The connection opening of V-type engine body goes deep into the core, and the heat dissipation is slow. Compared with the outer wall, the time interval from molten iron pouring to complete solidification becomes longer, and the probability of forming hot crack casting defects is greater.
The V-type engine body adopts the bottom injection process. The molten iron at the top has low temperature and begins to solidify first; The molten iron temperature at the bottom is high, and the pouring weight of the casting is mainly concentrated in the lower part, resulting in the delay of the starting solidification time. At this time, the solidified top is subject to linear shrinkage, and the outer wall of the top surface and the opening are subject to shrinkage stress. The molten iron in the lower part has high temperature and large temperature difference. When the bottom solidifies, the superposition of liquid shrinkage and solid shrinkage will produce large linear shrinkage force; At this time, the top has basically completed solidification, but due to the existence of the middle core, the linear shrinkage force at the bottom will become a tensile stress transmitted to the top surface due to leverage. When the core at the top can not completely offset the transmitted stress, the stress at each part of the top will become a tensile stress. If the connection opening is not fully solidified at this time, hot crack casting defects may be formed.
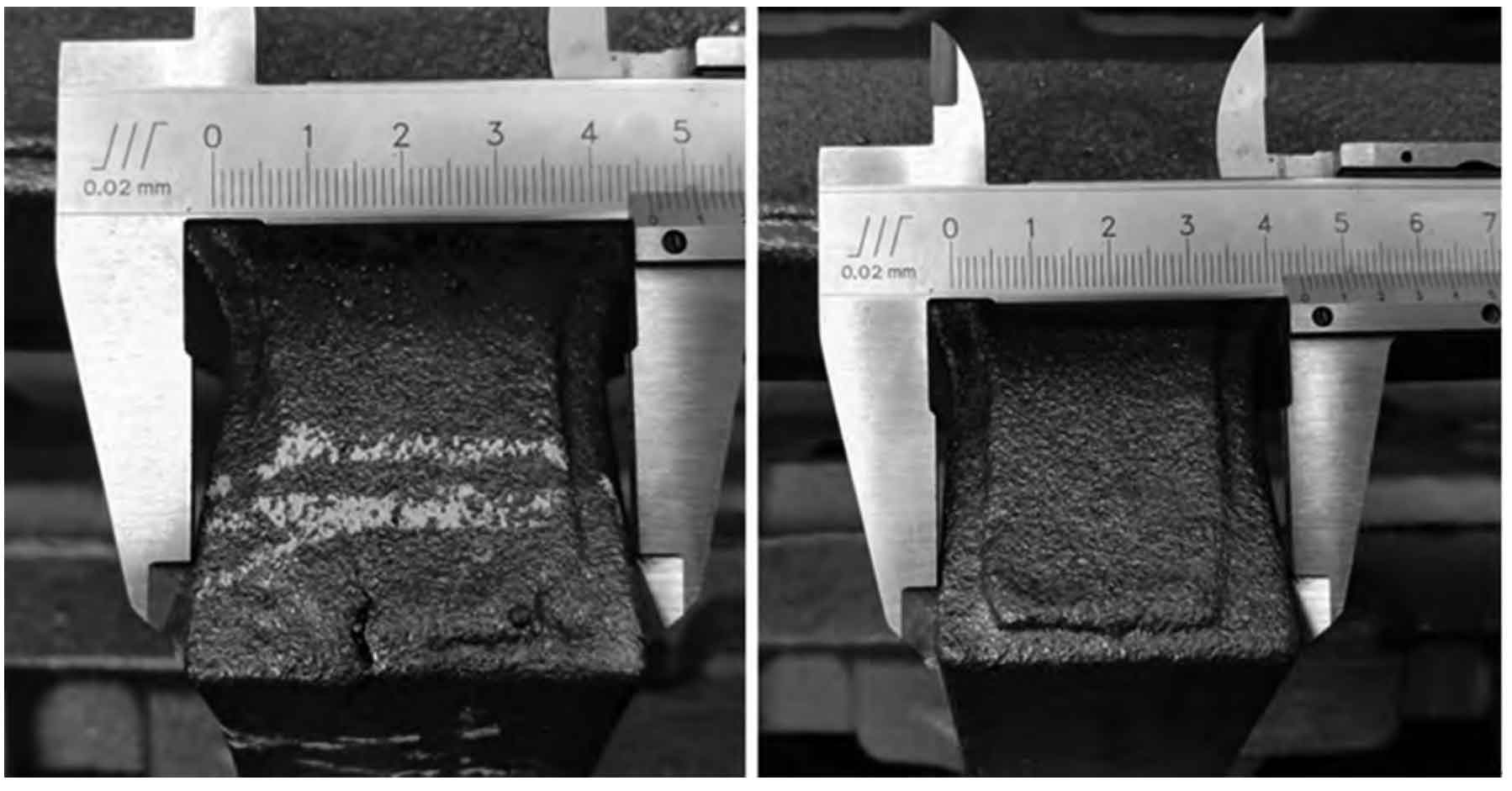
In order to further confirm the formation mechanism of hot crack casting defects, the opening thickness of the joint where the hot crack casting defects occur was detected. The detection method is shown in the figure. The average thickness of the connecting opening with crack casting defects is 46.05mm, while the average thickness of the intact opening is only 44.44mm, and the two phases are 1.61mm. The top of the opening with hot crack casting defects is generally thickened. This shows that during solidification, the resistance of the sand core is insufficient to offset the transmitted stress, resulting in the inward displacement of the sand core surface, the tension at the open gear, and the formation of hot crack casting defects.