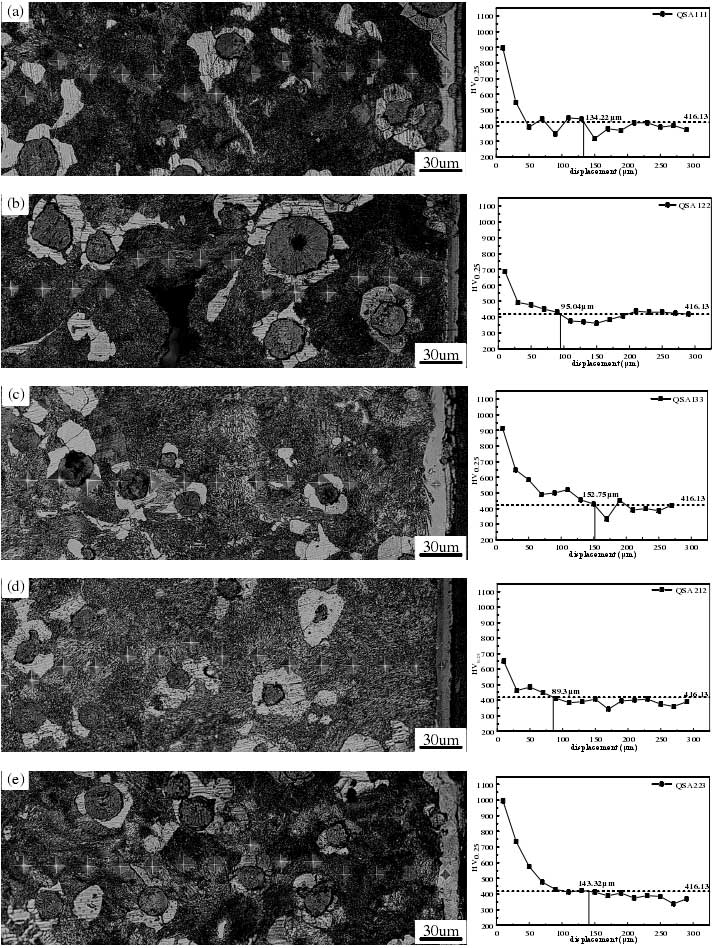
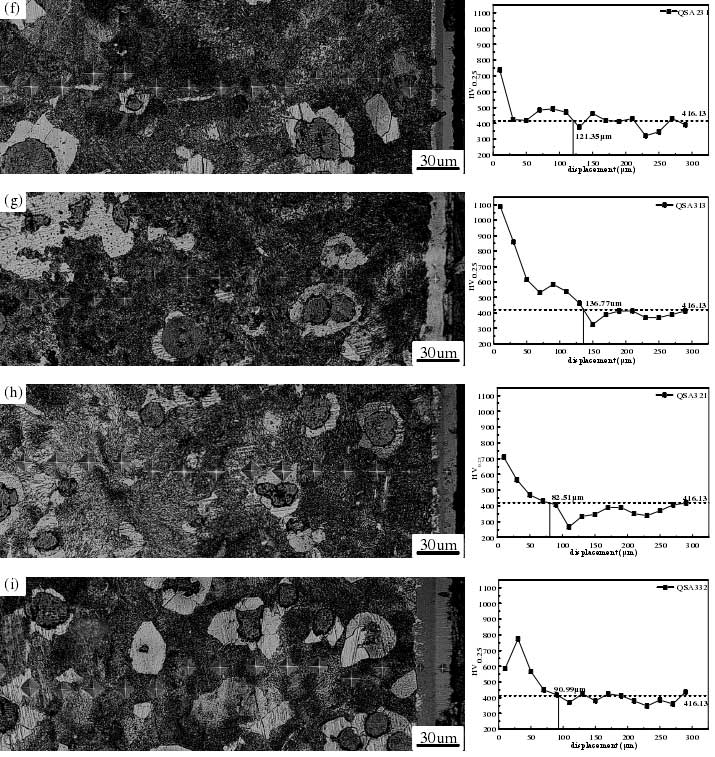
The microhardness of different sections of the nitrocarburized lzqt600-3 ductile iron profile was tested. The effective hardened layer depth of the sample was obtained by hardness distribution gradient and effective hardening depth limit. Take the edge as an example, draw the micro Vickers hardness metallography and hardness gradient diagram of the nitrided sample section at the edge of lzqt600-3 ductile iron profile as shown in Fig. 1. It can be seen from the figure that under different nitrocarburizing processes, the hardness gradient of each sample section decreases from the surface layer to the core. This is mainly because the surface of the sample after nitrocarburizing forms a layer, and the hardness of the layer is higher than that of the substrate, so the hardness value remains at a higher value within a certain distance from the surface, which depends on the thickness of the layer formed. Compared with the hardness of the matrix material, the surface hardness of the nitrocarburized sample is improved to a certain extent, especially the hardness of the compound layer and diffusion layer can reach 700 ~ 1100 hv0.25. In particular, according to Fig. 4-7 (I) hardness gradient diagram, the gradient of Nitrocarburized sample of lzqt600-3 ductile iron profile increases first and then decreases from the surface to the inside, and the hardness value reaches the maximum value at the sub surface 25 μ m away from the sample, which is due to the loose layer formed on the surface of the sample after nitrocarburizing, which reduces the surface hardness of the sample.
