Traditional nondestructive testing methods include ultrasonic testing, acoustic emission testing, magnetic particle testing and radiographic testing. Magnetic particle flaw detection and ultrasonic flaw detection are often used in nondestructive flaw detection of steel castings. Ultrasonic flaw detection is applicable to the nondestructive testing of forgings, castings, weldments, cemented parts, etc. this testing method is economical and effective, but the test results have no direct witness records; Magnetic particle flaw detection is applicable to the detection of surface or near surface defects of ferromagnetic materials.
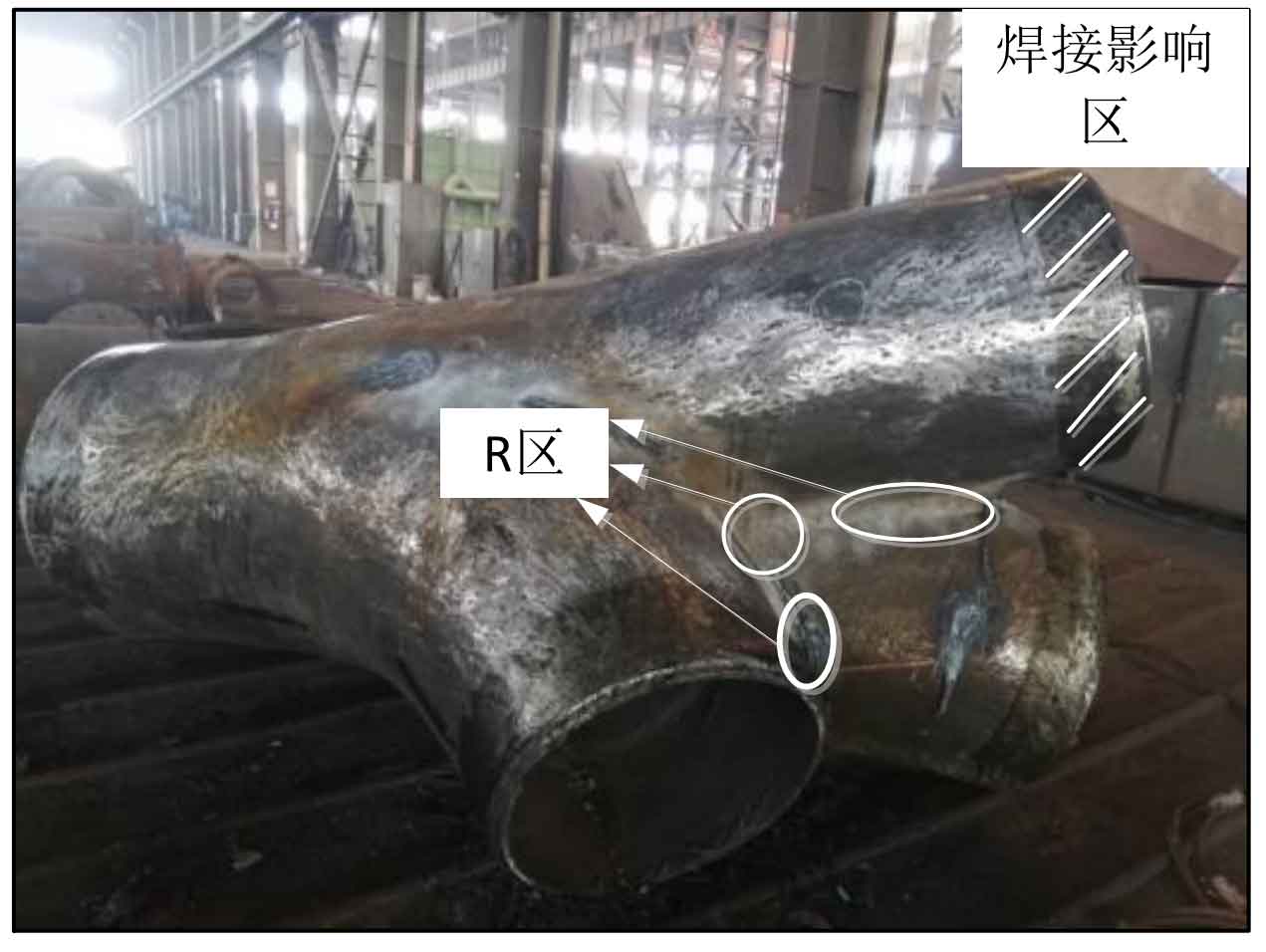
The supplier and the demander will put forward corresponding inspection requirements according to the structural shape and production process characteristics of the cast steel joint, and then the cast steel factory shall carry out ultrasonic flaw detection on the cast steel joint according to the inspection requirements before the casting leaves the factory. When carrying out ultrasonic flaw detection on cast steel joints, the flaw detection position needs to be polished smooth to ensure the accuracy of flaw detection results. However, because the ultrasonic nondestructive testing method requires good coupling between the probe and the tested body, there will be ultrasonic scanning blind areas for complex cast steel joints, such as the transition area and chamfer area between each branch pipe and main pipe. For the blind area of ultrasonic flaw detection, the steel casting plant will use the magnetic