1. Introduction
Large bearing housings are widely used in various industries. The quality of their manufacturing has a significant impact on national key projects. This article focuses on the sand casting process design and optimization for mass-producing bearing housing steel castings.
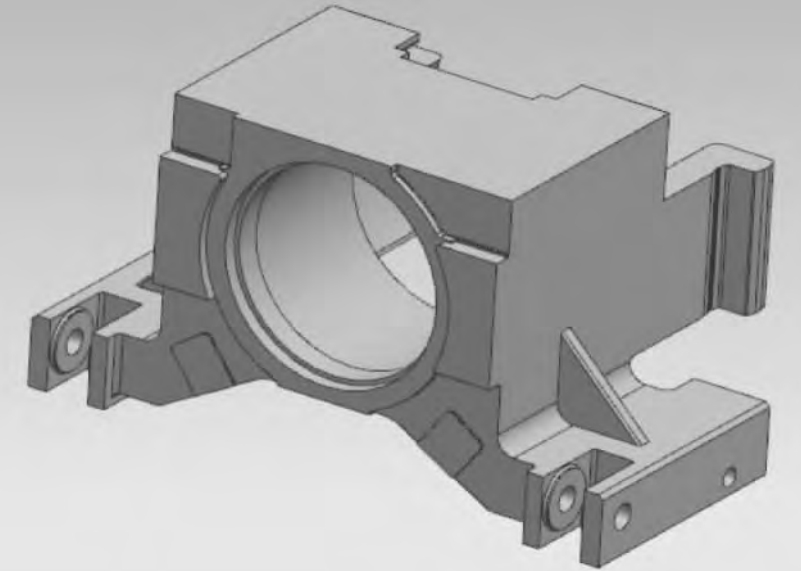
2. CAD Modeling of Bearing Housing
- The bearing housing is a large steel casting with dimensions of 2486mm×1639mm×1340mm and a main wall thickness of 50 – 254mm.
- UG software is used for modeling. The process involves creating a reference plane, determining positional relationships, and using commands like stretching, subtraction, and edge rounding to complete the 3D solid model.
3. Sand Casting Process Design
3.1 Process Plan
- Material: ZG310 – 570
- Production Nature: Mass production
- Casting Method: Sand casting with false box for upper and lower molds, mechanical and manual sand filling. The mold uses phenolic modified furan resin self-hardening sand. The coating is alcohol-based, and the parting agent is silver graphite powder for easy demolding.
3.2 Process Design Details
3.2.1 Parting Surface Determination
- Parting Scheme: Three-box curved surface parting (upper, middle, and lower boxes). The lower parting surface is curved, and a false box is used for molding to ensure size accuracy and improve production efficiency. The upper parting surface is flat.
3.2.2 Gating and Riser System Design
- Gating System: Open stepped gating system with a bottom pouring ladle. The pouring cup is made of refractory bricks, and all parts of the gating system are connected with ceramic tubes. The dimensions of each runner section are shown in Table 1.
| Pouring System | Sprue/mm | Runner/mm | Ingate/mm |
| D_bottom | 140 | 100 | 140 |
| D_to | 140 | 100 | 140 |
| H/L (upper/bottom | 1016/527 | 1668/1420 | 350/410 |
- Riser: General-purpose open risers are initially set. The sizes of 1#, 2#, 3#, and 4# risers are determined according to the solidification shrinkage rate of steel castings. Later, after optimization, two waist-shaped open risers are used symmetrically.
- Contraction Rib: Designed to prevent hot cracking in steel castings. The thickness t=(1/3 – 1/4)δ=65mm (δ is the thickness of the casting side wall), the length of the hypotenuse , and the interval . Only one contraction rib is set symmetrically.
3.2.3 Sand Core Design
- A cylindrical sand core is designed for the middle cavity of the casting, with a square core print. Four cavities on the two-week fixing seats are also cast, and the sand cores have air holes in the middle.
4. Casting Solidification Simulation
- The pouring temperature is determined to be 1530 – 1570℃, and the pouring time is about 65 – 110s for better casting quality.
- The solidification process simulation using Huacast CAE software shows that the original process has a large number of shrinkage cavity and porosity defects, indicating poor riser feeding effect.
5. Process Optimization
- By changing the riser design to two symmetrically arranged waist-shaped open risers using the modulus method, the shrinkage cavity and porosity defects are significantly improved, with most shrinkage concentrated in the risers.
6. Conclusion
The sand casting process for the bearing housing is designed and optimized. The process has certain guiding significance for actual production through simulation and optimization using Huacast CAE software.
