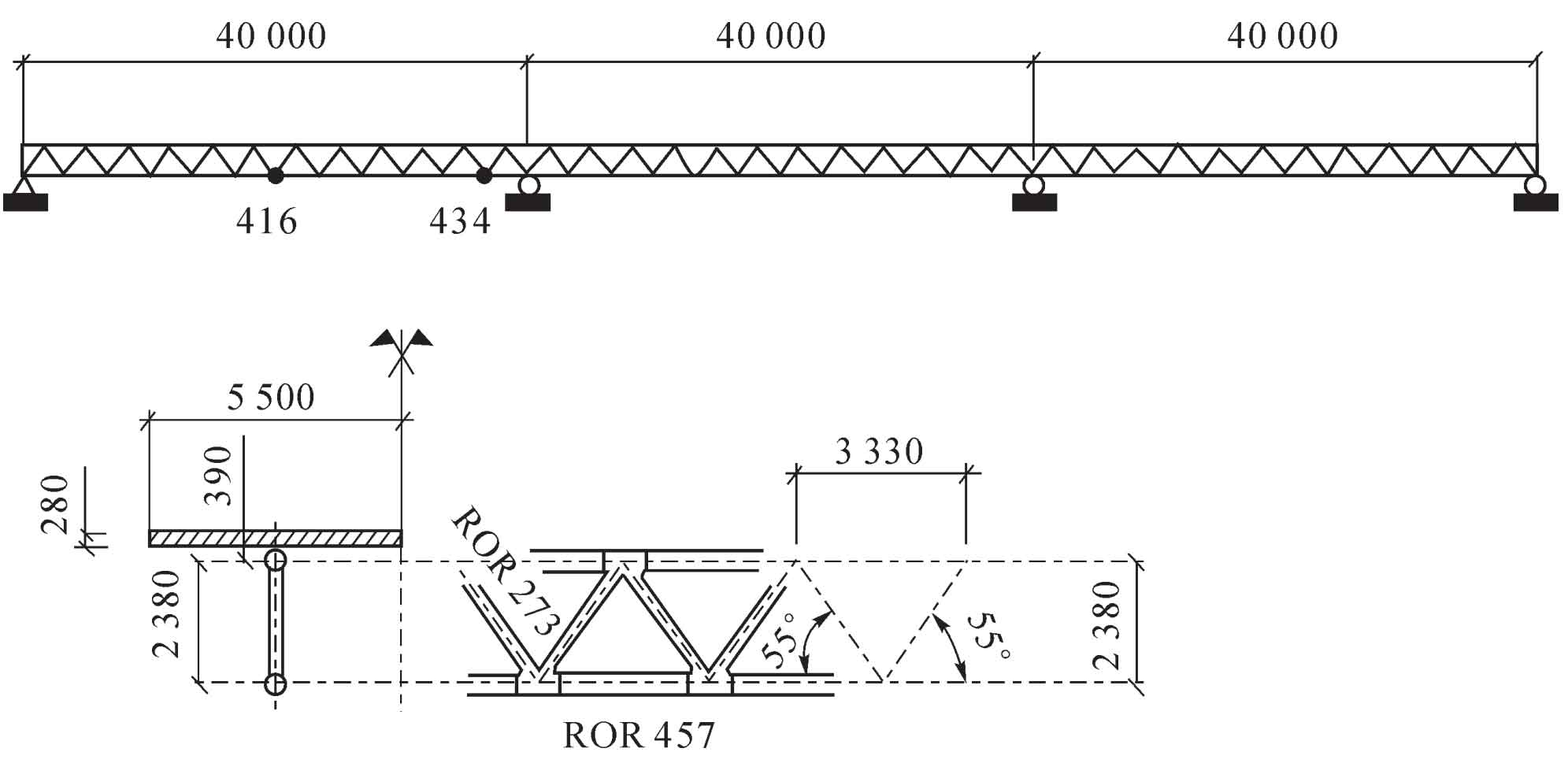
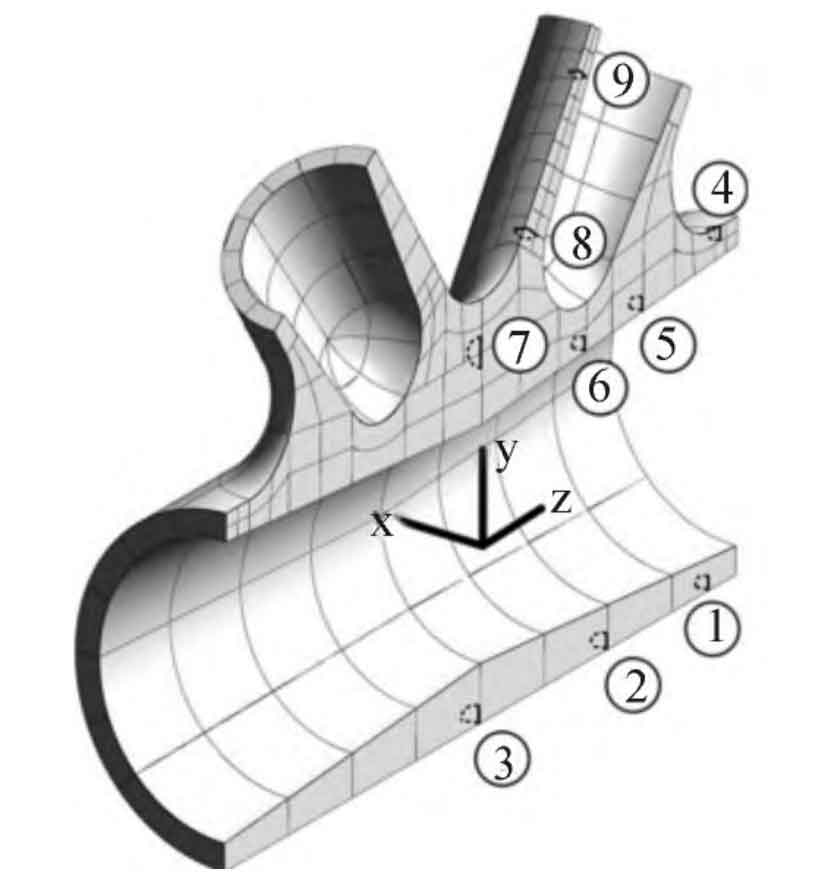
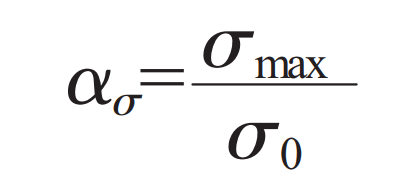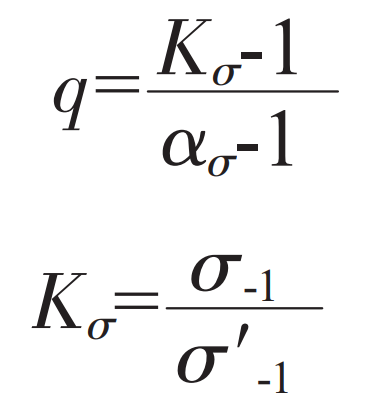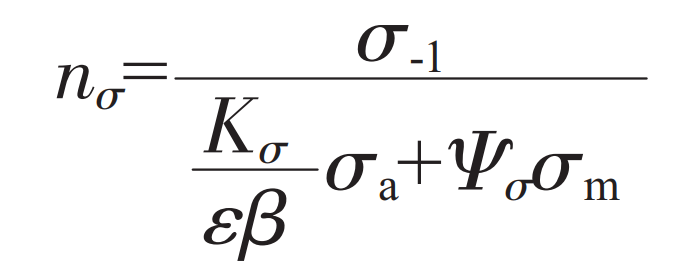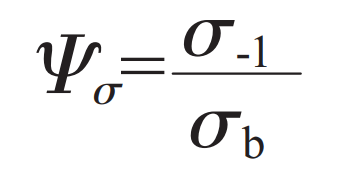Through the finite element calculation of fatigue strength and safety factor, the changes of fatigue performance caused by different casting defect size, location and distribution are analyzed.
1. Safety assessment method of fatigue strength
As we all know, local stress concentration will occur at the casting defect location of cast steel joints. Stress concentration is easy to cause fracture of joints due to fatigue problems, resulting in great harm. Carry out evaluation and calculation from the following aspects.
Stress concentration factor. Set ασ Represents the stress concentration factor, and its theoretical calculation method is as follows:
In the formula, σ Max is the maximum local stress, σ 0 is the nominal stress. In practical engineering application, the actual stress concentration factor K is mainly used σ To reflect the change of fatigue strength. Effective stress concentration factor K σ The size of is related to the structural shape of cast steel joint and casting material, and usually the specific stress concentration factor ασ Smaller. In order to effectively analyze the actual stress concentration factor K σ And stress concentration factor ασ The stress concentration sensitivity coefficient q is set according to the difference between them, and its calculation method is as follows:
In the formula, σ- 1 and σ′- 1 represents the fatigue limit of samples with different surfaces.
According to the dimension coefficient curve of reference steel parts and the thickness of each casting defect position in the pipe truss bridge model, the dimension coefficient of each casting defect position can be obtained, which is listed in Table 1.
