The tensile samples of room temperature nodular cast iron as cast and treated at different normalizing temperatures were tested at room temperature by electronic universal testing machine. The mechanical properties are shown in the table. It can be seen from the table that the tensile strength of as cast nodular cast iron is 688mpa and the elongation is 8.0%. After normalizing, the tensile strength and elongation of nodular cast iron change. When the normalizing temperature is 870 ℃, i.e. about 30 ~ 50 ℃ above the upper limit of eutectic transformation temperature, the tensile strength is 759 MPa and the elongation is 5.4%, in which the tensile strength increases by 10% and the elongation decreases by 20%. However, when the normalizing temperature is 930 ℃, the tensile strength basically remains unchanged, while the elongation is significantly increased to 9.5%. Zhao Xiaolong and others also found that with the disappearance of free cementite in steel structure, its tensile strength has a downward trend, and its elongation has a certain increase. This may be due to the decomposition of a small amount of cementite, while the matrix and graphite ball have hardly changed.
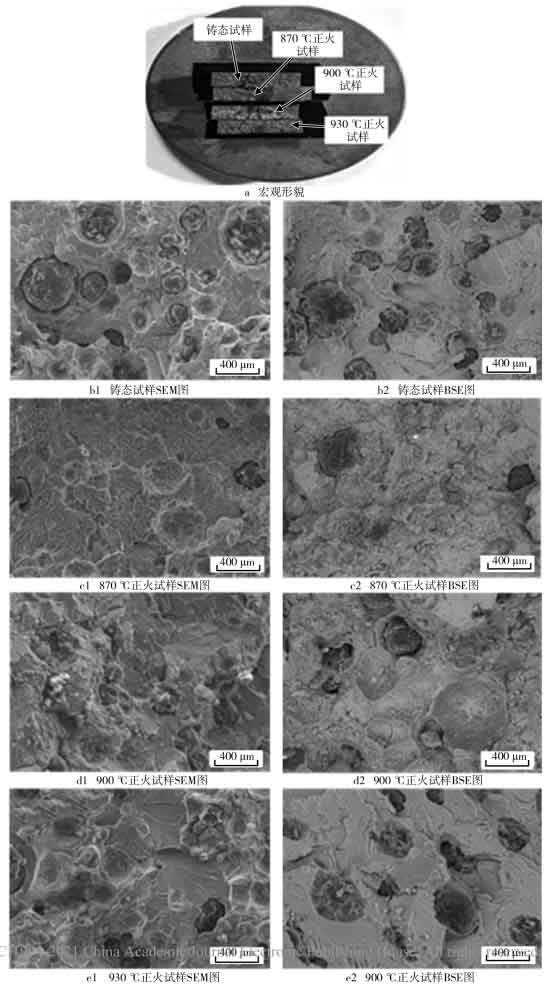
SEM and BSE diagrams of tensile fracture morphology of as cast and normalized nodular cast iron are shown in the figure. There are many reasons for the fracture of materials, which are not only related to the nature of the material itself, but also related to the shape, size and external conditions of its manufacture. In terms of macro fracture, fracture is generally divided into ductile fracture and brittle fracture. It can be seen from the figure that under the condition of as cast and 930 ℃ normalizing, it is found that the fracture surface of nodular cast iron sample presents uneven fibrous shape, and the fracture edge presents gray shear lip shape, which belongs to ductile fracture. The fracture surface of nodular cast iron samples normalized at 870 ℃ and 900 ℃ shows herringbone pattern stripes. The fracture surface is flat and gray, which belongs to brittle fracture. From the microscopic samples of nodular cast iron, there are cleavage small planes and river patterns spreading around at the fracture of 870 ℃ and 900 ℃ nodular cast iron normalized samples, which show the characteristics of quasi cleavage brittle fracture. However, the fracture surfaces of as cast and 930 ℃ nodular cast iron normalized specimens have less dissociation planes and shear tear ridges, and there are more dimples, which show ductile fracture.