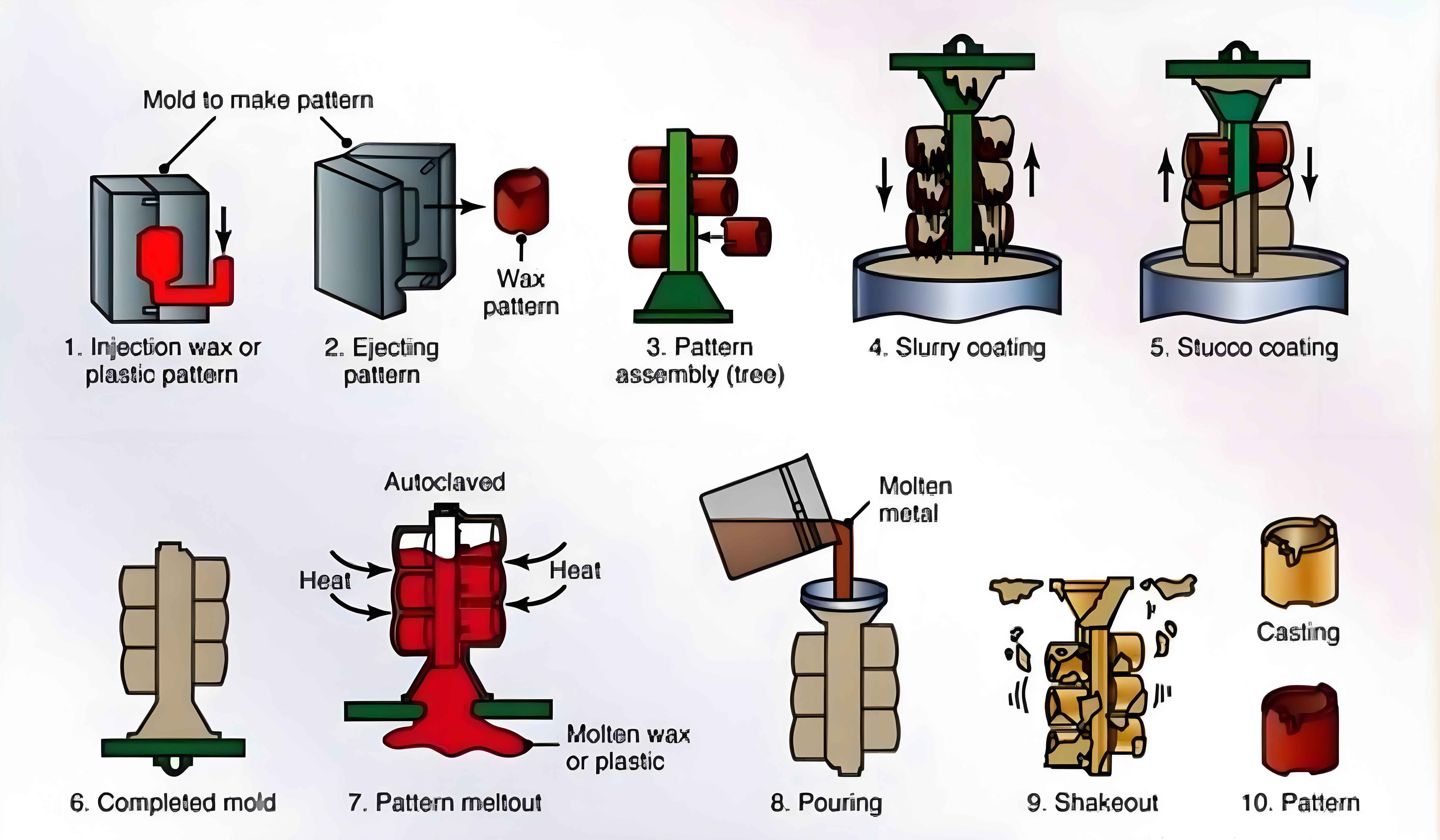
Introduction
Investment casting, also known as lost-wax casting, is a manufacturing process that excels in producing components with complex geometries and intricate details. This method is highly valued in various industrial applications where precision, material properties, and design flexibility are crucial. This analysis explores the benefits of investment casting for creating complex geometries in industrial applications.
