The steel castings of shell housing are made of low alloy steel and low carbon steel. The content requirements of major elements in the technical standards are: carbon content ≤ 0.30%, silicon content ≤ 0.60%, fierce content ≤ 0.70%, phosphorus content ≤ 0.040%, sulfur content ≤ 0.040%, copper content ≤ 0.30%. The content of chemical composition must ensure that the carbon equivalent CE ≤ 0.76%. [CE = C + 1 / 3 (Mn + CR) + 1 / 6 (Si + Ni) + 1 / 2Mo], the upper limit of Mn can be increased by 0.04% for every 0.01% reduction of carbon, but the total can not exceed 1%.
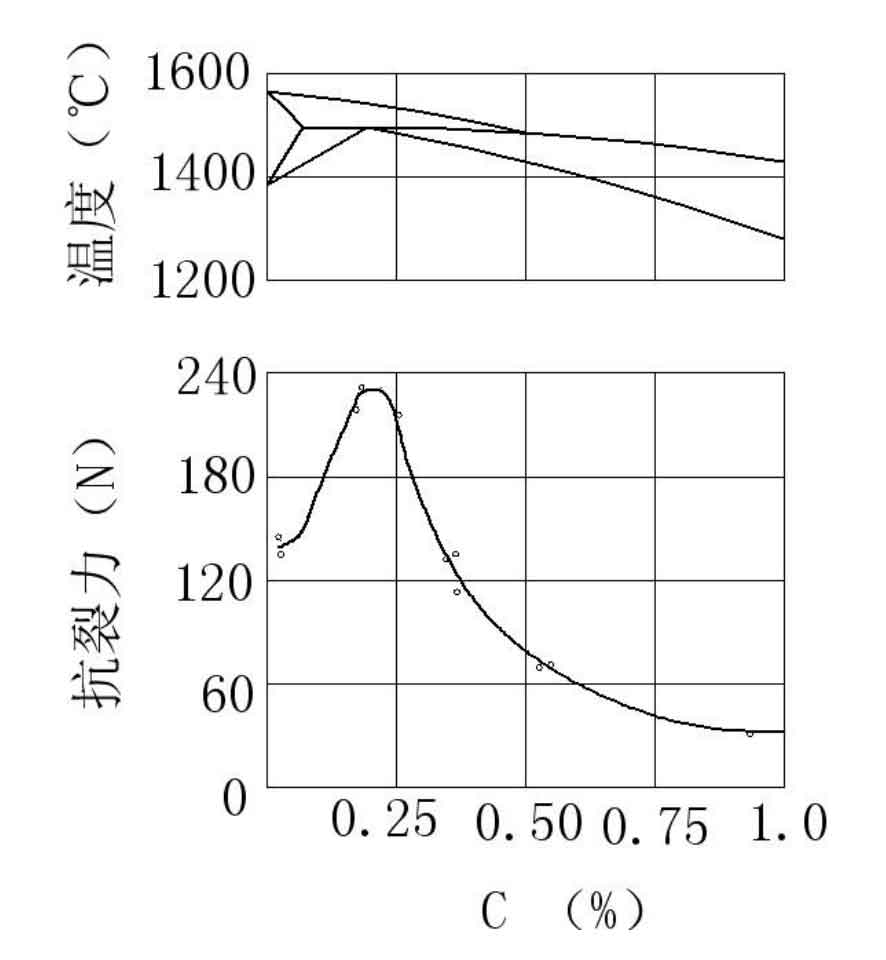
From the influence of carbon on hot crack casting defects in Figure 3.6, when the carbon content is less than 0.25, the crack resistance of the alloy gradually increases with the increase of carbon content, reaches the maximum value at 0.20-0.25, and gradually decreases with the increase of carbon content from 0.25-1.0.
