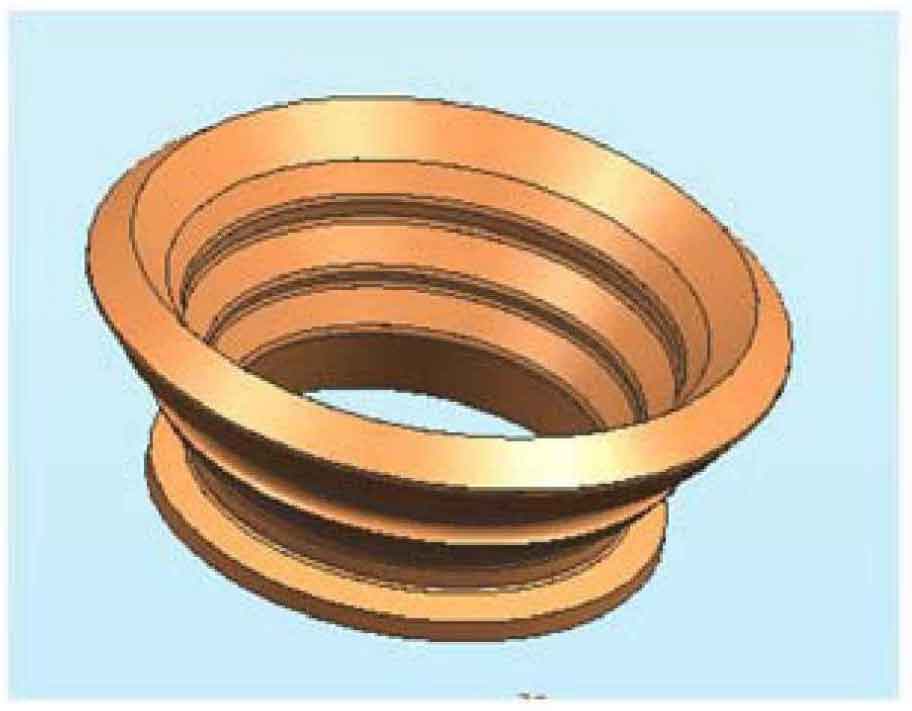
Bowl lining steel castings are the products produced by the machinery factory of Shougang Mining Company. The material is wear-resistant steel. Due to the special working environment of the bowl shaped lining, it is required to have strong wear resistance, and shrinkage and shrinkage defects are not allowed inside. During pouring, magnesia coating shall be applied.
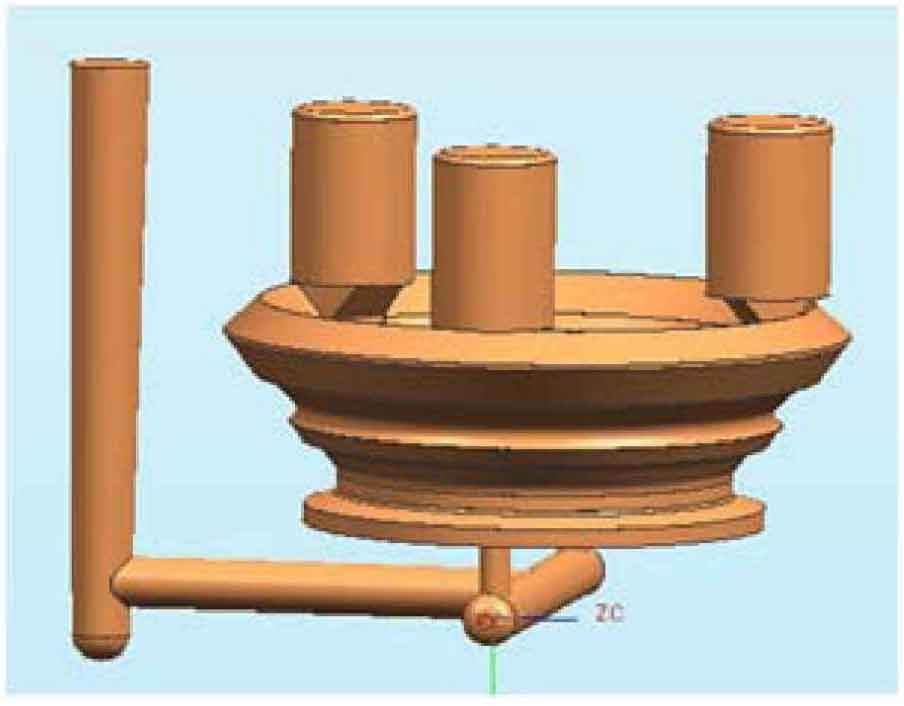
The net weight of the casting is 246kg, and the blank weight of the casting is about 400kg. The solid casting drawing and casting process drawing of the casting are shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2.