Key Benefits of Investment Casting for Complex Geometries
- Design Flexibility:
- Investment casting allows for the creation of intricate and complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with other manufacturing methods. This flexibility enables designers to optimize components for performance and functionality without being constrained by manufacturing limitations.
- Precision and Accuracy:
- The process produces components with high dimensional accuracy and tight tolerances, which are essential for parts that must fit together precisely in complex assemblies.
- Smooth Surface Finish:
- Investment casting provides a superior surface finish, reducing the need for extensive post-processing. This is particularly beneficial for components with complex geometries where finishing operations might be challenging.
- Material Versatility:
- A wide range of metals and alloys can be used in investment casting, including high-performance materials like stainless steel, aluminum, and superalloys. This versatility allows for the selection of materials that best meet the mechanical and thermal requirements of the application.
- Reduced Material Waste:
- Investment casting produces near-net-shape parts, minimizing material waste and reducing the need for additional machining. This efficiency is particularly advantageous for expensive or difficult-to-machine materials.
- Complex Internal Structures:
- The process can create complex internal features such as channels, cavities, and undercuts, which are often required in applications like fluid and gas handling systems, aerospace components, and intricate machinery parts.
Industrial Applications and Examples
- Aerospace Industry:
- Turbine Blades and Vanes: Investment casting is used to produce turbine blades and vanes with complex airfoil shapes and internal cooling passages, which are critical for the efficiency and performance of jet engines.
- Structural Components: Lightweight and high-strength components with intricate geometries, such as brackets and housings, are manufactured for aerospace applications.
- Automotive Industry:
- Engine Components: Complex parts like turbocharger housings, engine blocks, and transmission components are cast to achieve the desired performance and durability.
- Suspension Parts: Investment casting is used for suspension parts that require high strength and precision.
- Medical Devices:
- Orthopedic Implants: Custom implants with intricate shapes tailored to individual patients’ anatomy are produced for better fit and functionality.
- Surgical Instruments: Complex and precise instruments that require high levels of detail and smooth finishes are manufactured using investment casting.
- Energy Sector:
- Pump and Valve Components: Investment casting produces complex parts for pumps and valves used in oil and gas, chemical processing, and power generation, where precision and reliability are critical.
- Turbine Components: High-performance components for steam and gas turbines, including blades and nozzles, are made using this process.
- Industrial Machinery:
- Robotics and Automation: Components with intricate geometries required for robotic arms and automation equipment are cast to ensure precision and performance.
- Tooling and Molds: Investment casting is used to create complex tooling and molds for various manufacturing processes.
Advantages Over Other Manufacturing Methods
- Compared to Machining:
- Complexity: Investment casting can produce more complex geometries that would be difficult or costly to machine.
- Material Efficiency: Produces less waste and often requires less material removal compared to machining.
- Compared to Sand Casting:
- Precision: Offers superior dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
- Detail: Capable of producing finer details and thinner sections.
- Compared to Die Casting:
- Material Range: Suitable for a broader range of materials, including high-temperature alloys.
- Tooling Cost: Typically lower tooling costs for small to medium production runs.
Conclusion
Investment casting is a versatile and precise manufacturing process that excels in producing components with complex geometries. Its ability to create intricate shapes, use a wide range of materials, and achieve high dimensional accuracy makes it ideal for various industrial applications. Whether in aerospace, automotive, medical, energy, or industrial machinery, investment casting provides the design flexibility and performance required to meet the demanding specifications of complex parts. As industries continue to push the boundaries of design and functionality, investment casting will remain a critical technology for achieving advanced and efficient solutions.
