The formation mechanism of hot tears casting defects mainly includes liquid film theory and strength theory. According to the liquid film theory, when the casting is cooled near the solidus, there is still a small amount of non solidified liquid around the grain to form a liquid film. When the shrinkage of the casting is blocked, the deformation mainly occurs on the liquid film. When the deformation reaches a certain critical value, the liquid film breaks and forms tears and casting defects. According to the strength theory, when the casting cannot shrink freely due to the obstruction of sand mold, sand core, gating system and riser during solidification, the stress or strain generated in the casting exceeds the fracture strength or fracture strain of the metal at this temperature, resulting in hot tears casting defects.
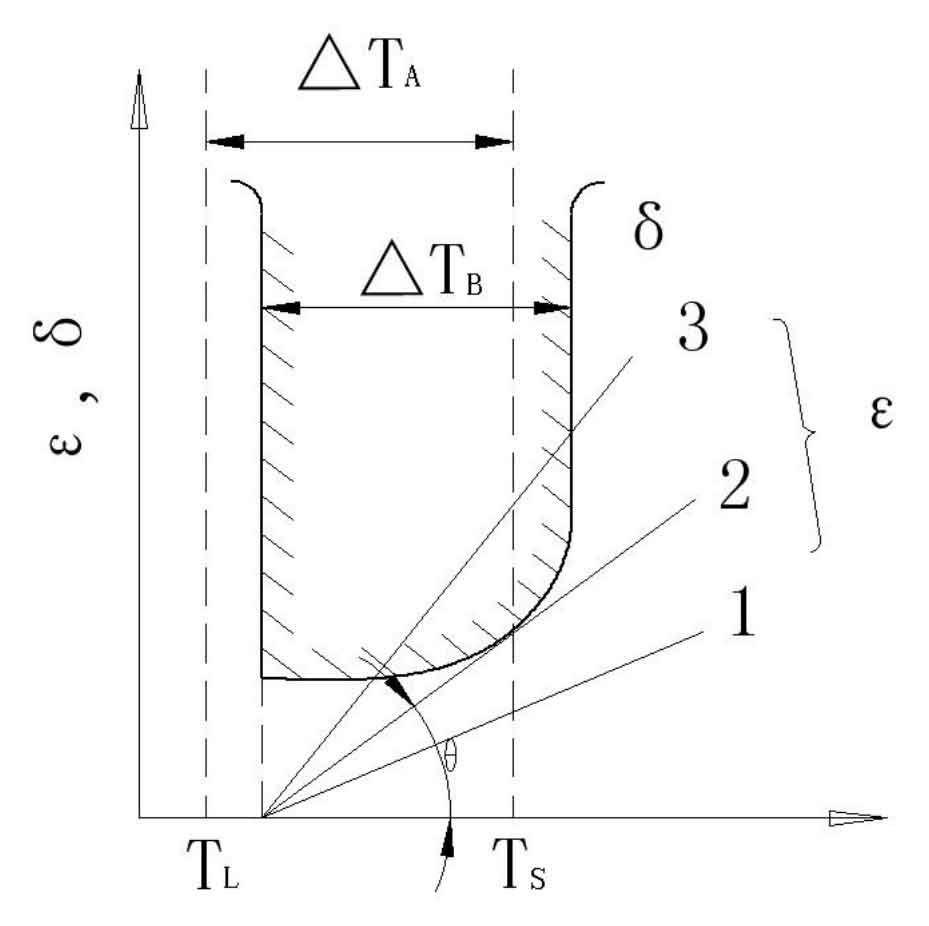
The forming conditions of hot tears casting defects mainly depend on the fracture strain of the alloy in the hot brittle zone △ TB δ And the strain of castings due to shrinkage obstruction ε, It can be described in the figure. Such as strain ε Change according to line 1, ε ﹤ δ, No tears casting defect will be formed; In case of straight line 2, ε=δ, It is the critical condition for the formation of hot tears casting defects; In case of straight line 3, ε ﹥ δ, It will inevitably form tears and casting defects. The results show that the fracture strain of the alloy in the hot brittle zone is much larger than the free linear shrinkage of the alloy at this temperature. Therefore, even if the shrinkage of the casting is blocked by rigidity, if the casting is uniformly deformed, there will be no tears casting defects. However, in actual production, due to the structural characteristics of the casting or other factors, the cooling speed of each part of the casting is inconsistent, resulting in different temperatures of different parts of the casting, different deformation resistance, and concentrated deformation at the hot spot. The temperature distribution of the casting is uneven, and the more serious the concentrated deformation at the hot joint is, the greater the possibility of hot tears casting defects. The stress and strain produced in the solidification process of castings depend on the free linear shrinkage of the alloy, the temperature difference in different parts of the casting, as well as the strength, stiffness and yield of sand mold and sand core.