The connecting rod is composed of a big end, a rod body and a small end.
1.Connecting rod small end
The small end of the connecting rod generally adopts the thin-walled circular ring structure to make it more evenly stressed and light. A large arc radius is used between the small end and the rod body to reduce the stress concentration at the transition.
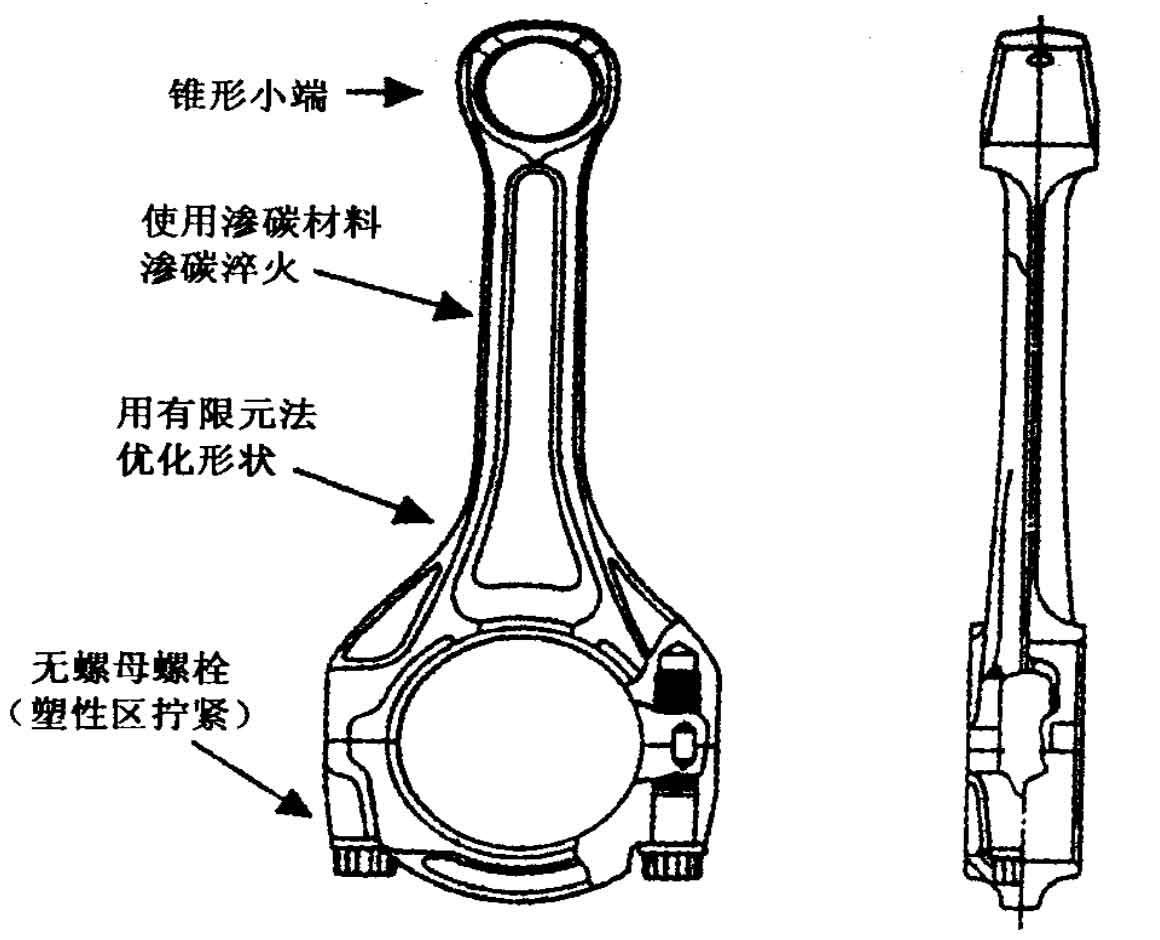
In the recent connecting rod design to reduce the weight of each part, for the gasoline engine, except for the high-power engine, almost all the small ends are designed without bushings. The width of the small end of the connecting rod is tapered, and the lower part of the small end bearing the combustion pressure load is large, which can adapt to the high output power of the engine. At the same time, it also reduces the weight compared with the previous equal width structure, as shown in Figure 1 light connecting rod design.
2.Connecting rod body
The longitudinal axis of the connecting rod body relative to the big end of the connecting rod is symmetrical. The connecting rod body with I-shaped section is suitable for die forging, with large rigidity and light weight. The depth width ratio of I-shaped section of automobile engine connecting rod is 1.4-1.8.
3.Connecting rod big end
The big end of the connecting rod is connected with the connecting rod journal of the crankshaft. The big end has two types: integral type and separate type. Generally, the separate type is adopted, that is, it is divided into big head body and big head cover, which are connected by special connecting rod bolts. Some small two-stroke gasoline engine crankshafts are combined. In order to simplify the structure, the connecting rod big end adopts integral type, and the big end bearing adopts roller bearing. Split type is divided into two types: bisection and oblique bisection.
Bisection – the split plane is perpendicular to the axis of the connecting rod body, as shown in Figure 2. The advantages of the flat notch are that the big end is easy to process, the rigidity is good, and the connecting rod bolts are not subject to shear, which is the preferred scheme for the big end split type. It is widely used in gasoline engine and small diesel engine. Because the transverse dimension of the connecting rod big end of general gasoline engines is smaller than the cylinder diameter, it can be easily disassembled through the cylinder, so the flat cut connecting rod is often used.
