The simulation results of the initial process defect distribution of precision casting turbine guide are shown in the figure. From the figure, it can be seen that the shrinkage and porosity defects of precision cast turbine guides are mainly distributed inside the blades, in the connection area between the blades and the inner ring, in the connection area between the blades and the outer ring, and in the flange area.
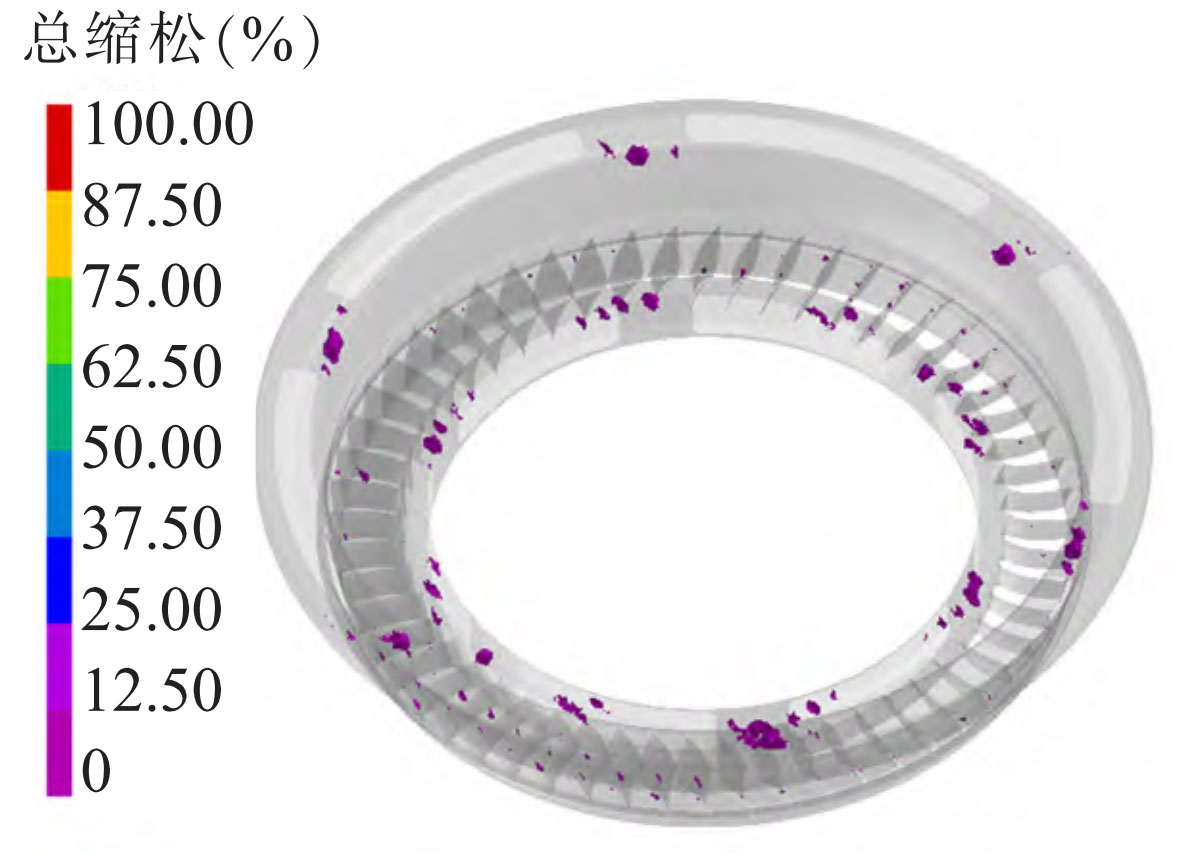
Based on the analysis of the filling solidification process, it can be seen that the internal and surrounding areas of the blade are caused by severe turbulence phenomena in the outer ring, which greatly affects the temperature distribution and the priority cooling solidification process in the thin-walled area; Combined with the unique “crescent” structure and cooling conditions of the blades, there may be a problem of low cooling rate, so it is not difficult to form shrinkage porosity casting defects in the internal and surrounding areas of the blades.
In addition, the defects in the flange area are mainly concentrated between two risers. This is due to factors such as large riser size, narrow spacing between the two risers, and heat dissipation in the top transverse runner of precision castings, which leads to heat concentration and the formation of hot spots, ultimately leading to shrinkage porosity and shrinkage defects.
