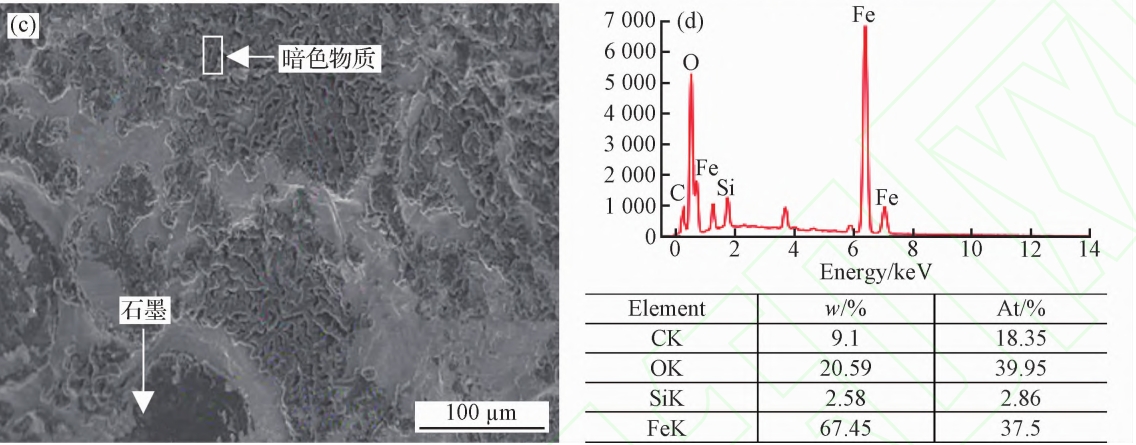
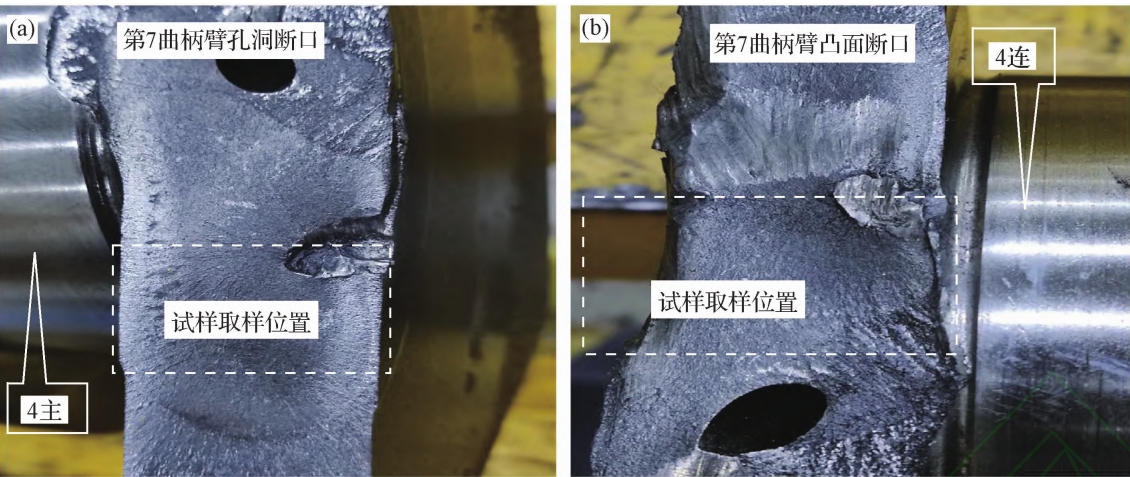
The failed crankshaft is a ductile iron crankshaft! material qualityStrengthening the process with rounded corners, nodular cast iron groove cutting, rolling, and E-axis diameter medium frequency induction quenching+solidVerify the use of a microscope (metallographic microscope, etc.)Don’t analyze the fracture morphology of the failed crankshaft!nodular cast iron On the source of fracture surface cracksPerform energy spectrum analysis on micro components using an energy spectrometer! To the fracture zoneTake samples for metallographic analysis and determine the environment during the operation of the crankshaft (bearingLoad received! Combined with the inherent characteristics of crankshaft materials! Comprehensive analysis songThe failure mechanism of the shaft! So as to identify the true cause of early fractures.