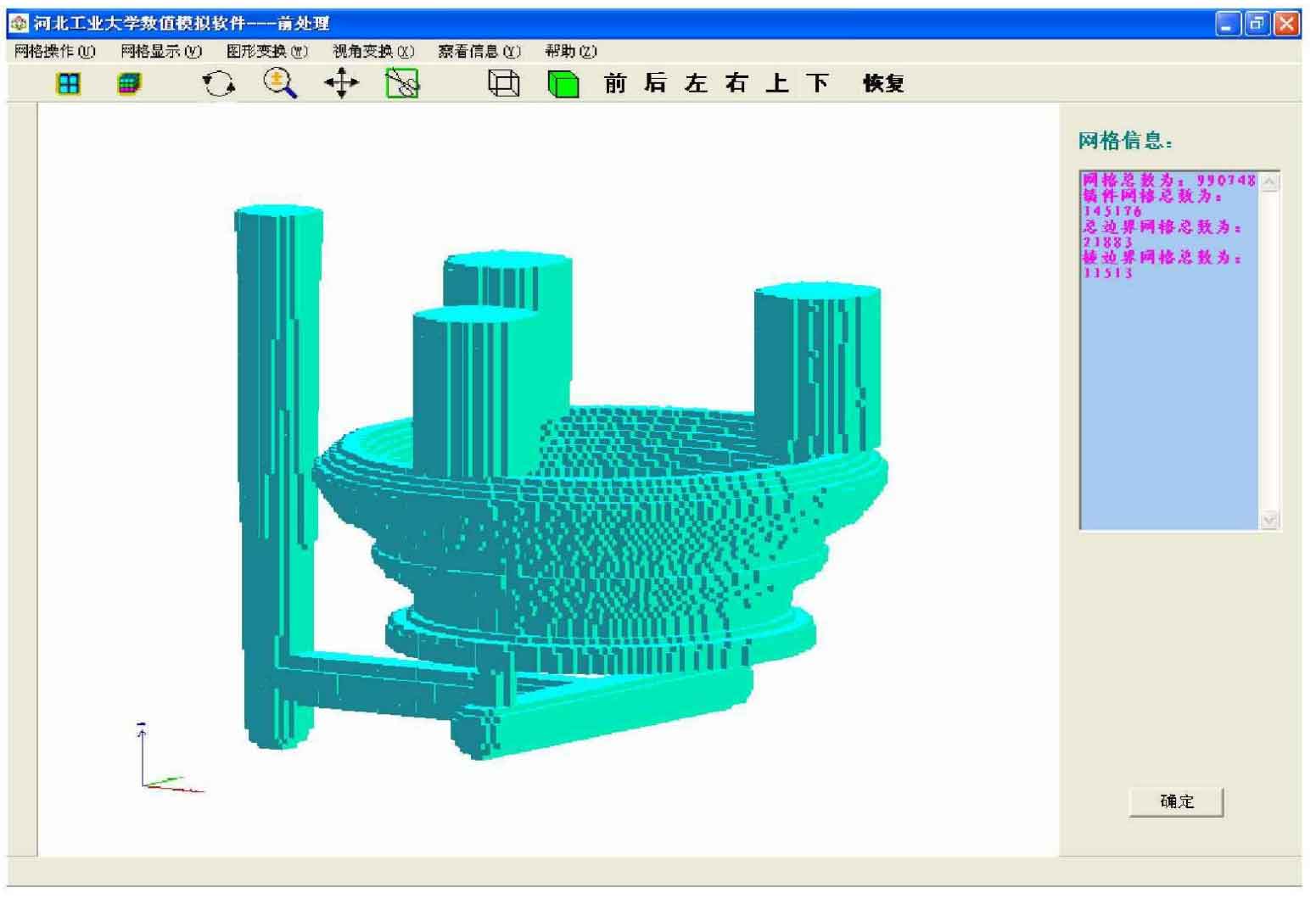
The bowl lining is simulated according to the original process. The figure after grid division is shown in Figure 3. The grid division size is 10x10x10 cubic mm. In the calculation of thermophysical parameters, the shrinkage rate of casting material is 3%, and the total number of units including mold, riser and gating system is 990748.
