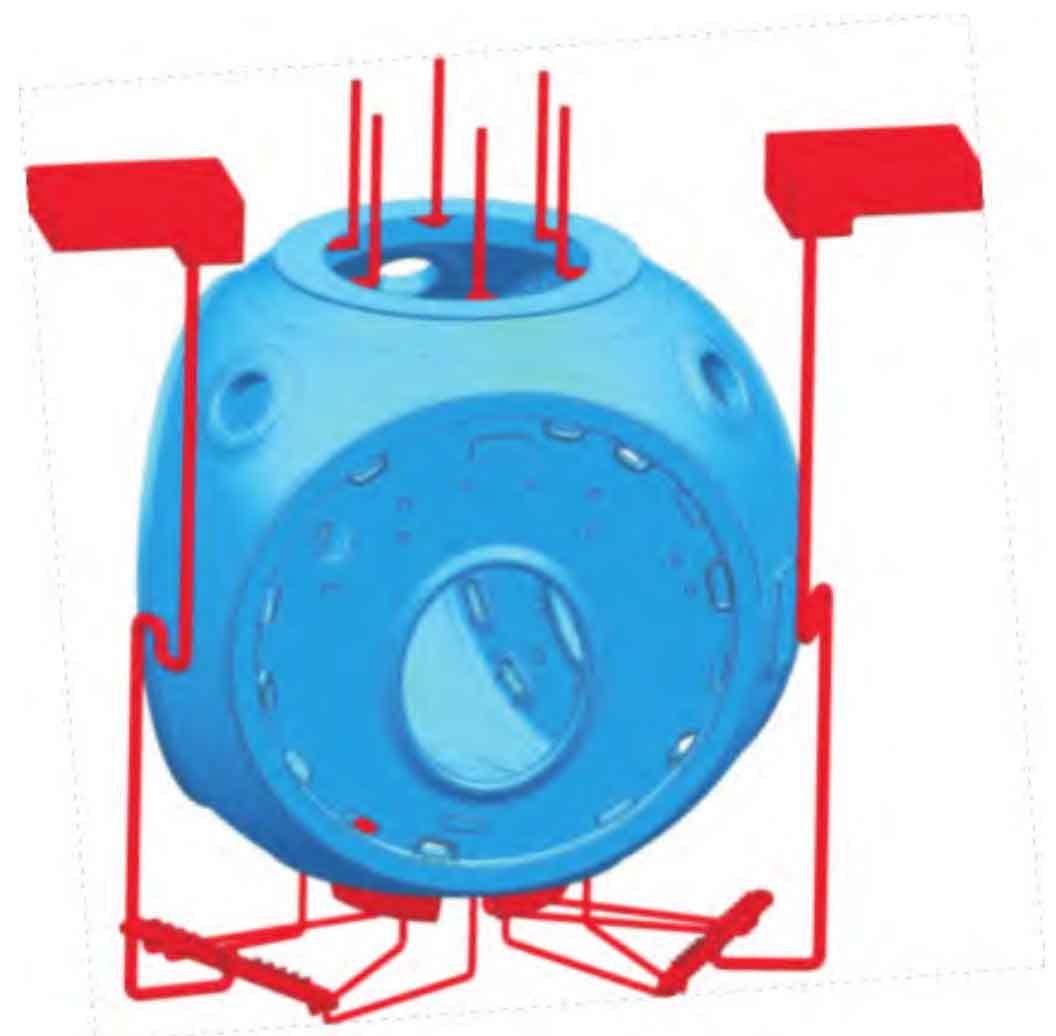
According to the diameter, wall thickness and inspection requirements of the main shaft hole of the wheel hub, the pouring position of the nodular iron castings of the wheel hub has two design schemes: the main shaft hole faces up and down, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
(1) Spindle hole upward scheme (see Figure 1)
Advantages: the main shaft hole has large wall thickness, large heat capacity and slow cooling. It is easy to design and control the pressure riser for liquid feeding, and cooperate with the cold iron to adjust the temperature field distribution to eliminate shrinkage cavity and porosity. At the same time, the end face area of the spindle hole is large, which is conducive to the floating of gas and slag.
