1. Improvement of cavity arrangement process
As shown in the figure, the improved ductile iron casting process changes the original strip arrangement into a star arrangement. The star arrangement is relatively concentrated, and heat sources are added to each other at the outer wall. The heat dissipation rate of the sand mold is slowed down, the cooling rate of the outer wall is slowed down, and the solidification time is extended. The solidification time difference between the inner hole and the outer wall is reduced, which conforms to the solidification characteristics of ductile iron and can better realize the proportional solidification.
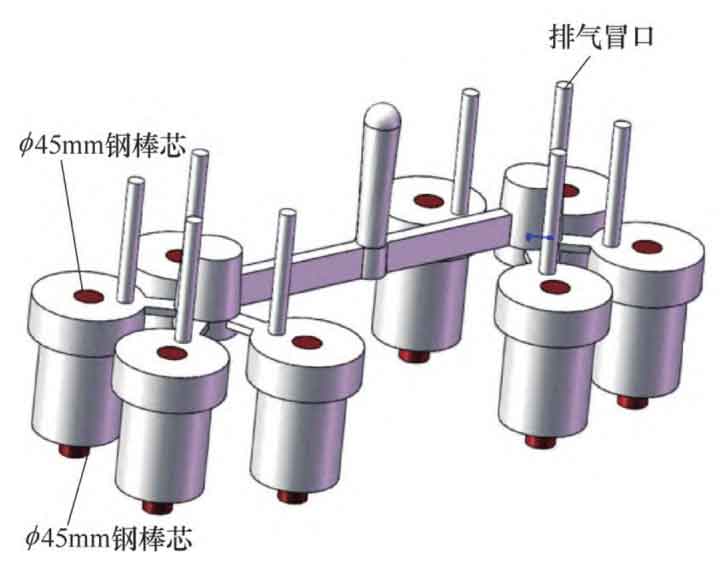
2. Improvement of inner hole core material
The original resin sand core is replaced with a steel core with a higher heat storage coefficient (see figure). The steel core can not only form an inner hole, but also has the chilling effect of cold iron. It can also increase the heat conduction rate in the hole, improve the cooling rate of the inner hole, accelerate the solidification in the hole, shorten the time difference between the solidification and the outer wall, and basically solidify at the same time or slightly in advance with the outer wall, so that the solidification process of ductile iron castings is closer to the balanced solidification, It also conforms to the paste solidification characteristics of nodular cast iron.
3. Improvement of gating system and riser
(1) The gating system is improved with a box of 8 pieces, 4 pieces in a group, which are arranged in a star shape. Each piece has an ingate, and one group shares a dark riser. The over dark riser of the ingate is in a star shape (see figure). The heat distribution of each piece is relatively uniform, and the size of the ingate is (wide × Height) 35mm × 12mm, its section is flat (width height ratio is 3 ∶ 1), and the section is larger than the original process, which is convenient for rapid filling and timely closure of the ingate at the initial stage of molten iron solidification, to prevent the reflux of molten iron, maximize the application of graphitization expansion characteristics, and more consistent with the characteristics of balanced solidification of ductile iron.
(2) The riser improvement summary summarizes the chemical composition analysis of smelting QT600 within a period of time, and the results are shown in Table 1.
According to the table, the carbon equivalent of QT600 is 4.7% ~ 4.8%. At the same time, special pig iron for nodular cast iron is used, and other raw materials are strictly controlled. The metallurgical quality of molten iron is good. In addition, the air outlet is moved to the vicinity of the hot spot formed by the ingate (see figure) to adjust the solidification temperature field of molten iron and balance the overall heat distribution of the ductile iron casting to achieve balanced solidification.
| Element | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Al | Mg | RE |
| Detection value 1 | 3.639 | 3.115 | 0.485 | 0.0542 | 0.0173 | 0.0224 | 0.0429 | 0.0169 |
| Detection value 2 | 3.77 | 3.074 | 0.485 | 0.0549 | 0.0181 | 0.0215 | 0.0398 | 0.0163 |
| Detection value 3 | 3.759 | 3.101 | 0.482 | 0.0589 | 0.0174 | 0.0206 | 0.0443 | 0.0153 |
The original conjoined feeding riser is omitted, and the pouring system is used to feed the liquid shrinkage of molten iron. The ingate is closed in time at the initial solidification stage to maximize the use of graphitization expansion. According to the above conditions, the nodular cast iron can be cast with small feeding riser or without riser. The mechanical properties of nodular iron castings cast without riser decrease slowly from the edge to the center, while those cast with riser decrease sharply from the edge to the center. It is concluded that the internal quality of castings without riser is better than that of castings with riser. Therefore, the adoption of no riser casting not only eliminates the top integrated feeding riser, but also overcomes the defects of shrinkage porosity and shrinkage cavity in the process of solidification shrinkage, and greatly improves the yield of nodular iron castings.
