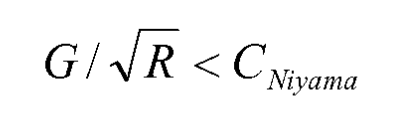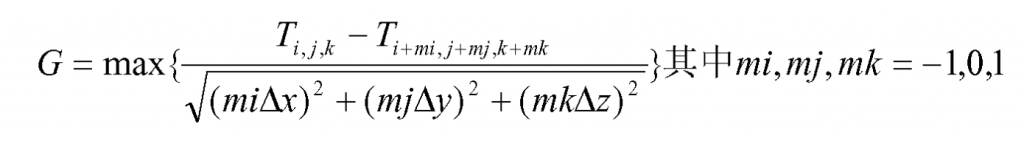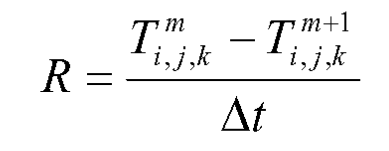The prediction of shrinkage defects in sand castings during solidification is mainly realized by using shrinkage defect criterion. Shrinkage porosity defects are generally related to the speed of solidification process, the size of section and alloy composition. When the shrinkage rate of each element is divided by the critical value of the shrinkage element in the early stage, it means that the shrinkage rate of each element is less than the critical value of the solidification element. At present, this method is adopted by most numerical simulation software, namely:
Where:
G — local temperature gradient of the identified area;
R — cooling rate;
Cniyama – is the critical value of the criterion, generally 0.8-1.2, the upper limit for large parts and the lower limit for small parts.
For the three-dimensional temperature field, the G and R values of 26 adjacent units of each unit shall be calculated respectively in the program, and the largest one represents the feeding capacity between dendrites. The calculation method is as follows:
The calculation method of cooling rate is:
According to the above calculation formula, the niyama of each grid can be calculated, so that the shrinkage porosity defects of sand castings can be predicted.