There are five basic elements: carbon, silicon, manganese, phosphorus and sulfur.
1.Carbon
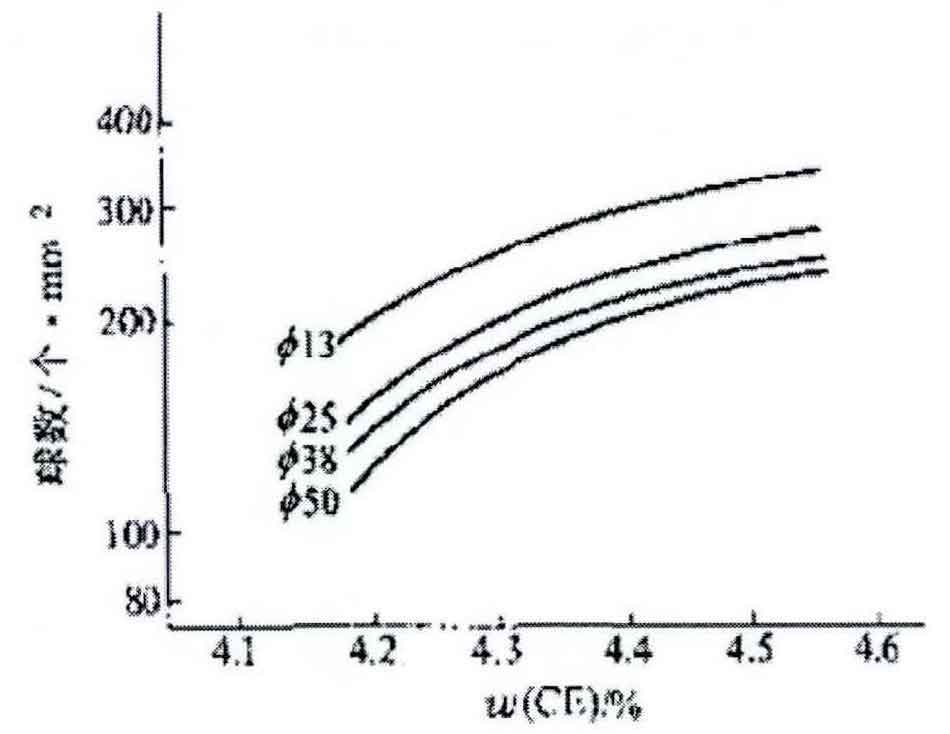
Carbon is the direct source of graphite ball. Because the weakening effect of spherical graphite on the matrix is small, when the carbon content changes from 3.2% to 3.8%, it has no obvious effect on the mechanical properties of nodular cast iron. Therefore, in the choice of carbon , It is mainly considered from the aspect of carbon equivalent. Carbon equivalent has a significant effect on the number of graphite spheres, as shown in Figure 1. It can be seen from the figure that when the carbon equivalent is 4.4%, the number of graphite balls is about 1.5 times that when the carbon equivalent is 4.2%. With the increase of carbon equivalent, the total number of graphite balls is gradually increasing. In the actual production of nodular cast iron, the suitable range of carbon equivalent is 4.2% – 4.6%.
2.Silicon
The influence of silicon on the microstructure and properties of nodular cast iron has two sides. On the one hand, silicon can increase the eutectic temperature of molten iron, expand the temperature range of three-phase coexistence zone of eutectoid transformation, reduce the tendency of crystallization undercooling and white mouth, increase the ferrite content and improve the plasticity and toughness of nodular cast iron. On the other hand, silicon can be dissolved in ferrite and play the role of solid solution strengthening. It not only improves the tensile strength and hardness of nodular cast iron, but also increases the low-temperature brittle transition temperature of nodular cast iron and reduces the low-temperature impact toughness of nodular cast iron.