| Defect location | ① | ② | ③ | ④ | ⑤ | ⑥ | ⑦ | ⑧ | ⑨ |
| Size factor | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.82 | 0.92 | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.82 | 0.92 | 0.95 |
Under the influence of fatigue load, the fatigue performance of local area of cast steel joints in pipe truss bridge is evaluated by calculating the safety factor. The greater the value of safety factor, the higher the safety of cast steel joint under this loading. Generally, it is necessary to analyze the influence of average stress, and the safety factor can be derived by calculating the ratio between fatigue strength and local effective stress amplitude of parts. The calculation formula of safety factor is as follows:
In the formula, σ- 1 indicates the fatigue limit of the material. As cast steel is used, so σ- 1=202.8 MPa。 σ A represents the stress amplitude, K σ Represents the effective stress concentration factor, σ M is the average stress, ε Indicates the size factor. β Represents the surface finish coefficient. According to the analysis data of literature, the surface finish coefficient of steel parts is β= 0.65。
In the formula, σ B is the ultimate strength of cast steel, σ b=491 MPa。
2. Defect grade and specific distribution
In order to more comprehensively analyze the influence of multiple casting defects on the fatigue performance of cast steel joints, eight pipe truss models with casting defects are constructed based on the model shown in Figure 1 from three different angles: quantity, size and location. The specific defect locations are shown in Figure 2. There are 3 casting defect grades corresponding to each casting defect grade, as shown in Table 2.
| Model | Casting defect location | Casting defect grade |
| 1 | ①③④ | Grade II |
| II2 | ①④⑤ | Grade II |
| 3 | ②⑦⑧ | Grade II |
| 4 | ①②④⑧ | Grade II |
| 5 | ③④ | Grade III |
| 6 | ① | Grade II |
| 7 | ① | Grade III |
| 8 | ⑧ | Grade III |