The figure shows the matrix structure of as cast ductile iron. It can be seen from figure a that the structure of nodular cast iron treated at temperature is graphite spheroidal carbide pearlite, and the content of pearlite is less, the content of carbide is more, and the nodular cast iron has been seriously white cast; When the treatment temperature is reduced to 1510 ° C, the structure of nodular cast iron is composed of graphite ball + pearlite + ferrite + carbide. Compared with the nodular cast iron with the treatment temperature of 1560 ° C, the volume fraction of pearlite and ferrite in the alloy matrix increases, and a typical “ox eye” structure appears. In the nodular cast iron, the volume fraction of pearlite is 83%, The microstructure of nodular cast iron treated at 1460 ° C is composed of graphite ball + pearlite + ferrite. The content of ferrite increases significantly, and the content of pearlite decreases from 83% of 1510 ° C nodular cast iron to 49%. Moreover, no carbide is observed in the matrix structure of nodular cast iron treated at 1460 ° C.
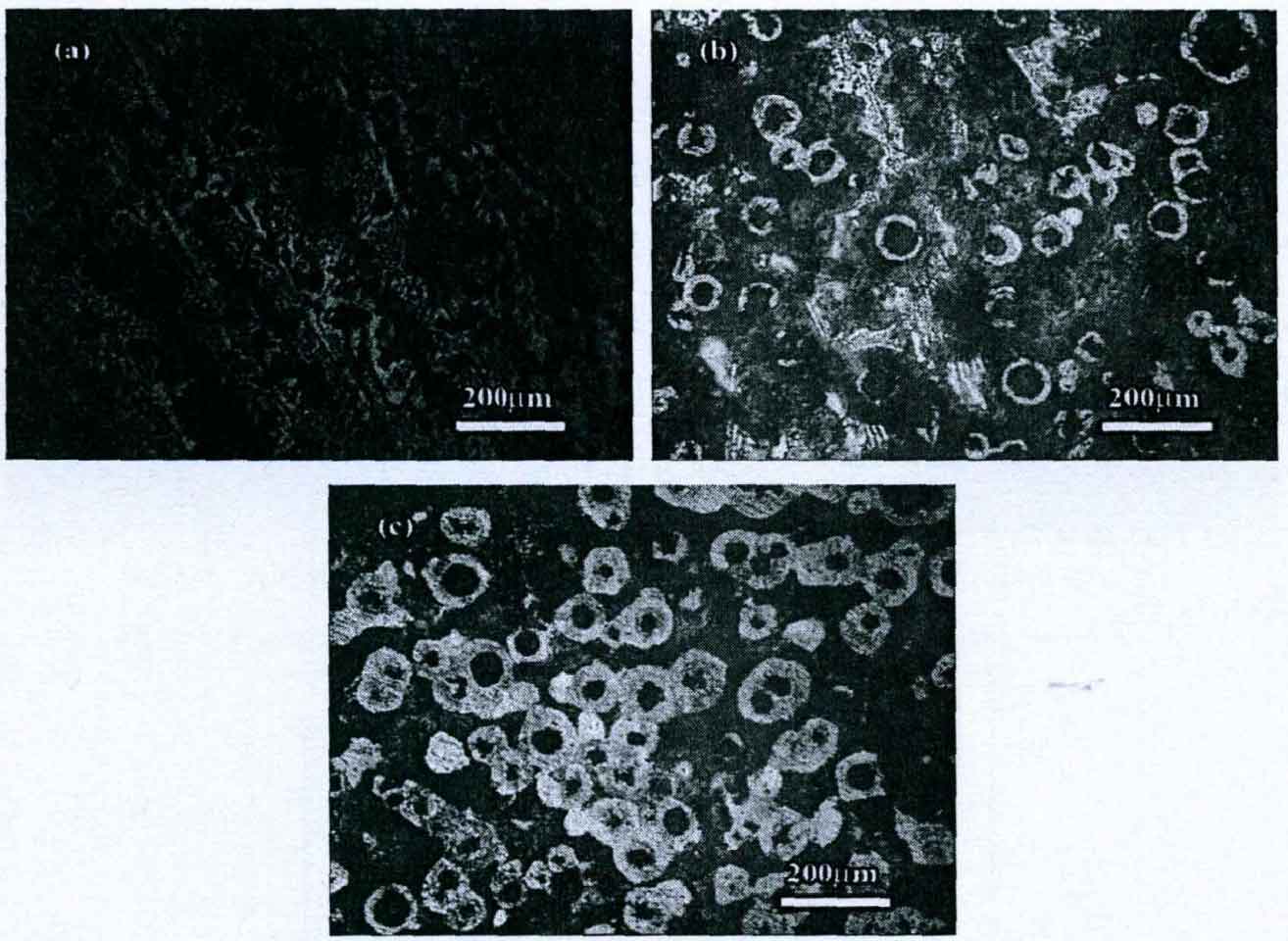
The nodular cast iron with a treatment temperature of 1560 ° C has white cast iron. The main reason is that the treatment temperature is high, and the nodular agent is burned seriously during melting and solidification, which reduces the content of graphitized elements in nodular cast iron and significantly increases the white cast iron trend. Therefore, a large number of carbides are generated in nodular cast iron. When the treatment temperature is reduced to 1510 ° C, the burning loss of carbon, silicon and spheroidizing agent is reduced, the carbide content in nodular cast iron is reduced, and the content of pearlite and ferrite is increased. Further reducing the treatment temperature further reduces the burning loss of carbon, silicon and spheroidizing agent, increases the graphitization tendency of the alloy and reduces its white mouth tendency. Therefore, no carbide is observed in the alloy. In addition, the increase of silicon content in nodular cast iron promotes the formation of ferrite structure. The ferrite content in nodular cast iron increases and the pearlite content decreases.