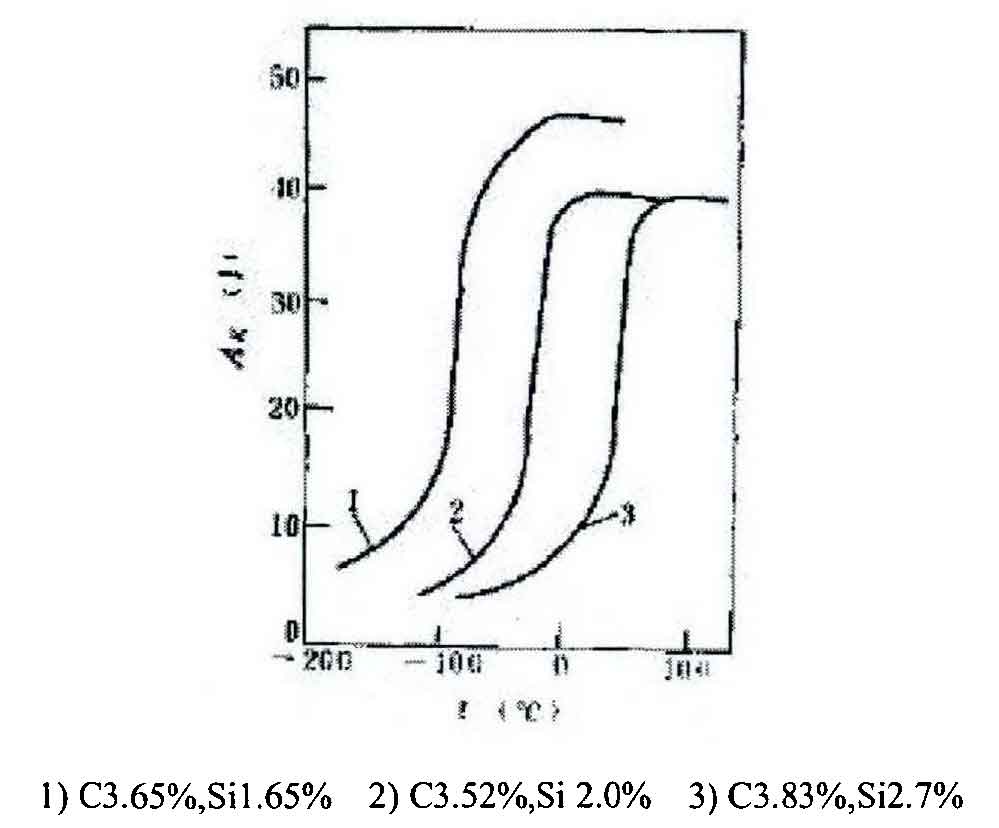
As shown in Figure 2, when the silicon content is 1.65%, the low-temperature brittleness transition temperature of nodular cast iron is about 100 ℃. When the silicon content increases to 2.0%, the low-temperature brittleness transition temperature increases to about 50 ℃. When the silicon content continues to increase to 2.7%, the low-temperature brittleness transition temperature has risen to room temperature, with obvious low-temperature brittleness.
It is also shown that in the appropriate range of carbon equivalent, the range of Si / C value with the best toughness value is 0.5-0.7. When the Si / C value is too high, the ferrite hardens seriously and becomes brittle, and the plasticity and toughness decrease significantly. When Si / C is too low, carbon oxidation will be serious. Based on this comprehensive consideration, the selection of carbon and silicon of nodular cast iron for wind power accessories should follow the principle of high carbon and low silicon, with WC = 3.6% – 4.0% and WSI = 1.8% – 2.3%.
3.Manganese
Manganese can stabilize the pearlite structure, increase the content of pearlite in the structure, and form intergranular carbides. When the manganese content is low, the cementite is distributed in isolation on the grain boundary. With the increase of manganese content, the cementite gradually forms a network, which reduces the impact toughness of nodular cast iron. Some data show that the low temperature brittle transition temperature of nodular cast iron will increase by 10-12 ℃ with the increase of 0.1% manganese. Therefore, in order to ensure the low temperature impact toughness of nodular cast iron Manganese content shall be strictly controlled below 0.4%.
4.Phosphorus
Phosphorus is a harmful element, which will do great harm to the mechanical properties of nodular cast iron. When the phosphorus content is high, it is easy to segregate in nodular iron to form phosphorus eutectic brittle phase, which seriously reduces the toughness of nodular cast iron. The data show that the low temperature brittle transition temperature of nodular cast iron increases by 4-4.5 ℃ with the increase of 0.01% phosphorus. When the content increases from 0.08% to 0.1% – 0.12%, the impact toughness at – 40 ℃ decreases by more than 50%. When it increases to 0.2%, the phosphorus eutectic content will increase twice, the casting is prone to cold crack, and the impact toughness decreases by 80%. Since dephosphorization cannot be realized in the production process, low phosphorus pig iron must be selected in the production process, and the phosphorus content of molten iron must be strictly limited to less than 0.04%.
5.Sulfur
After adding spheroidizing elements into molten iron, most of the sulfur elements combine with spheroidizing elements to form slag, and a small amount of sulfide can be used as the core of graphite balls to promote the formation of graphite balls. Sulfur is a surface active element that interferes with graphite spheroidization. Only when the sulfur content in molten iron is below 0.02%, can the spheroidization effect be good. When the sulfur content is too high, it will affect the stability of spheroidization, form more inclusions in the structure, and reduce the toughness of nodular cast iron. Therefore, the sulfur content in molten iron should be controlled below 0.02%.