Disadvantages: shrinkage cavity, porosity and coarse structure are easy to appear at the root of the riser, which affects the density of nodular iron castings. When designing the riser, we must pay attention to the modulus proportion matching of the Fed part of the main shaft hole, riser neck and riser body.
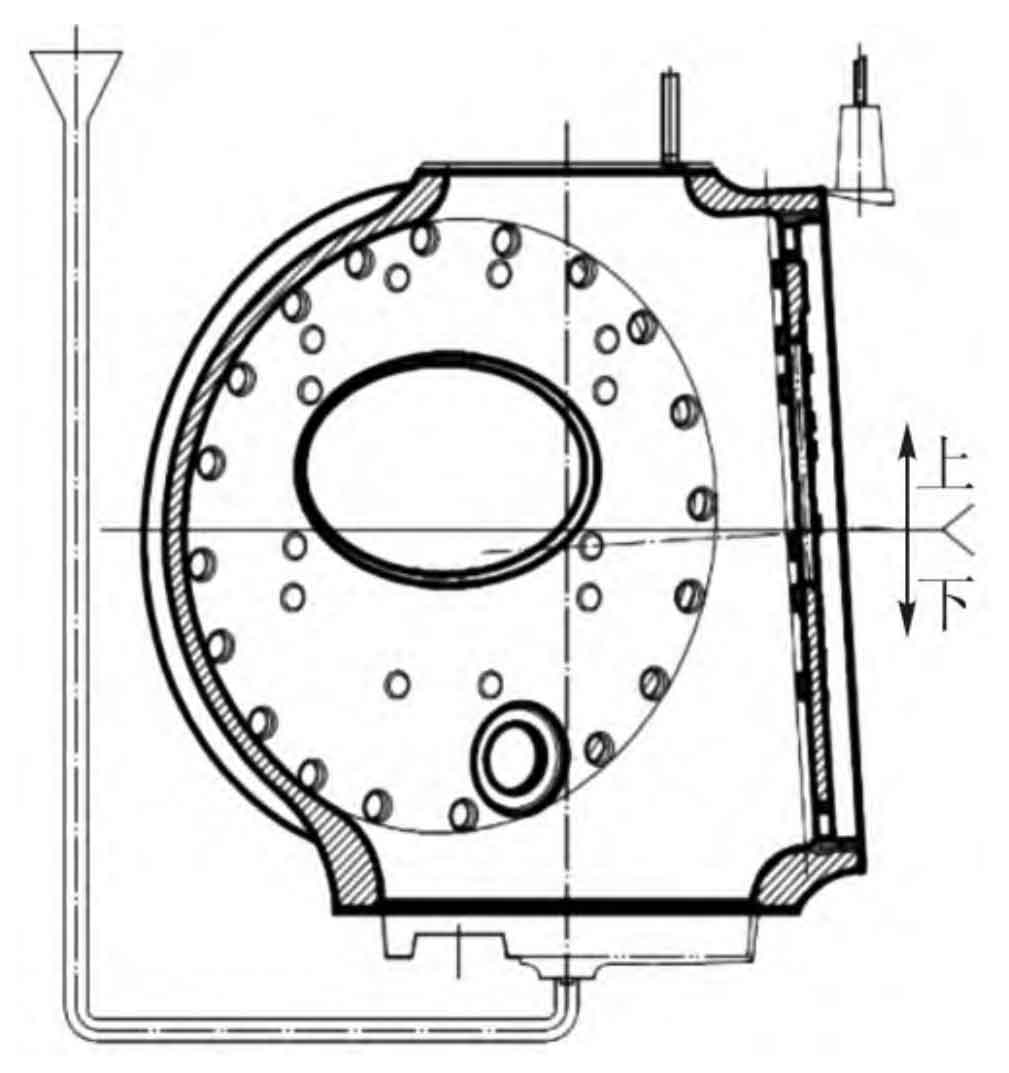
(2) Spindle hole downward scheme (see Figure 2)
Advantages: This is a typical design concept with the important side down, which is theoretically conducive to improving the tissue compactness of the spindle hole.
