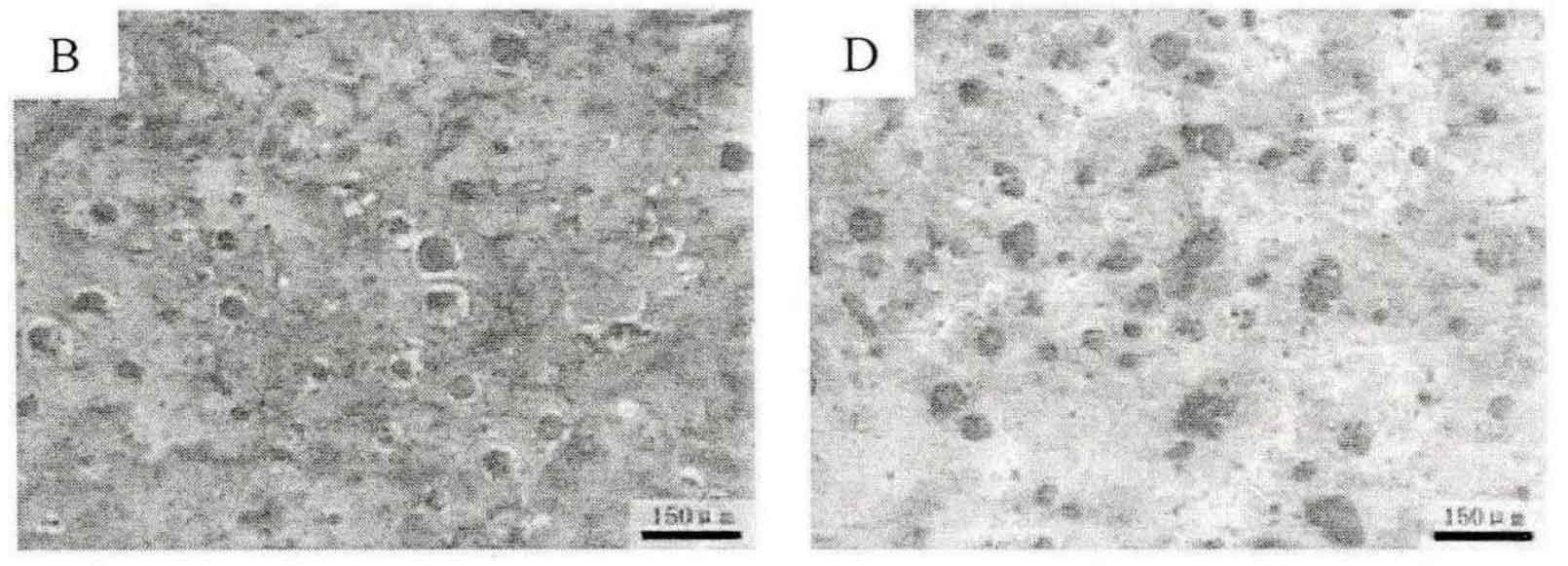
In order to explore the effect of ultrasonic treatment time on the microstructure and properties of ductile iron, a group of comparative experiments were carried out. The experimental operation is basically the same as that of the previous experiment, except that the ultrasonic action time in the spheroidizing bag of nodular cast iron is extended to 2min, and the current and output power are 1.5A and 81% respectively. After pouring molten iron, it is loaded in one of the cavities for 25s, and the current and output power are 1.2A and 81% respectively. The test piece with two ultrasonic waves applied is recorded as C, and the test piece with only one ultrasonic wave applied in the spheroidizing package of nodular cast iron is recorded as D. The metallographic test and mechanical property test of test piece D are compared with that of test piece B to explore the influence of ultrasonic application time on it. The metallographic phase of specimen B and D is shown in the figure.
Calculate the number of graphite balls in multiple fields of view of test pieces B and D respectively and take the average value. In the field of view of 1.08mm2, the average number of graphite balls in test piece B is 41, D is 63, and the number of graphite balls in D is more than 1.5 times that of B. At the same time, the morphology of graphite balls in B and D is basically the same. The graphite balls are large and small, but the number of smaller graphite balls in D is more. The software is used to analyze the ferrite content of B and D. the ferrite content of B specimen is 10.60%, and that of D is 2.254%. The ferrite content in B is much less than that in a. According to the metallographic test standard of nodular cast iron, the graphite balls of B and D are classified as grade 3; Ferrite is classified according to the ferrite map. B ferrite is 10a and D ferrite is 5B. The specific ferrite content and mechanical properties are shown in the table.
Comparing the mechanical properties of test pieces B and D, the tensile strength, impact bremsstrahlung and hardness of test piece D are better than those of test piece B, and the tensile strength and initial impact of test piece D are about 5% higher than those of test piece B. It can be seen that the increase of ultrasonic application time can improve the strength and toughness of nodular cast iron.
| Test piece No | Number of graphite balls | Ferrite content /% | Tensile strength / MPa | Elongation after fracture /% | Impact toughness / J | Hardness / HB | Process parameters |
| B | 41 | 10.60 | 822 | 6.6 | 35.7 | 249 | Spheroidizing bag for 1min |
| D | 63 | 2.254 | 864 | 4 | 37.4 | 270 | Spheroidizing bag for 2min |
This is mainly because with the increase of ultrasonic application time, the cavitation effect and sound flow effect of ultrasonic continue to produce impact vibration in the solution. In the process of spheroidization, the dendrite is interrupted and the nucleation rate is increased; Moreover, the thermal effect of ultrasound makes the temperature of molten iron near the action of ultrasound higher and the rate of temperature reduction reduced. The high-temperature liquid molten iron is conducive to the growth of graphite balls. Because of the effect of ultrasound, the number of graphite balls increases and the ferrite content decreases, so the comprehensive mechanical properties of nodular cast iron have been improved.