1. Layout design
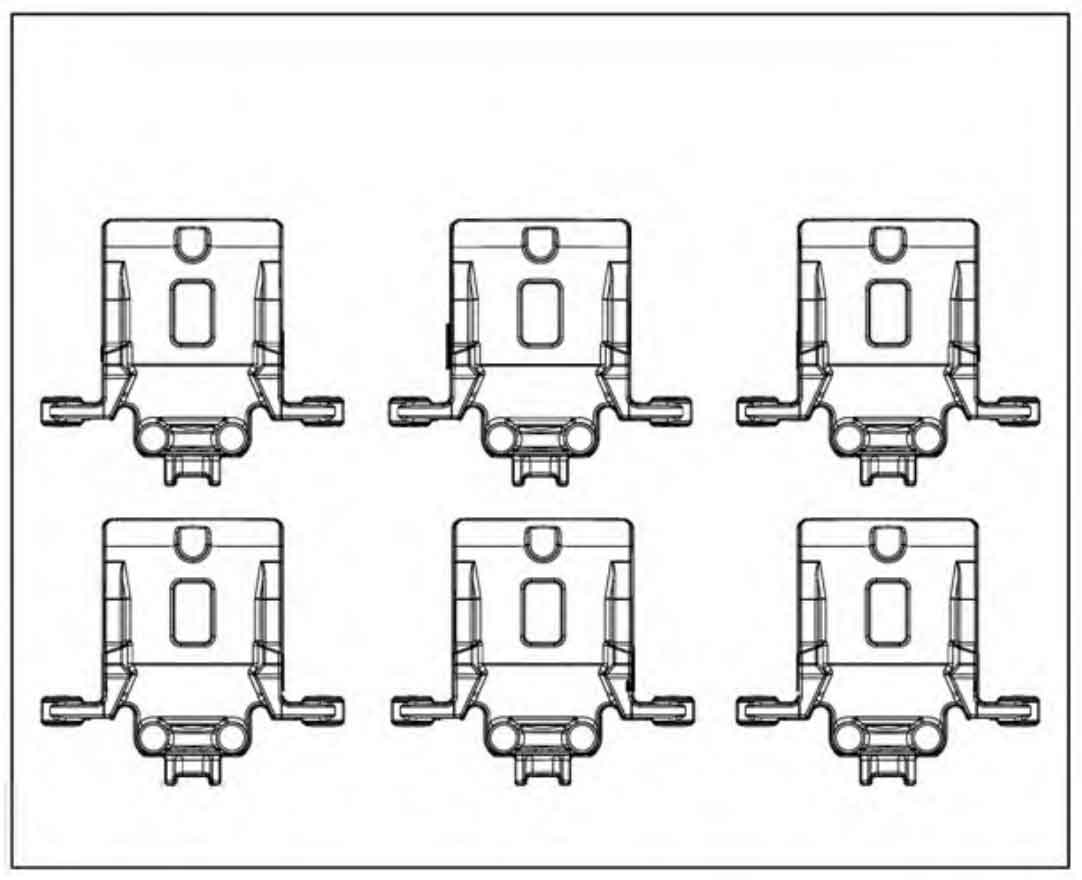
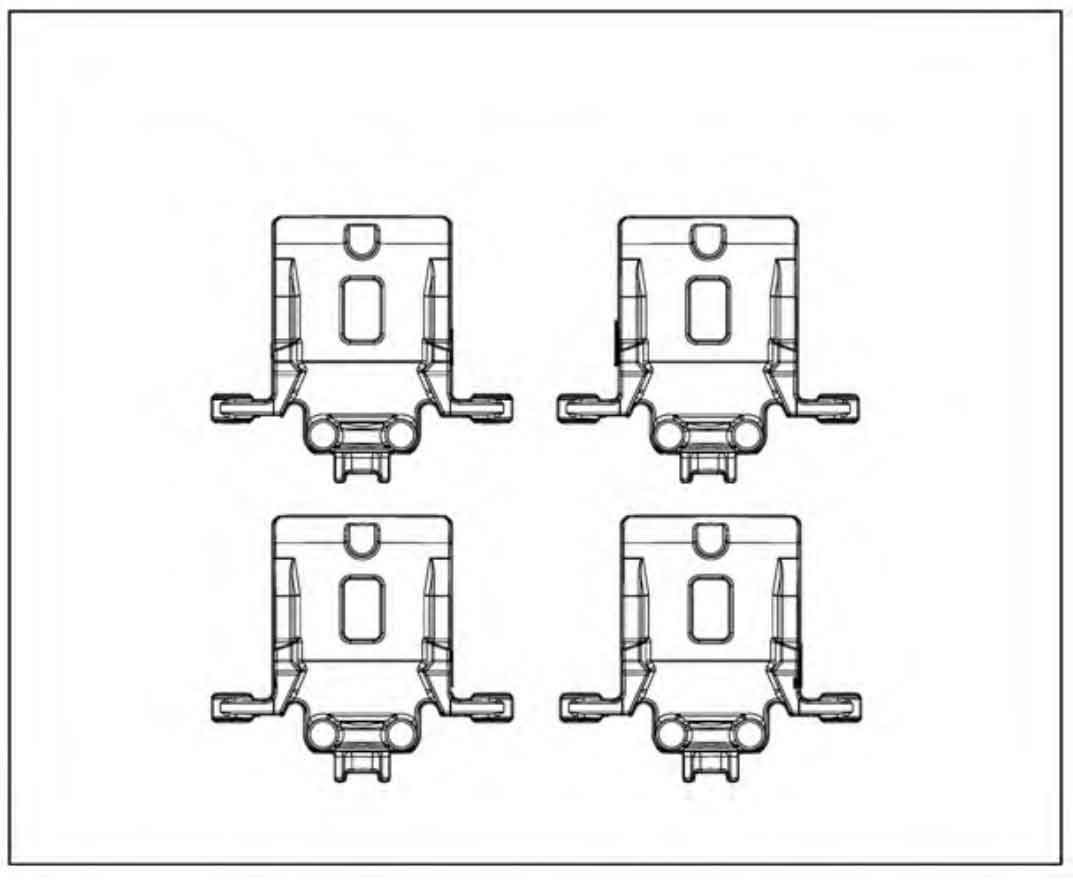
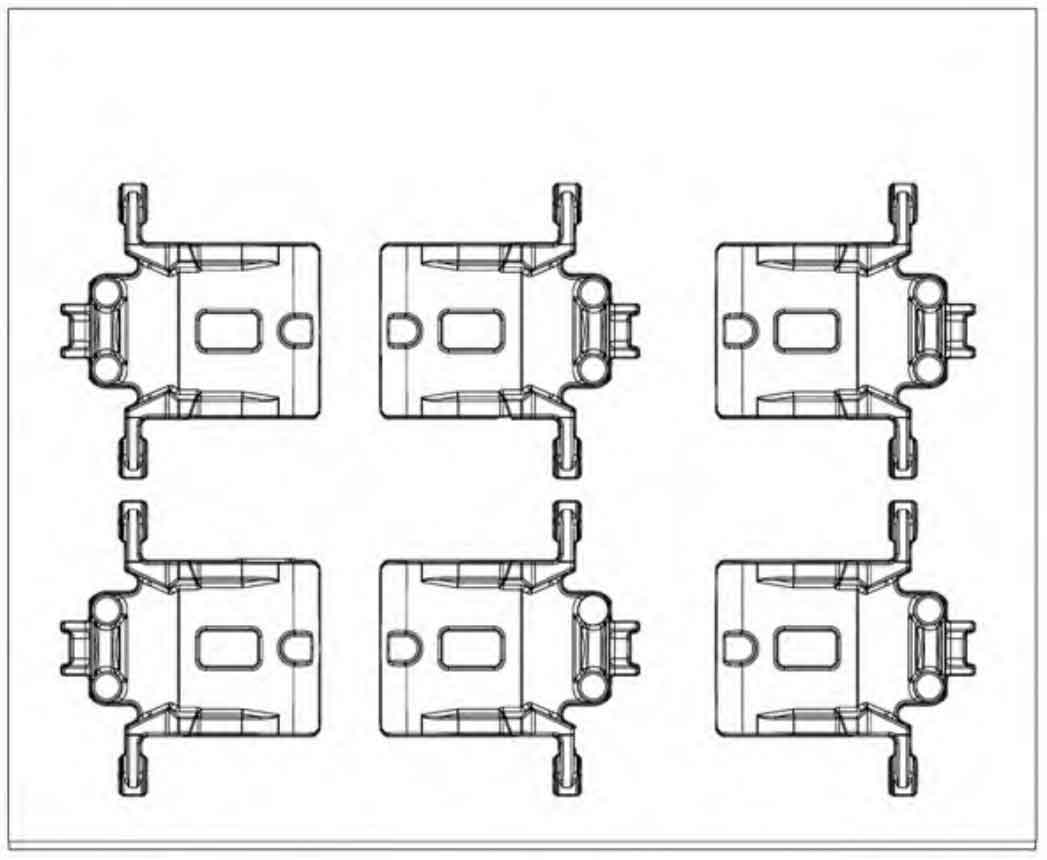
Disa230b vertical parting boxless injection molding machine is adopted, and the size of molding machine plate is 650 mm × 535 mm。 According to the conventional process layout (the cylinder barrel is placed vertically), if 6 ductile iron automobile brake calipers are placed, the pouring system cannot be placed on both sides, and the sand consumption is insufficient, as shown in Figure 1, so only 4 ductile iron automobile brake calipers can be placed per type, as shown in Figure 2. If the cylinder barrel is placed horizontally, the horizontal space of the molding plate can be saved, so three nodular cast iron car brake calipers can be placed horizontally and two nodular cast iron car brake calipers can be placed vertically, that is, six nodular cast iron car brake calipers. As shown in Figure 3, the process yield reaches 61.6%, which is increased by 19% compared with the conventional process.
