In order to obtain as cast ferrite pearlite nodular cast iron with high strength and good plastic toughness, the production process of castings, including chemical composition selection, melting process and spheroidizing inoculation process, must be strictly controlled.
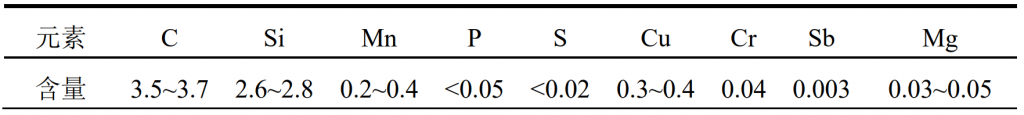
Based on the comprehensive composition design and analysis, combined with the specific structure and performance requirements of as cast nodular cast iron automobile hub support, the chemical composition range is finally determined, as shown in the table.
The original nodular cast iron molten iron without spheroidization and inoculation has an important influence on the microstructure and properties of castings. Qualified molten iron usually needs to meet the following requirements:
(1) The element mass fraction meets the requirements;
(2) Overheat the molten iron properly and keep it at a higher temperature;
(3) Ensure that there is no excessive oxidation of furnace charge in the smelting process.
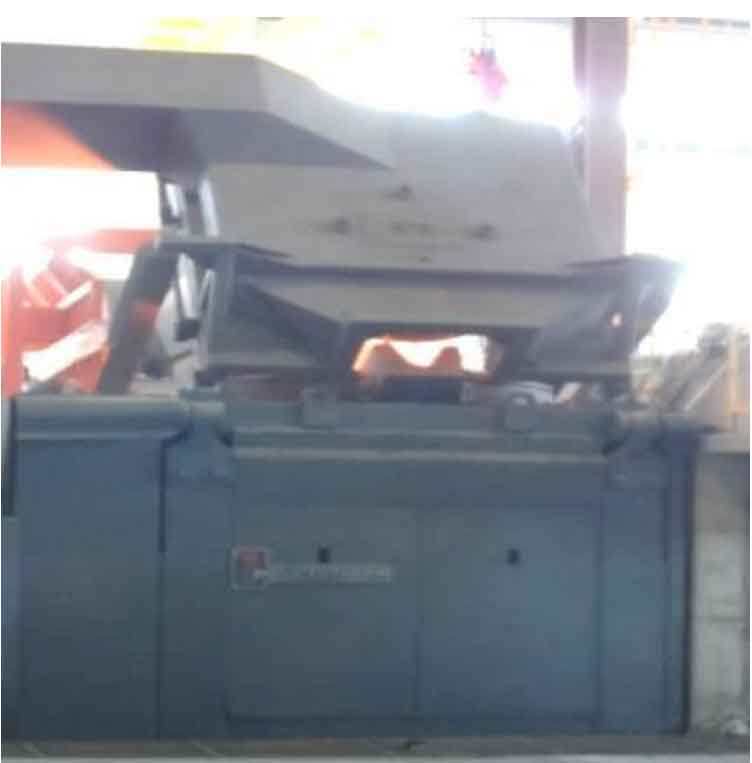
Therefore, in order to ensure the quality of molten iron, it is necessary to carry out reasonable design and control of the smelting process. The excellent molten iron suitable for the production of nodular cast iron should ensure high temperature and low content of phosphorus, sulfur and other impurities. Therefore, the charge ratio (mass fraction) is 10% pig iron, 30% scrap steel and 60% nodular cast iron return charge. The melting equipment is American Yingda induction furnace as shown in the figure, which is added to the charge for smelting according to the determined proportion, and the slag is removed in time after the charge is cleaned, Then increase the temperature of molten iron and analyze the chemical composition of molten iron by photoelectric direct reading spectrometer, and then add carburizing agent and silicon carbide as appropriate to adjust the composition. After melting, the molten iron of nodular cast iron also goes through the spheroidization inoculation process, and the fluidity of nodular cast iron is worse than that of gray cast iron. In order to meet the subsequent pouring temperature, it is necessary to ensure a higher tapping temperature, which should be controlled at least 1505 ℃ ~ 1525 ℃, which can be discharged only after passing the measurement with an electronic temperature measuring gun.