particle nondestructive testing method to detect the surface or near surface defects before ultrasonic nondestructive testing. The transition area and chamfer area between the branch pipe and the main pipe of a cast steel joint are also called R area. Figure 1 shows the location diagram of R area of a cast steel joint.
1. Ultrasonic nondestructive testing
Ultrasonic testing (UT) is a nondestructive testing method that uses the reflection or attenuation of casting defects to ultrasonic to determine defects.
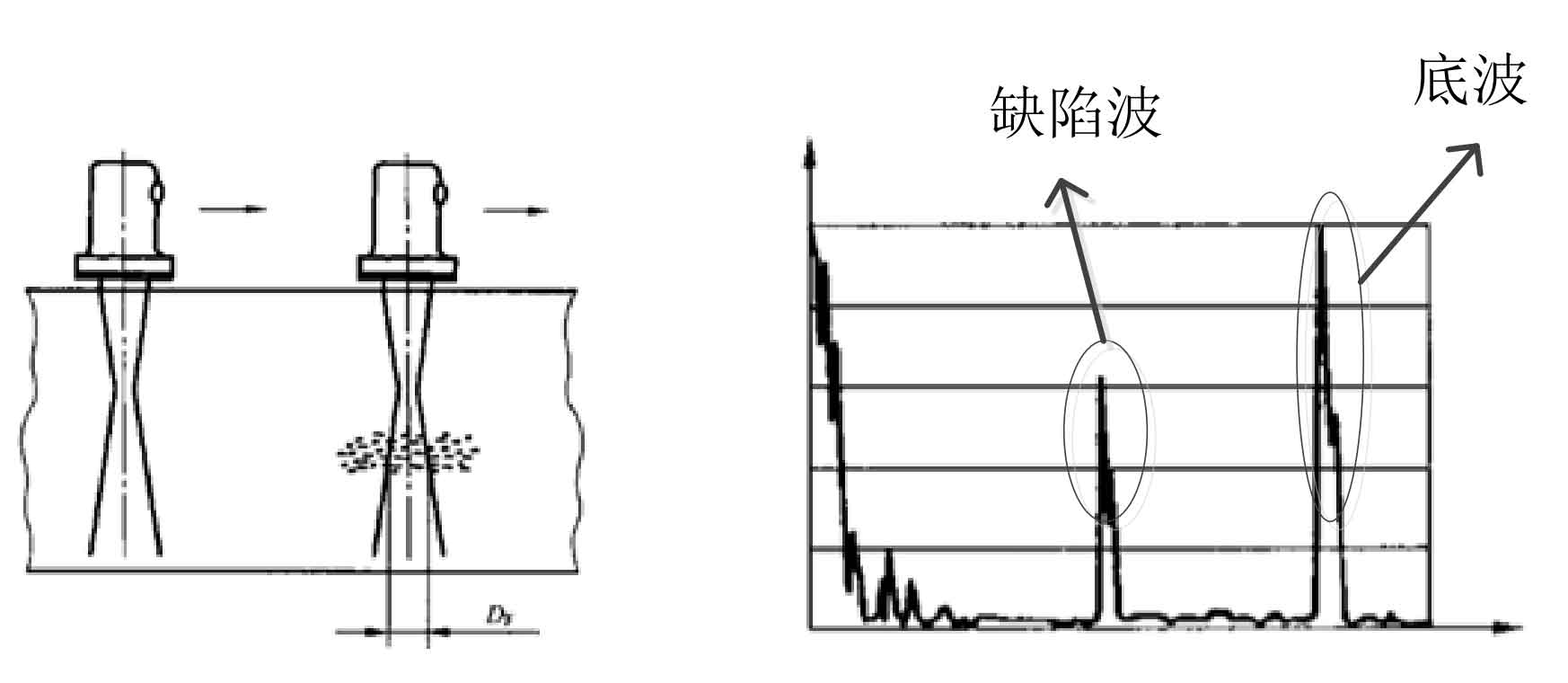
Ultrasonic wave is a kind of strong energy, which will have a certain loss when it propagates in the material. When it encounters defects in the propagation process (can be pores, slag inclusions, cracks, etc.), the acoustic impedance will change. Different acoustic impedances have different sound pressure transmittance and reflectivity. According to the change of transmittance or reflectivity, there will be corresponding reflected waves, and at the same time, with the loss of energy, the echo amplitude of bottom wave will be reduced, which is the basic principle of ultrasonic nondestructive testing. During the inspection, the ultrasonic wave will be reflected at the defect, and the defect wave will appear on the fluorescent screen of the ultrasonic detector. The waveform and amplitude of defect wave change due to the different geometry of defect. The nature of defect can be estimated according to the wave pattern characteristics of defect wave. Compared with X-ray flaw detection, eddy current flaw detection, magnetic particle, penetration and other methods, ultrasonic flaw detection method has the advantages of harmless to human body and environment, high sensitivity and many kinds of applicable materials.