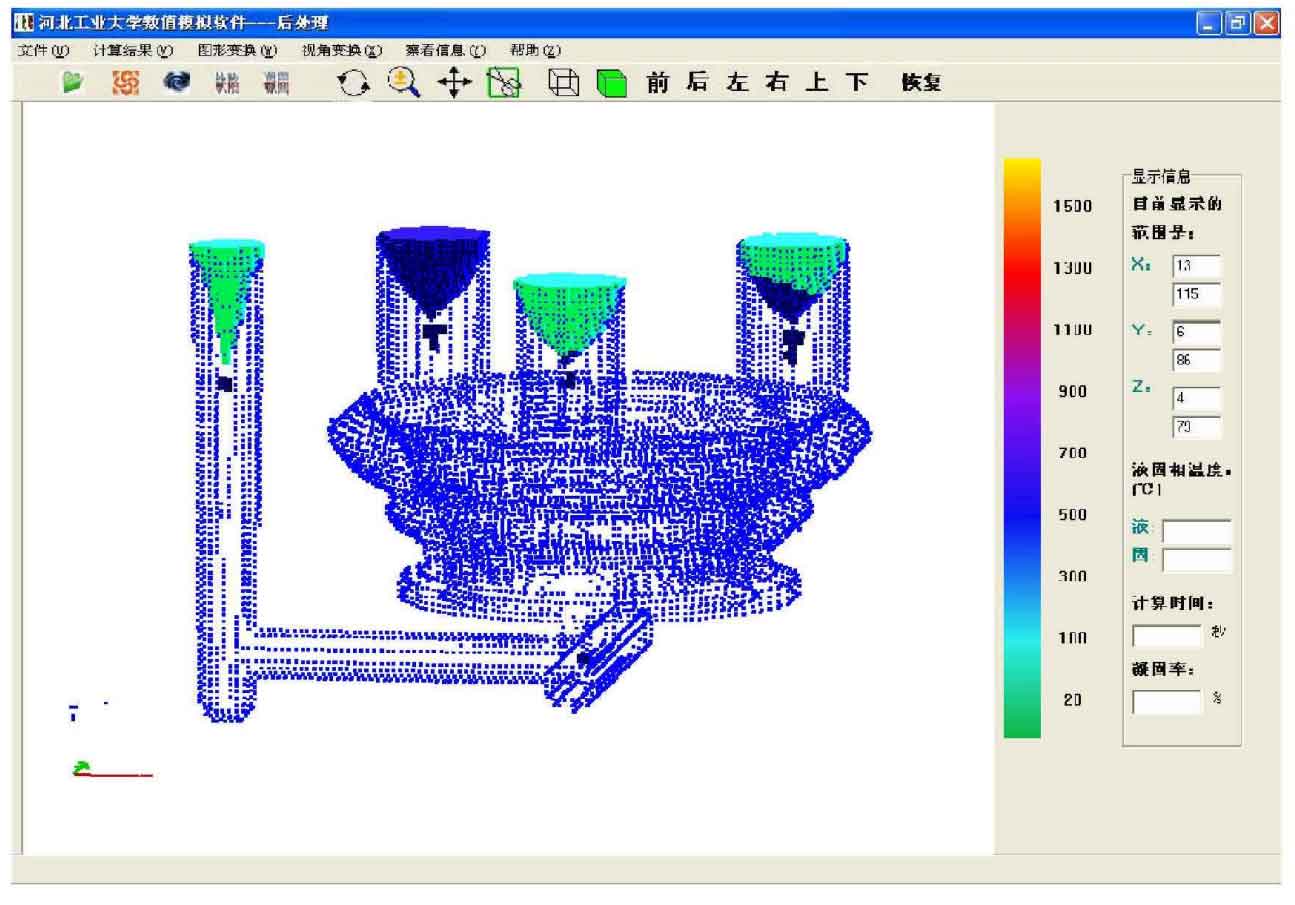
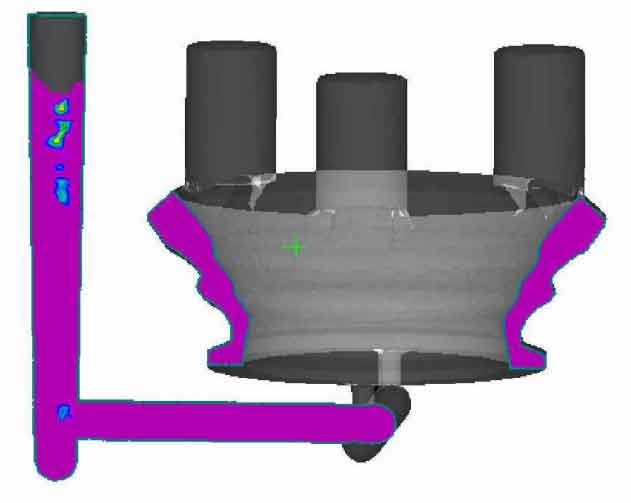
According to the above casting process, after the simulation calculation, figure 4 is the display diagram of the final shrinkage defects simulated by the numerical simulation software. From the calculation results, it can be seen that the shrinkage defects are distributed in the riser and gating system, the shrinkage defects are located below the shrinkage defects, and the internal casting quality of the casting is good. The actual production results have proved that the production of the casting can fully meet the requirements and the casting quality is good.
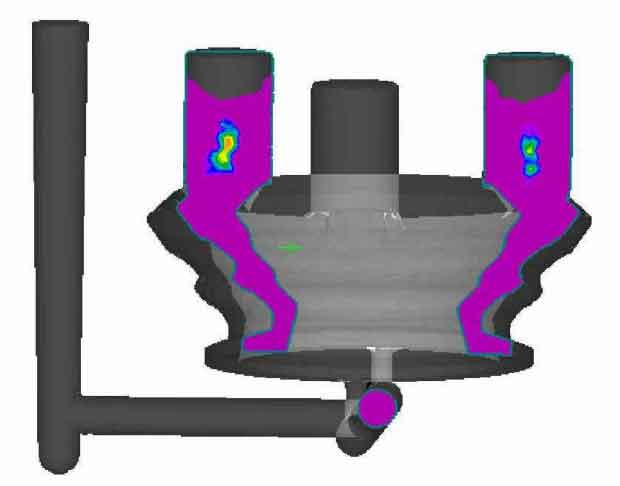
The above castings are compared and simulated with mature commercial numerical simulation software with the same materials, the same material physical properties and the same simulation conditions. The simulation results of ProCAST are shown in Figure 5. Figure 5.1 shows the distribution of shrinkage defects. It can be seen that shrinkage defects are distributed on the top of riser and gating system; Figure 5.2 and Figure 5.3 show the distribution of shrinkage defects. From the simulation results, it can be seen that the defects are mainly distributed in the middle of the riser, the lower side of shrinkage defects, and the hot spot of the gating system. From the comparison of the simulation results, it is completely consistent with the shrinkage defects predicted by this software.