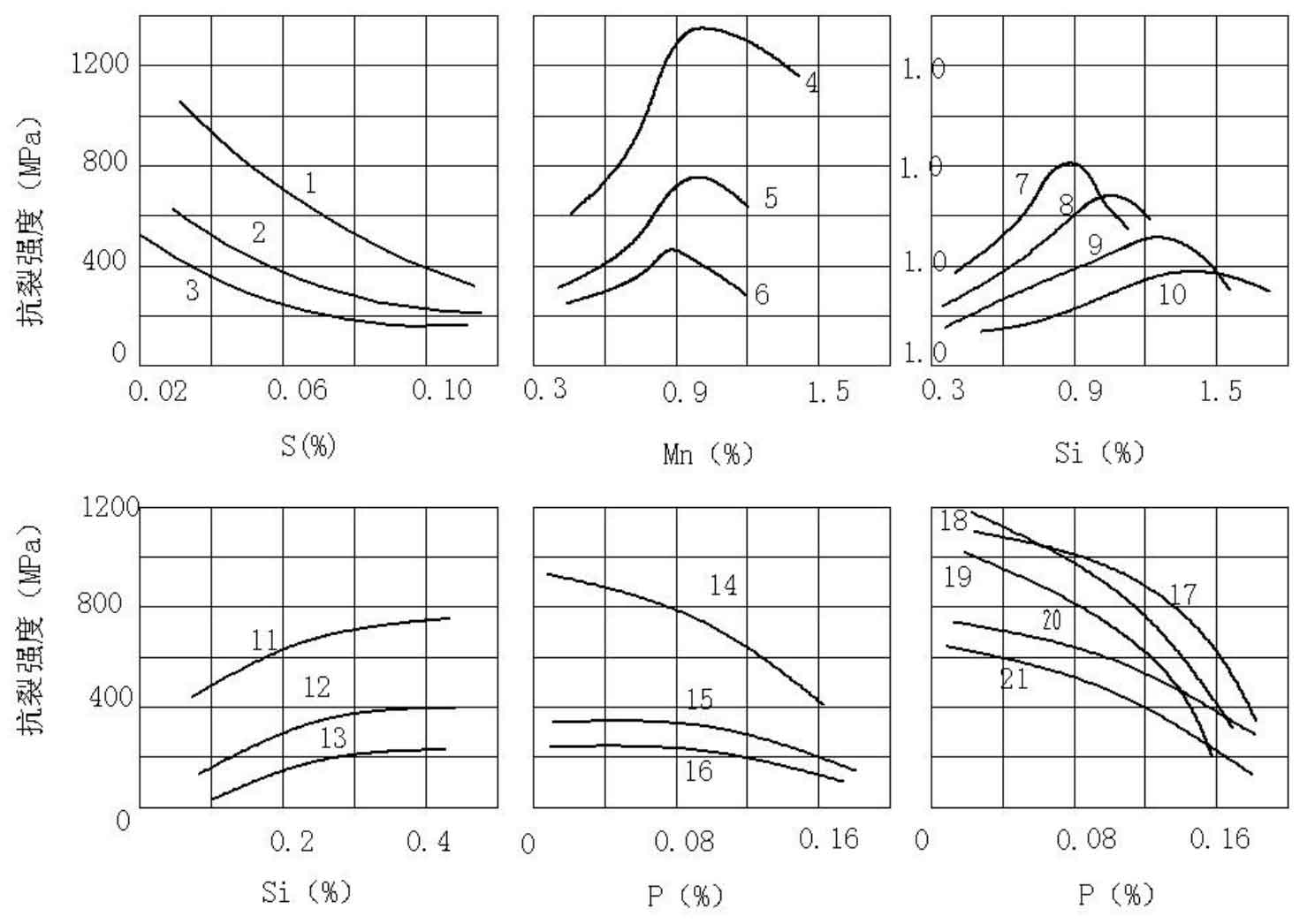
It can be seen from figure 3.7 that when the silicon content is in the range of 0.1-0.45, the crack resistance strength of carbon steel gradually increases with the increase of silicon content; When the content of manganese is in the range of 0.3-0.9, the crack resistance of carbon steel gradually increases with the increase of manganese content, and decreases with the increase of manganese content from 0.9-1.5; The cracking strength of carbon steel decreases gradually with the increase of phosphorus content; Among various chemical compositions, sulfur has the greatest influence on the formation of hot crack casting defects. According to statistical research, the relationship between the occurrence rate of hot crack and sulfur content is almost exponential. The higher the sulfur content, the lower the temperature of hot crack.
Sulfur exists in the form of (Fe, Mn) s in steel. After solidification of most liquid steel, sulfur rich liquid film will remain between dendrites. When the liquid film solidifies and shrinks, the sulfur rich liquid film with low strength and plasticity will crack due to stress concentration. It is found that sulfur comes not only from the liquid steel itself, but also from the mold, which leads to the increase of sulfur content on the surface of the casting and the tendency of forming cracks and casting defects. From the above analysis, it can be seen that if the content control of major elements during molten steel smelting is unreasonable, especially the content control of carbon and sulfur, it will reduce the crack strength of carbon steel and increase the tendency of forming crack casting defects. The chemical composition of the motor shell steel castings produced by ZHY casting is basically strictly implemented according to the technical standards in the molten steel smelting process, but the crack resistance of each element is reduced within some ranges of the standards, which is also a factor leading to the formation of crack casting defects of the motor shell steel castings.