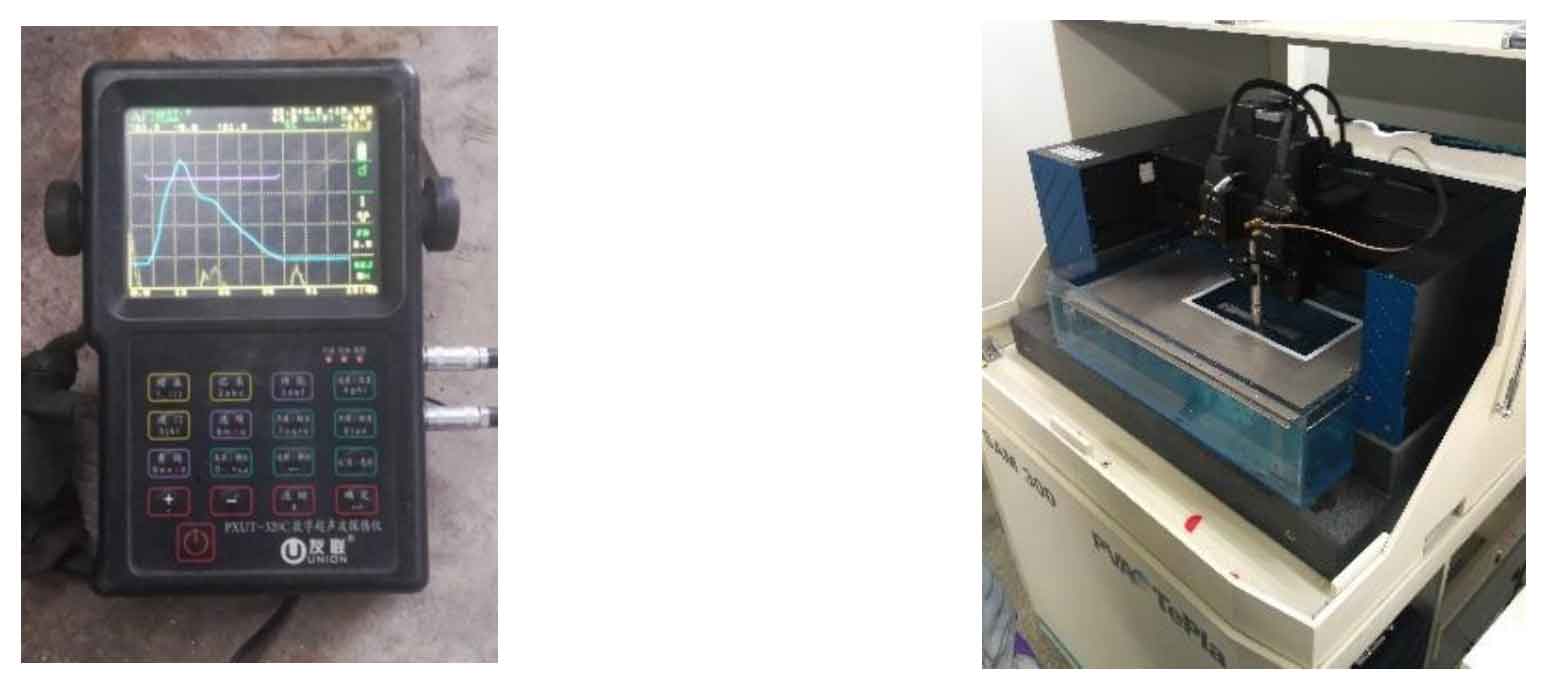
Ultrasonic testing equipment is divided into portable hand detection equipment (Fig. 3a) and water immersion automatic scanning equipment (Fig. 3b). Portable hand detection equipment is characterized by low cost, convenience and flexibility. It can detect special-shaped workpieces, but it has a large workload, is easily affected by the strength and methods of different operators, and has poor accuracy and stability. The water immersion automatic scanning equipment just solves the shortcomings of portable equipment, with high efficiency and stability, but the cost is high, so it can not be applied to the flaw detection of large castings.
According to the scanning display, ultrasonic flaw detection can be divided into: A-scan, B-scan, C-scan, etc. A-scan is the most basic signal source. It is the wave displayed on the screen according to the sound pressure signal received by the ultrasonic transducer (i.e. probe). It has a certain width. Using the basic signal source of A-scan, using automation technology and powerful computer imaging technology, it has developed two scanning modes of B-scan and C-scan, They are the projection of the defect in the depth direction and the projection of the defect in the scanning direction. In addition, ultrasonic testing is a comparative testing method, which mainly determines the equivalent size of natural defects in materials based on artificial defects (such as flat bottom hole, V-groove, etc.). The reflection characteristics of A-scan defect wave are shown in Table 2.
| Defects | Waveform characteristics |
| crack | The reflected wave is sharp, and the bottom wave attenuates seriously or even disappears |
| Stomata | The injury wave is high and the boundary between waves is clear |
| Shrinkage porosity | The amplitude of injury wave is low, and the bottom wave is very low or even disappears |
| Inclusion | The injured wave is round, blunt and short, and there is a secondary wave near the main wave, accounting for a large width, which has a certain impact on the reflection of the bottom wave |
2. Magnetic particle nondestructive testing
Magnetic particle testing (MT) takes advantage of the difference between the permeability of surface and near surface defects (such as cracks, slag inclusions, hair lines, etc.) of iron and steel products and the permeability of iron and steel. After magnetization, the magnetic field at the discontinuity of these materials will be distorted, resulting in the leakage of magnetic field lines, resulting in the leakage of magnetic field on the surface of the workpiece, so as to attract magnetic particles to form the accumulation of magnetic particles at the defect, and show the location and shape of the defect under appropriate light conditions, Magnetic particle inspection is realized by observing and explaining the accumulation of these magnetic particles. Magnetic particle inspection can only detect the near surface defects of cast steel joints.