There are two process schemes of low-temperature fast casting and high-temperature slow casting for nodular iron castings of wind power hub.
(1) Low temperature quick Pouring Scheme: the low temperature quick pouring scheme fully considers the characteristics of furan resin sand, such as good thermal insulation, easy sand washing, large and concentrated gas generation, large temperature difference between the bottom and the top, and uneven distribution of the overall temperature field. Low temperature is mainly to reduce liquid shrinkage and reduce the tendency of shrinkage cavity and shrinkage porosity. The purpose of quick pouring is to fill the mold cavity with molten iron as soon as possible, stabilize it, form static pressure and prevent air holes before a large amount of resin sand is aerated. However, when the molten iron is filled to the top surface during low-temperature pouring, the temperature may be very low, the oxidation tendency of molten iron increases, the fluidity becomes poor, the scum capacity is poor, and it is not conducive to gas floating. The overall temperature field of low-temperature rapid casting scheme is more uniform and closer to simultaneous solidification. Generally, it is combined with the process scheme with the main shaft hole facing down. According to production experience, the recommended pouring temperature is 1330 ~ 1340 ℃, and the mold filling time is generally 100 ~ 180 s.
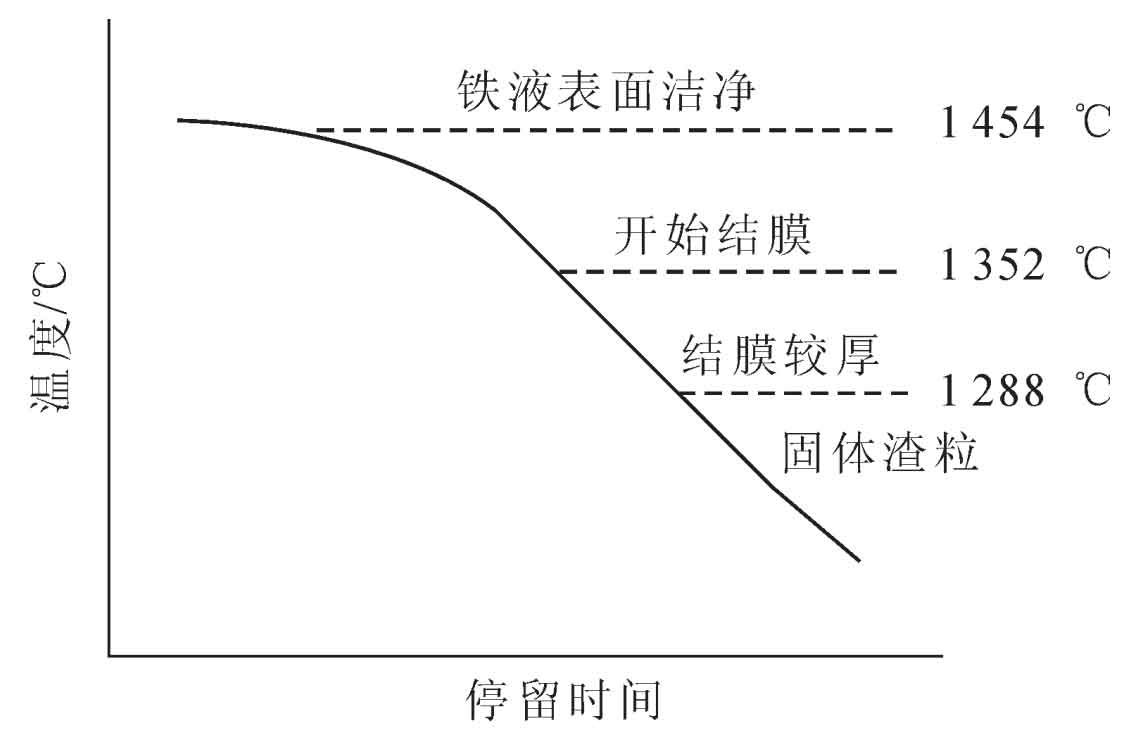
(2) High temperature slow Pouring Scheme: with the increasing size of wind power nodular iron castings and higher pressure head, the requirements for surface magnetic particle flaw detection are becoming more and more strict. Taking 5 MW nodular cast iron as an example, the height of nodular cast iron is more than 4 m and the weight of molten iron is more than 30 T. If low-temperature pouring is adopted, the temperature of molten iron rises to the top surface is very low, and the problem of secondary oxidation inclusion is more prominent. The figure shows the relationship between molten iron temperature and oxidation inclusion. After increasing the pouring temperature, the feeding capacity of molten iron at the top riser is also relatively good, but there is a risk of spheroidization and inoculation decline due to the high discharge temperature and pouring temperature. According to the production experience, the pouring temperature is recommended to be 1350 ~ 1370 ℃. In order to prevent the turbulent flow caused by mold filling, make the molten iron rise as smoothly as possible, and allow sufficient time for impurities and gases to float up, the general mold filling time is 180 ~ 300 S. the high-temperature slow pouring is generally combined with the process scheme with the spindle hole facing upward.
Both schemes have advantages and disadvantages. Both schemes can pour qualified nodular iron castings and can be used flexibly according to specific conditions. However, the gating system with large flow, low flow rate and no turbulence needs to be followed by both schemes.