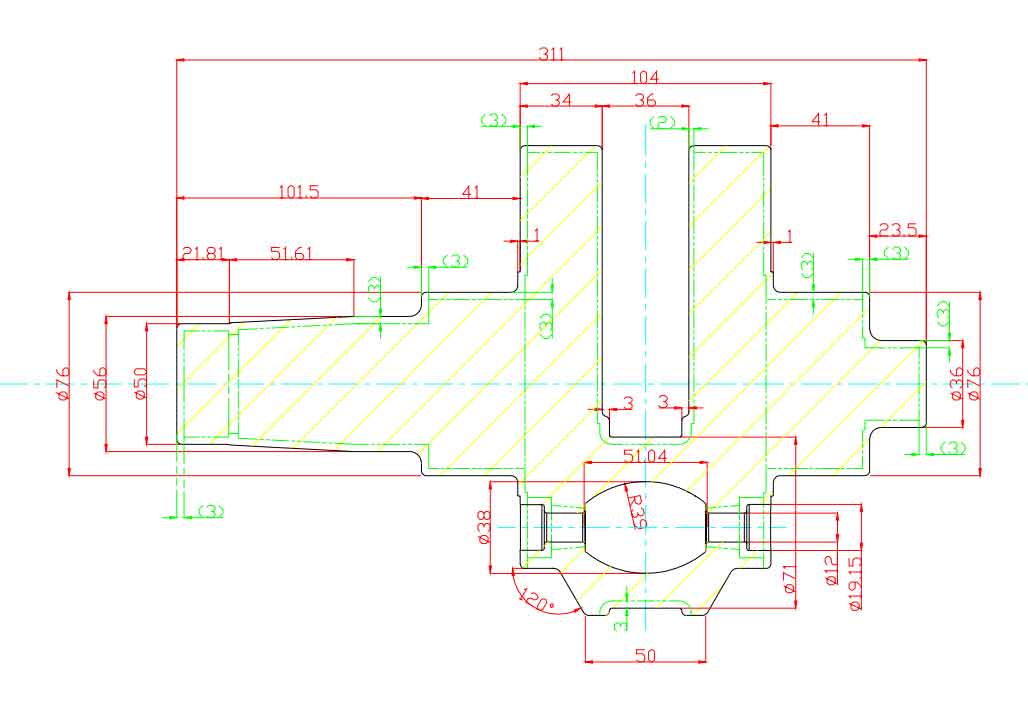
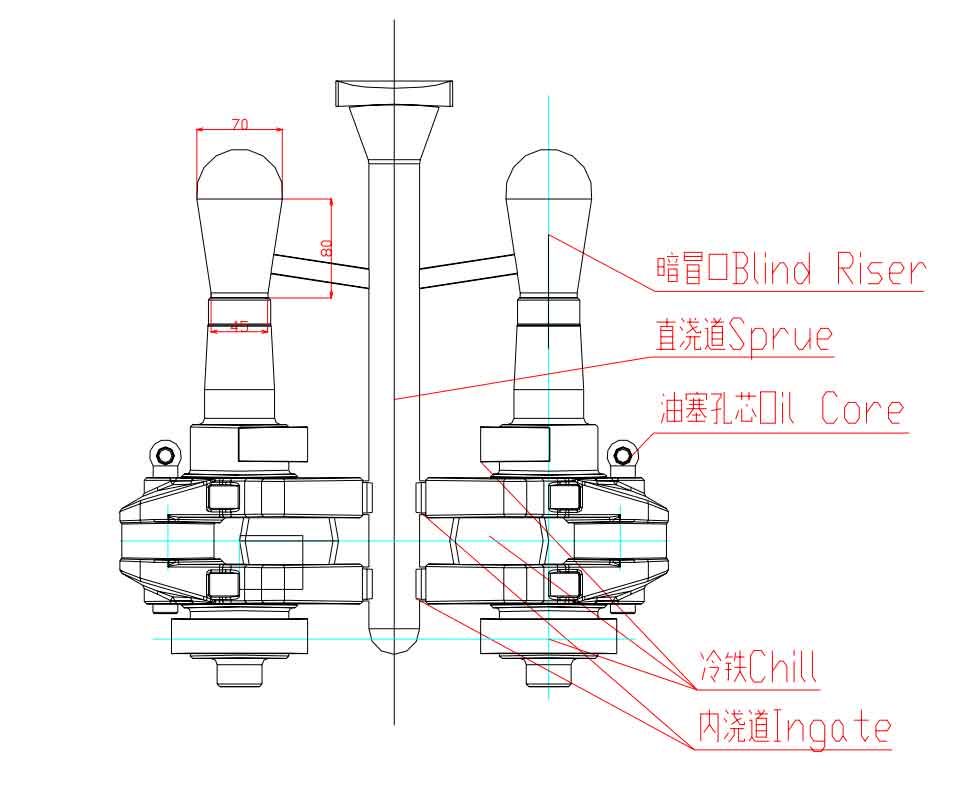
The design of crankshaft castings for S1100 single cylinder diesel engine is shown in Figure 1:
In order to minimize the casting defects of shrinkage porosity and shrinkage cavity inside the casting caused by graphitization expansion during nodular iron solidification, the design of crankshaft casting shall, on the premise of considering the machining allowance, minimize the allowance placed by the casting and increase the feeding of the riser to the casting. In particular, the thickness of the two plates shall be minimized. According to the working characteristics of the crankshaft, the machining allowance of 1-1.5mm shall be placed on the inner side of the two plates according to the principle of scraping and one knife. In the part drawing of S1100 diesel engine crankshaft in this subject, the opening size of the two fan plates is 38mm, the blank opening size of the two fan plates in the casting design is 36mm, and the machining allowance of one side on the inner side of the fan plate is 1mm.
Using iron shot coated sand process, the casting shrinkage is 0.8-1%, which is similar to that of iron mold coated sand process. For single crank crankshaft, the processes of shell casting, feeding of top concealed riser, feeding of molten iron into two plates, vertical shell making, filling of iron shot, vertical pouring and vertical cooling (see Fig. 2) are adopted to meet the requirements of mass production.
Volume change mode of nodular iron during cooling and solidification: after high-temperature molten iron is poured into the mold, liquid shrinkage occurs first, and the volume decreases continuously. When the temperature decreases to a certain value, it changes from shrinkage to expansion; Near the end of solidification, the volume change turns into shrinkage (secondary shrinkage) and then solidification. According to the cooling rate, chemical composition and process conditions, the volume change mode can be divided into three types: a (liquid shrinkage, expansion and secondary shrinkage are small), B (liquid shrinkage, expansion and secondary shrinkage are slightly increased) and C (liquid shrinkage and expansion). Slowing down the cooling rate can increase the graphitization tendency as by adjusting the chemical composition or process, which is conducive to changing the volume change mode in the direction of c-b-a. even if the liquid shrinks, the subsequent expansion and secondary shrinkage become smaller, so the shrinkage and shrinkage tendency can be reduced.
Therefore, in the hot spot where it is difficult to dissipate heat, appropriate measures (such as placing cold iron) should be taken to strengthen the cooling of the surface layer of the casting, so as to solidify the crust on the surface layer of the hot spot as soon as possible, so as to prevent the shrinkage and casting defects caused by the expansion of its shape.