The microhardness test was also carried out at 1 / 2R of the nitrocarburized lzqt600-3 ductile iron profile and at the edge of the core section imitated. The hardness distribution is shown in Fig. 2. The effective hardened layer depth of the sample can be obtained through the hardness distribution gradient and the limit value of the effective hardening layer depth. The surface hardness of Nitrocarburized samples has been improved, especially the hardness of compound layer and diffusion layer can reach 700 hv0.25 ~ 1100 hv0.25. It can be seen from Fig. 2 that the hardness gradient of the sample at 1 / 2R and the core is generally in a downward trend from the surface to the inside. The hardness of compound layer and diffusion layer at 1 / 2R are 620 hv0.25 ~ 2000 hv0.25 and 490 hv0.25 ~ 1800 hv0.25, respectively. The hardness gradient of a few samples increases first and then decreases, and the hardness reaches the maximum value in the subsurface layer. This is because the active nitrogen atoms continuously diffuse to the matrix, and the nitrogen content is more in some part of the interior, which promotes the formation of γ′ – fe2-3n and ε – Fe4N phases, and reaches the maximum value.
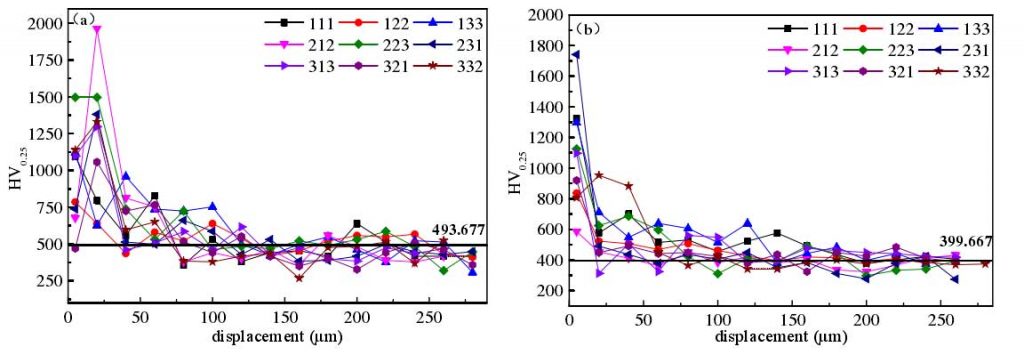
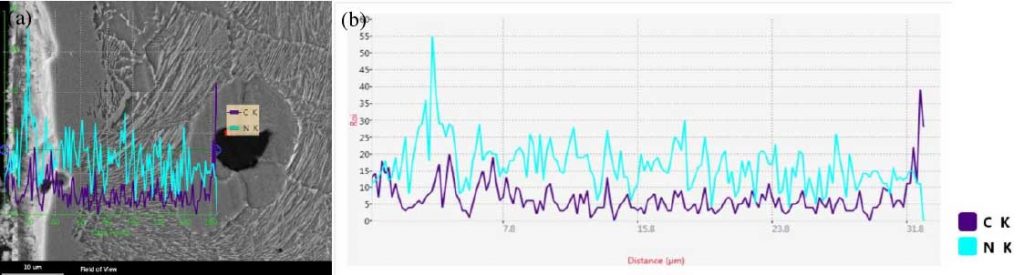
Figure 3 shows the sample at the edge of lzqt600-3 ductile iron profile. The temperature is 540 ℃, the time is 6 h, and the ratio of NH3 and CO2 is 4:1 After nitrocarburizing, the concentration distribution curve of nitrogen and carbon in the sample shows obvious gradient change, and gradually decreases to a certain stable value from the surface strengthening phase layer to the matrix material, and the carbon element reaches stability at about 10 μ m from the surface layer, with only slight fluctuation. According to Fig. 2, the hardness decreases gradually from the surface layer to the matrix, which is due to the formation of strengthening phase due to the infiltration of nitrogen and carbon, which improves the surface hardness of the sample.