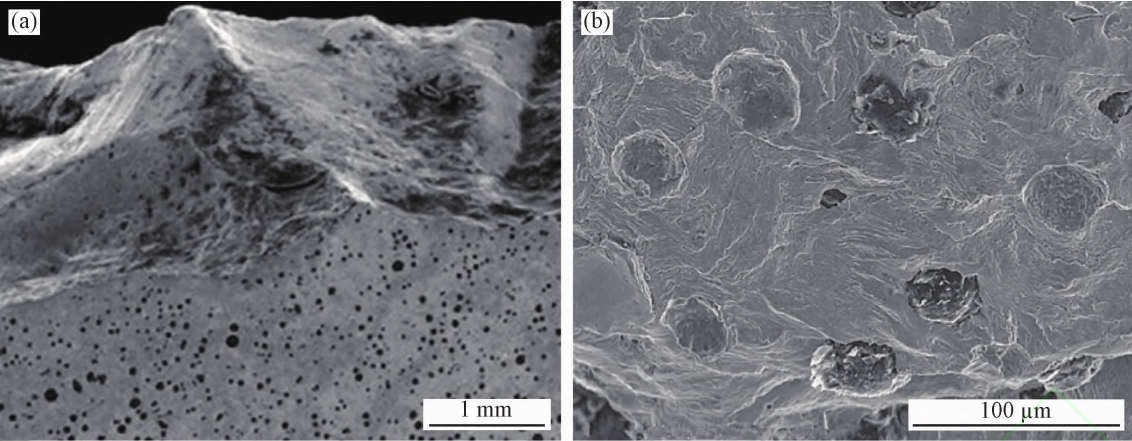
The fracture morphology of the failed workpiece shows that the workpiece is under load and its ownThe failure mechanism and process of the comprehensive effect of materials and operating environment! Regular workersThe failure of components starts from surface or near surface layer damage! And leave it aloneSome features and traces! nodular cast ironThese features and traces include the surface of the fracture surfaceMorphology, metallographic structure (changes in color and other states+analysis of fracture characteristics,It is to search for these features and traces on the fracture surface of the failed workpieceThe origin location of failure and fracture, the direction of fracture propagation ,force at failure)Features, etc! Confirm whether there are macroscopic defects in the crack source area! Further judgmentMain crack, nodular cast iron crack source or failure nature, etc.
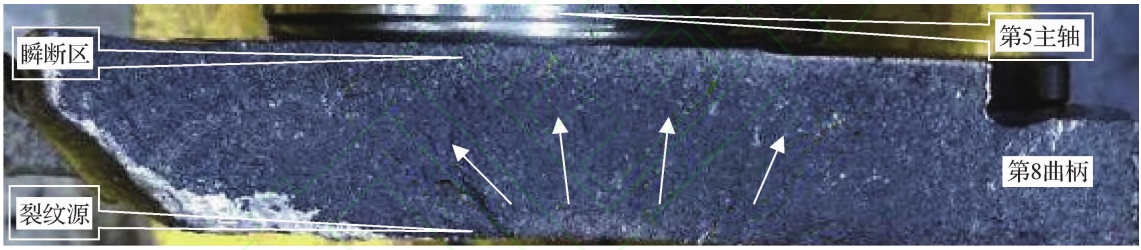
The strengthening process for the rounded corner of a fractured crankshaft involves groove cutting and rolling,nodular cast iron as well as through rollingStrengthen! The transformation of tensile stress on the surface of the fillet into compressive stress+tensile stress is the main factor causing fatigue failure of the crankshaft journal fillet! And the rounded surface remainsThe residual pressure stress can effectively offset some of the tensile stress during crankshaft operation and reduce itPeak stress! This greatly improves the fatigue strength of the crankshaft fillet.nodular cast iron The fatigue source location where the rounded corners have not been strengthened by rolling! Generally, in stress concentrationThe center of the rounded corner! And after the rounded corners are rolled and strengthened! Due to residual compressive stressThe pressure relief and peak shift effect! The fatigue source generally transfers to rollingPosition the edges on both sides of the groove.
It can be seen! The crack source is also perfectly locatedAt the intersection of the edge of the rolling groove at the bottom dead center of the crankshaft and the connecting rodSet it up!nodular cast iron Section: Near surface of crankshaft+crack propagation direction and axial base of crankshaftThis is $; Angle i! Finally, roll the groove edge near the rounded corner of the $th spindle neckInstantaneous fracture occurs along the position.
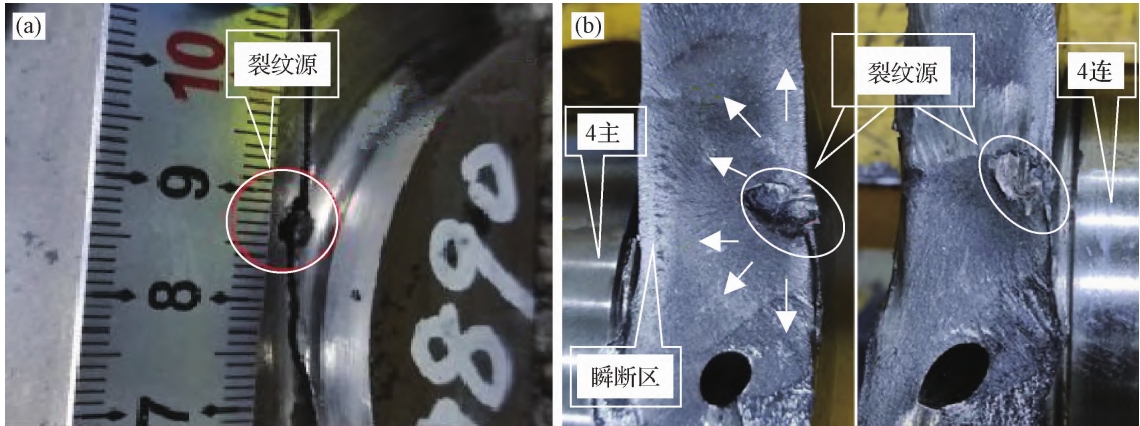
For ductile iron crankshafts! The crankshaft failure position is often locatedThe reasons for the occurrence near the bottom dead center of the connecting rod journal and the transition fillet of the crankshaft also include! The transition radius near the lower dead center of the connecting rod journal belongs to the hot spot area!nodular cast iron It is easy to have many shrinkage pores (such as porosity (slag inclusion and other casting defects).