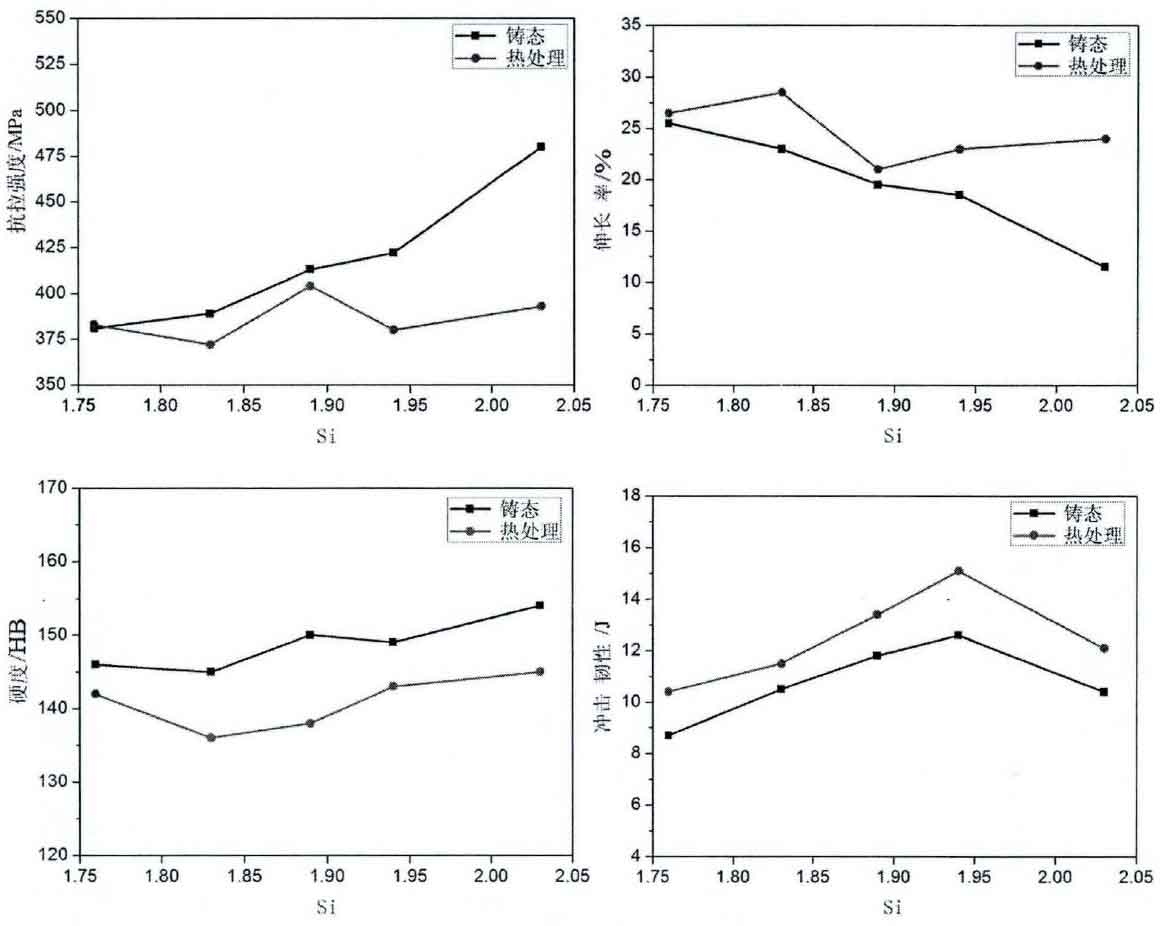
The effects of silicon, copper and Bismuth on mechanical properties were analyzed. The figure shows the effect of silicon on the mechanical properties of nodular cast iron.
It can be seen from the figure that under the as cast condition of nodular cast iron, when the silicon content increases from 1.76% to 1.95%, the tensile strength increases from 381mpa to 422mpa, the elongation decreases from 25.5% to 18.5%, the Brinell hardness is about 145, and the impact toughness at – 40 ℃ increases from 8.7j to 12.6j; When the silicon content continues to rise to 2.03%, the tensile strength increases to 480mpa, the elongation decreases to 11.5%, the Brinell hardness increases to 154, and the impact toughness at – 40 ℃ decreases to 10.4j. After heat treatment, the tensile strength no longer increases with the increase of silicon content, and basically remains at 375-400mpa. The elongation decreased slightly with the increase of silicon content, but remained above 20%. Brinell hardness is about 140- The impact toughness at 40 ℃ is improved compared with that as cast, and the change law is similar to that as cast. When the silicon content increases from 1.76% to 1.95%, it first increases to 15.1j, and when the silicon content continues to increase to 2.03%, it decreases to 12.1j.
The effect of silicon on the mechanical properties of nodular cast iron can be obtained; When WSI > 1.95%, with the increase of silicon content, the tensile strength increases slightly, the elongation and impact toughness decrease significantly, and the hardness increases slightly. The critical content of silicon is 1.95%. When it is lower than this value, the solid solution strengthening effect of silicon is weak, which is beneficial to the improvement of low-temperature impact toughness. When it is higher than this value, the solid solution strengthening effect of silicon is gradually strengthened, and the tensile strength is significantly improved.