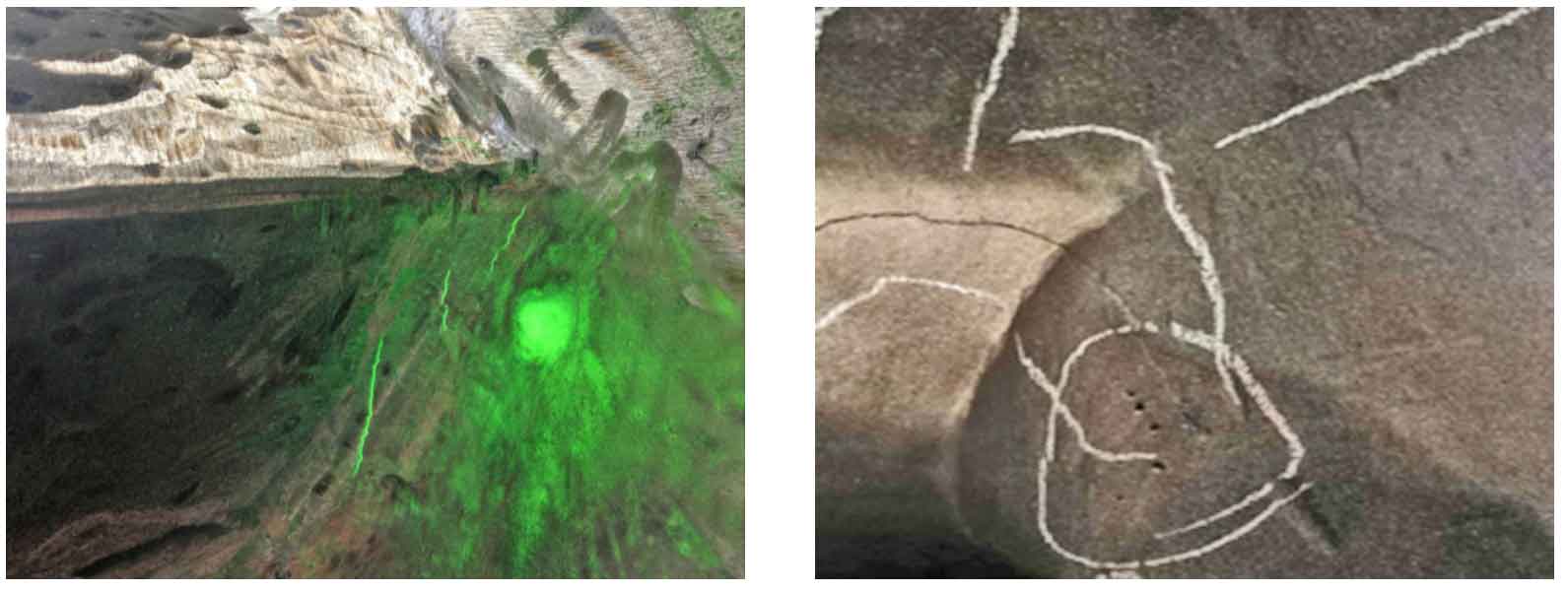
1. Manifestations of cold crack defects
Under the joint action of welding stress and other embrittlement factors, the bonding force of metal atoms in the local area of the welded joint is destroyed to form a new interface. The gap generated by the new interface is a cold crack defect. Other embrittlement factors such as restraint stress, hardened structure and diffused hydrogen can produce cold crack defects. The details of cold crack defects are shown in the figure.
Welding cracks are divided into hot cracks and cold cracks. Cold cracks are the most common defects in the welding process of large steel castings. Therefore, the analysis of cold cracks is focused on. Cold cracks mainly occur in the welding heat affected zone of medium carbon steel, low alloy steel and high alloy steel. Some occur immediately after welding, while others will be delayed for a period of time. Crack defects are one of the most harmful defects in welding defects, which need to be managed and controlled from the whole process of welding.
2. Main measures to prevent cold crack defects
In order to prevent cold crack defects, the following measures need to be taken:
① Preheating is an effective measure to prevent cold cracks. The main purpose of preheating is to increase the low-temperature parameters of thermal cycle and make it conducive to the full diffusion and escape of hydrogen. According to the carbon equivalent of the casting, the preheating temperature in line with the actual production shall be reasonably selected to slow down the cooling rate after welding and ensure the timely escape of diffused hydrogen. For large steel castings, the overall preheating method is generally adopted before the first welding, and the local preheating method can be adopted for individual small defects. During the preheating process, the casting can be heated slowly to avoid excessive temperature difference caused by rapid heating. The post heat treatment shall be carried out in time after welding, and the appropriate post heat time shall be selected according to the different defect depth. Generally, the post heat time shall be controlled every 25 mm / 1 H + 1 h according to the defect depth, so as to ensure the purpose of hydrogen and stress elimination;
② Strictly implement the welding process. The welding parameters in the welding process qualification are the process documents for the welding engineer to guide the on-site operation after practical evaluation. The operator needs to strictly implement them. In particular, pay attention not to use the illegal operation of low preheating temperature, high current and high heat input due to the fast pace of production. In addition, the cleaning of defective groove and drying of welding materials are the key control points of the whole welding process, which should be paid special attention by welding quality management personnel.