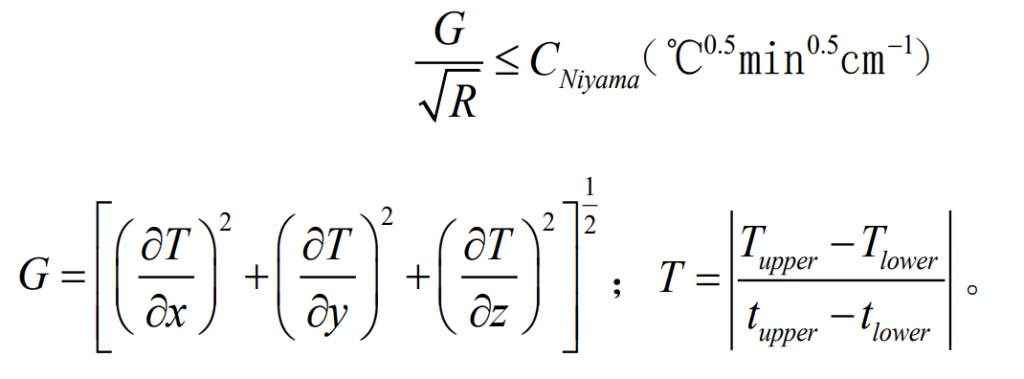The flow of liquid metal and the change of casting system will affect the defects of castings. However, due to the full consideration of all factors, the simulation process is complex and inefficient, and the heat transfer phenomenon is the main cause of shrinkage porosity and shrinkage cavity. Therefore, researchers from various countries have put forward several effective prediction criteria from the perspective of heat transfer, which are mainly based on time, temperature, solid rate, flow, etc. There are temperature gradient method, solid rate gradient method, niyama criterion method, etc. Niyama criterion is also generally used to predict the defects of cast steel. At present, casting simulation software such as magma, FTSolver and ProCAST all use niyama criterion method to predict the shrinkage cavity and porosity of castings, and some results have been achieved.
Niyama’s research shows that the ratio of the temperature gradient g at the end of solidification to the quadratic root of the cooling rate R is the function value that can best reflect the distribution of shrinkage cavity and porosity in the casting. When the niyama value is less than a certain critical value, shrinkage cavity and shrinkage porosity defects will occur in this area, and within the studied range, the critical value is independent of alloy composition, casting shape and size, that is:
Where,
Tupper: liquidus temperature;
Tlower: solidus temperature;
Tupper: liquidus temperature time;
Tlower: solidus temperature time
The research shows that the casting simulation value of the cast steel joint is 0.6.