The whole process from molten iron smelting to casting completion is a complex and irreversible process. In the process of high temperature smelting and pouring, it is impossible to ensure that the oxide slag is completely removed and does not enter the mold cavity. Theoretically, in order to effectively prevent and avoid the first slag inclusion defect, the main way is to increase the pouring temperature, strengthen the quality control of molten iron smelting, reduce the amount of residual magnesium and thoroughly remove the slag, and the main effective technological measures are reasonable design of gating system. Based on the analysis of the source and production process of slag inclusion and inclusion in castings, the prevention and control measures must be taken from the aspects of gating system design and molten iron smelting quality to reduce the slag inclusion defects completely. For the design of gating system, this part analyzes and studies the matching of each component of gating system through successful practical cases, so as to better play the role of effective slag avoidance of gating system and prevent slag inclusion defects on casting surface.
In the early stage of the experimental study, a wind turbine bearing block with the same surface inclusion and inclusion problems was selected as the experimental casting for theoretical verification. The pouring system scheme of the bearing pedestal casting is basically the same as that of the pilot production scheme and gating system theory of the gas turbine inlet cylinder; the bearing pedestal casting and the inlet cylinder casting have the same wall thickness area with wall thickness of 60mm-350mm In the casting process of the bearing pedestal, only the gating system is used to block the slag and prevent the slag inclusion on the surface of the casting, which has a strong dependence and sensitivity on the slag blocking effect of the gating system. Based on this reason, as a successful practice case, the bearing seat has accurate guiding significance for the research of feeding cylinder gating system. The results of practical case study are as follows:
(1) “Closed bottom return + pool type gate Cup” and “closed bottom return gap + gate Cup” gating system
There are serious slag inclusion defects on the upper surface of the casting. Ut inspection after processing shows that there are slag inclusion defects with different severity in the range of 0 ~ 40mm in the upper table of the casting.
The closed gating system can ensure that the liquid iron can fill the mold cavity smoothly and rapidly during the filling process, and the impact on the mold can be reduced at the same time. The runner of the closed gap gating system is set at the bottom of the casting, and the runner is submerged in the molten iron during the filling process, which can effectively prevent and avoid the splashing and oxidation of the molten iron, thus effectively ensuring the stability of the filling process. The runner of the slit gate is always full during the pouring process, which is conducive to the smooth discharge of gas in the mold cavity.
Under the same pouring head height and the same ladle nozzle and sprue area, the velocity of molten iron at the outlet of closed gating system is higher than that of open gating system. If the area of slag absorption zone of gating system is not enough, or the actual pouring time is deviated from the theoretical design, the slag in the runner will be absorbed into the mold cavity by the runner without enough and sufficient floating time, resulting in slag inclusion in the casting. At the same time, part of the process design attempts to extend the pouring time to make up for this deficiency, but the location of the skin joint between the gating system and the casting is formed by sand mold, and the heating area is relatively large When the temperature of molten iron is above 1300 ℃, it is easy to cause sand washing, which will change the actual area of each component in the gating system and form a pseudo closed gating system, resulting in serious sand inclusion and slag inclusion defects.
(2) “Open bottom return + pool type gate Cup” and “open bottom return + transfer ladle” gating system
A small amount of scattered slag inclusion defects were found on the surface of the casting. The excessive slag inclusion defects were found in the thickness range of 0-15mm after grinding and processing. After ultrasonic flaw detection and processing, it is verified that there are no other over standard defects on the upper surface of the casting within the range of 0-100 mm.
Based on the analysis of casting surface quality improvement and slag blocking capacity of gating system, the opinions of casting process designers on slag retaining capacity of closed gating system is better than that of open gating system. However, in the actual production practice, reasonable selection and matching of open gating system can effectively prevent slag from pouring large nodular cast iron castings. In the open gating system, the cross-sectional area of cross runner and inner pouring component is large, and the velocity of molten iron is slow, which can avoid turbulence and further oxidation in the process of filling and flowing of molten iron, so as to effectively reduce the formation of secondary slag. The research of a ductile iron manufacturer in Shaanxi Province shows that the effect of using open gating system to solve the secondary slag inclusion is obvious in the diesel engine block with complex structure. The research results also prove that the turbulence phenomenon can be effectively prevented by using open gating system in large complex ductile iron castings with complex structure and long pouring time Secondary slag inclusion defect.
(3) “Open bottom return + gating system filtration + transfer ladle” gating system scheme
The surface of the casting is basically free of slag inclusion and other defects, and the casting surface is smooth after shot peening. After ultrasonic testing and machining, there are no over standard defects on the upper surface of the casting within the range of 0-100 mm. The scheme can fully meet the requirements of slag blocking and slag avoiding in casting process.
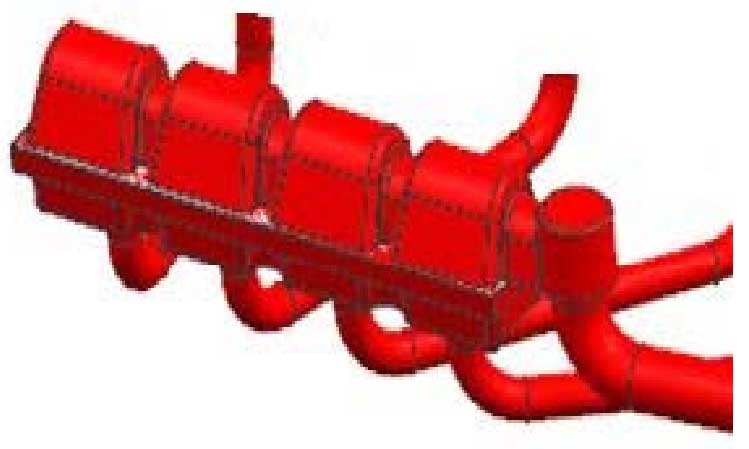
The process scheme of the filter slag blocking pouring system is shown in Fig. 1.
The process adopts the filtering technology of adding foam ceramic filter on the transverse runner, and the transverse runner is overlapped on the bottom of the filter base, and the filtering slag collecting bag is designed in the middle of the runner. The filter is used as a foam ceramic filter for the internationally renowned foundry material supplier FOSECO (size: 150 mm * 150 mm * 25MM, pore size: 10PPI). The maximum temperature of the filter can reach 1500 C, which has the best slag removal and flow control capability, and can reduce the turbulence of molten iron. After entering the sprue, the molten iron first flows into the slag collecting ladle of the filter seat, and then enters the casting cavity through the filter plate. The design of slag collecting ladle can not only reduce the damage caused by the direct erosion of the high pressure head of molten iron on the filter plate, but also play an important role in the transfer of molten iron to ensure that the molten iron enters the mold smoothly and evenly through the filter.