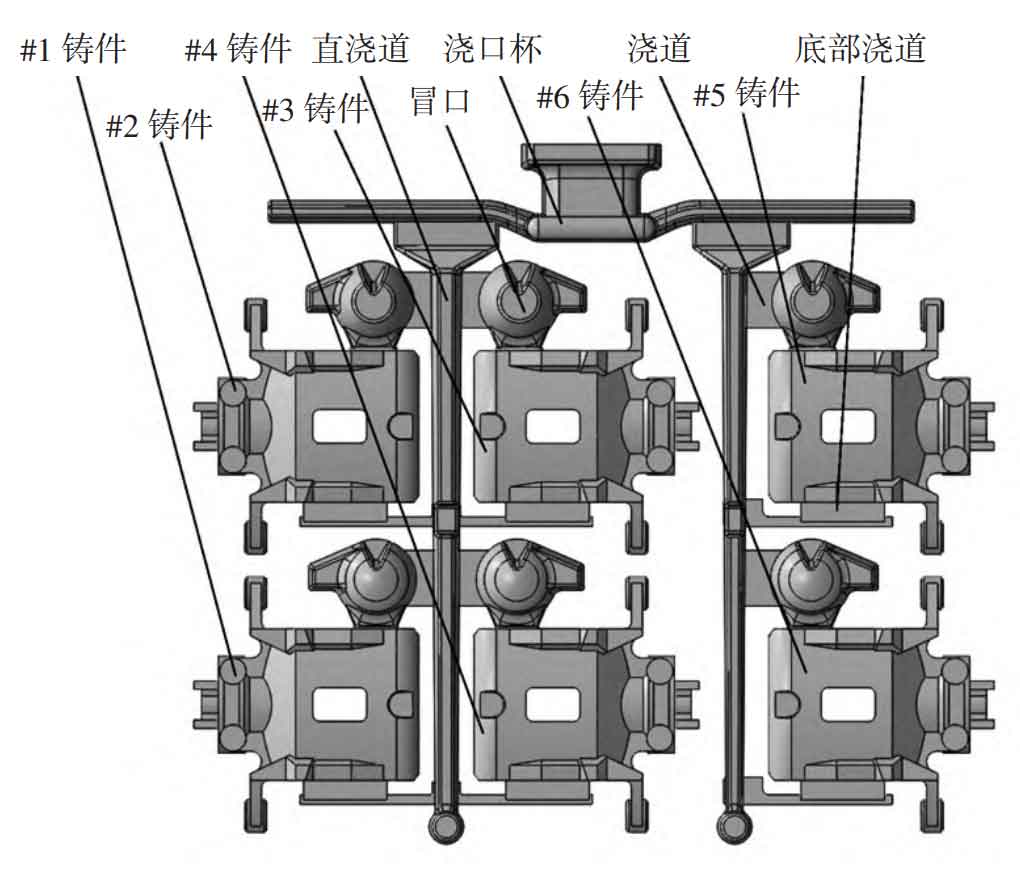
By adjusting the distribution of the distance between the brake calipers of nodular cast iron cars, the process layout in Figure 3 is adopted. Among them, 4 pieces are placed in the same direction, and the remaining 2 pieces are placed in the opposite direction, which is conducive to the placement of risers and the placement of gating system.
2. Riser design
With the layout method of horizontal placement of cylinder barrel, the riser can be placed directly above the nodular cast iron automobile brake caliper, which is more conducive to feeding, and can better ensure the internal quality of nodular cast iron automobile brake caliper. Each nodular cast iron automobile brake caliper only needs to design one riser for feeding.
The modulus of nodular cast iron automobile brake caliper is m pieces =v pieces /s pieces =5.27 mm; The modulus of hot joint of nodular cast iron automobile brake caliper is m hot joint =5.9 mm; Set the riser modulus as m riser =1.3m hot joint =7.67 mm.