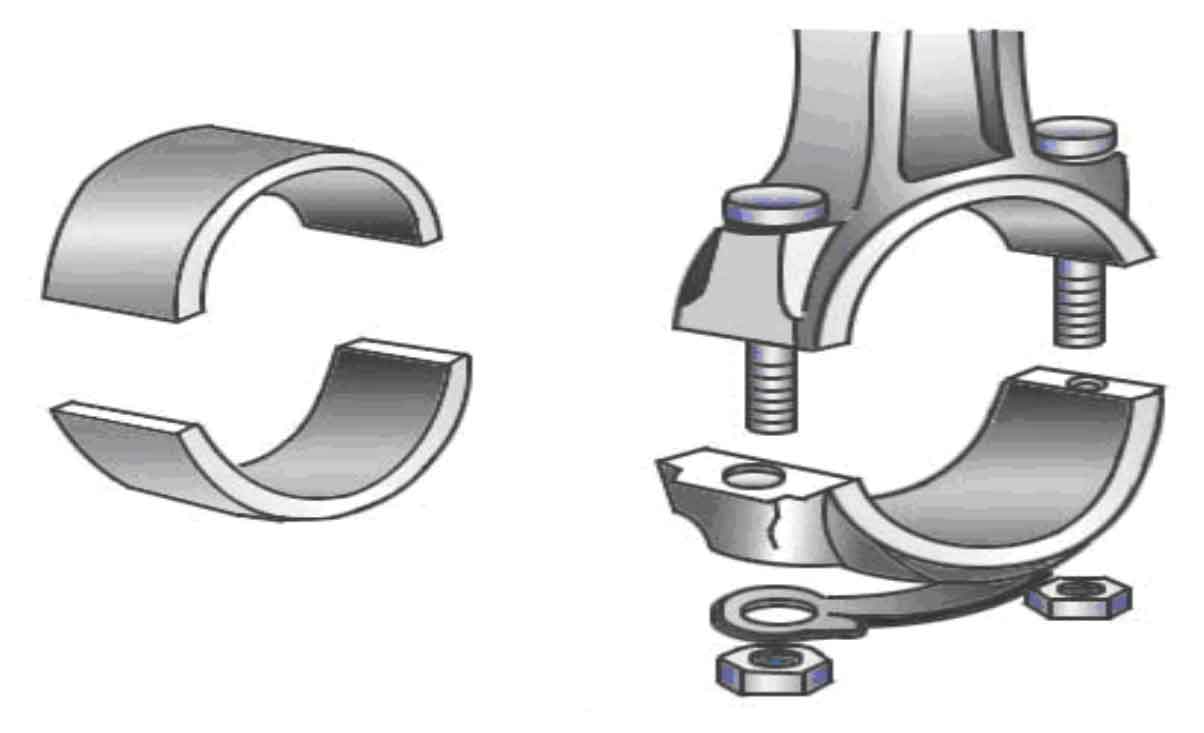
Oblique split – the split is at an included angle of 30 ~ 60 ° with the axis of the connecting rod body. Most diesel engines use this kind of connecting rod. Because the compression ratio of the diesel engine is large, the stress is large, the connecting rod journal of the crankshaft is relatively thick, and the size of the corresponding connecting rod big end often exceeds the cylinder diameter. In order to make the connecting rod big end pass through the cylinder and facilitate disassembly and assembly, inclined cuts are generally used, and the most common is the 45 ° included angle.
In order to improve the bending stiffness of the connecting rod big end cap and reduce its mass as much as possible, the big end cap is often reinforced in the middle.
Following the above principles, in the design of connecting rod, the length of connecting rod shall be determined first, which is a parameter closely related to the whole machine, and it determines the basic configuration of connecting rod. Then determine the size of the small end hole of the connecting rod, which is related to the design of the piston pin hole and the piston pin. The size of the connecting rod big end hole is determined together with the diameter of the connecting rod diameter of the crankshaft, which is also one of the important dimensions that determine the basic configuration of the connecting rod.
The connecting rod is mainly made of forged steel by plastic forming. In order to ensure the quality and strength, it is generally subject to heat treatment. In recent years, it is directly used in quenched state without quenching and tempering treatment. The connecting rod is made of non quenched and tempered steel with vanadium (V). After forging, it shall be cooled carefully to make vanadium precipitate as hard carbide to strengthen the forging stock material. In addition, carburizing and quenching treatment has recently been used to make the surface more
Strengthen, reduce the thickness of each part of the connecting rod, and ensure high strength while reducing the weight, or apply shot peening to greatly improve the fatigue strength and improve the strength dispersion.
The global automobile is developing towards lightweight, high output, low cost, safety, energy saving, environmental protection and comfort. The engine is the heart of the automobile, and the engine connecting rod is the dynamic load component that bears the strongest impact force and the highest dynamic stress. Its load is proportional to its mass. Therefore, the lightweight of the connecting rod is of greater significance to the engine. If the mass of the connecting rod is reduced, it will inevitably lead to the reduction of the mass of all oscillating objects, which will have a good effect on the operating noise, shimmy (vibration) and rigidity of the main moving parts of the engine (such as piston, piston ring, connecting rod, crankshaft, etc.), fuel consumption and mechanical stress of engine parts. The main way to lighten the connecting rod is to improve the manufacturing process and materials, that is, the use of new processes and materials can effectively reduce the weight of the connecting rod.