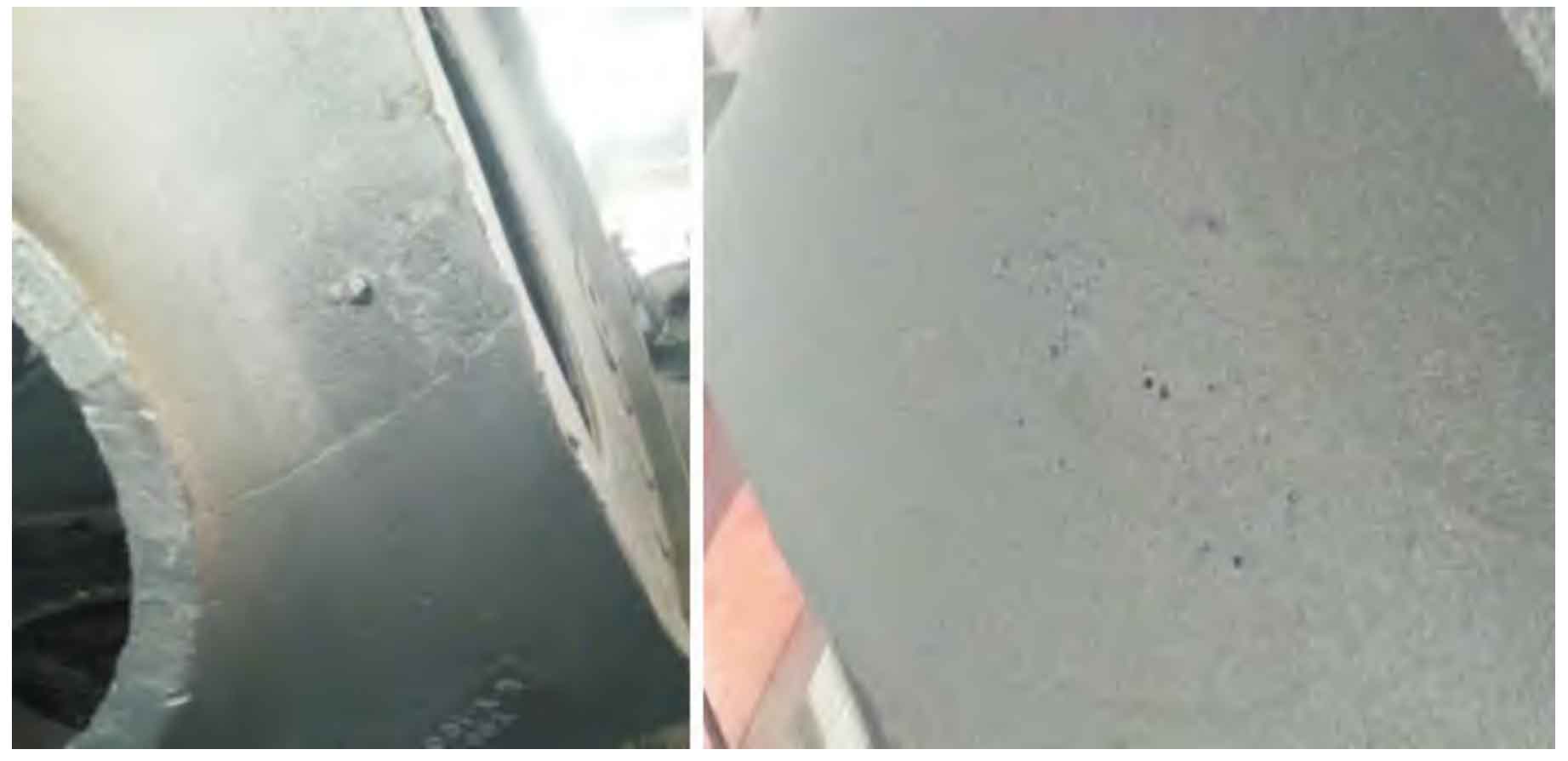
Disadvantages: the top surface of the shroud hole is prone to quality problems such as suffocation, oxidation inclusion (see Figure 3) MT exceeding the standard and shrinkage and looseness of the transition area of the side flange R. at the same time, due to the reverse inclination of the side flange, it is relatively difficult to locate the clay core of the side flange, so the process needs to be considered in operation.