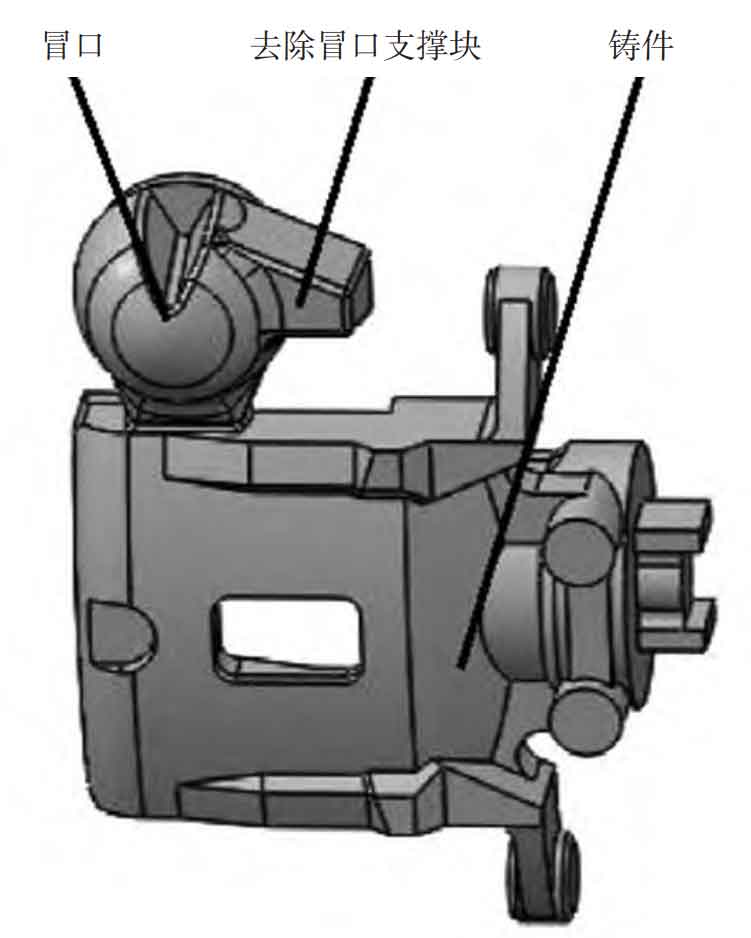
Due to space constraints, the diameter of the riser cannot be too large, and the size of the riser needs to be set reasonably. After calculation, a spherical riser with a diameter of 58mm is selected. In order to increase the feeding effect, the middle of the riser is thickened by 15 mm, and the final riser module M riser =8.6 mm, which can meet the feeding needs. The location and size of the riser are shown in Figure 4. In order to ensure the feeding effect, hot risers are used to enhance the feeding effect.
3. Pouring system design
According to the design of the riser, the riser is a hot riser, and molten iron needs to be introduced from the riser. Because the riser is placed on the top of the nodular cast iron automobile brake caliper, if the molten iron is completely injected from the top, the scouring effect on the mold cavity is strong, the nodular cast iron automobile brake caliper will have various defects of the top pouring system, and the appearance quality of the nodular cast iron automobile brake caliper cannot be guaranteed. In order to solve this problem, we choose to increase the sprue at the bottom of the casting at the same time, adjust the size of the sprue after many designs, and ensure the advanced molten iron at the bottom through computer numerical simulation, which can buffer the scouring of the top injection and make the molten iron fill smoothly [4-5]. In order to save the space of the mold plate and simplify the gating system, #1 casting, #2 casting, #3 casting and #4 casting share one sprue, #5 casting and #6 casting use one sprue, and 1 mm thick thin sheet is used at the bottom to introduce molten iron to improve the slag avoidance effect, as shown in Figure 5. Semi closed pouring system is adopted, Σ F straight: Σ F horizontal: Σ F internal =1:0.7:1.2, the sectional areas of the sprue, transverse sprue and internal sprue are 500 mm2, 350 mm2 and 600 mm2 respectively, the initial pouring temperature is 1420 ℃, the final pouring temperature is 1370 ℃, and the pouring time of each type is 8 s.
4. Numerical simulation
Magma simulation software is used to simulate and analyze the mold filling process and solidification process of the casting process. Figure 6 shows the temperature field distribution of the casting mold filling process. It can be seen that the nodular cast iron automobile brake caliper is filled smoothly without air entrainment. Figure 7 shows the simulation results of the solidification process. It can be seen that there is no isolated liquid phase area in the nodular cast iron automobile brake caliper, which reduces the probability of shrinkage defects.








