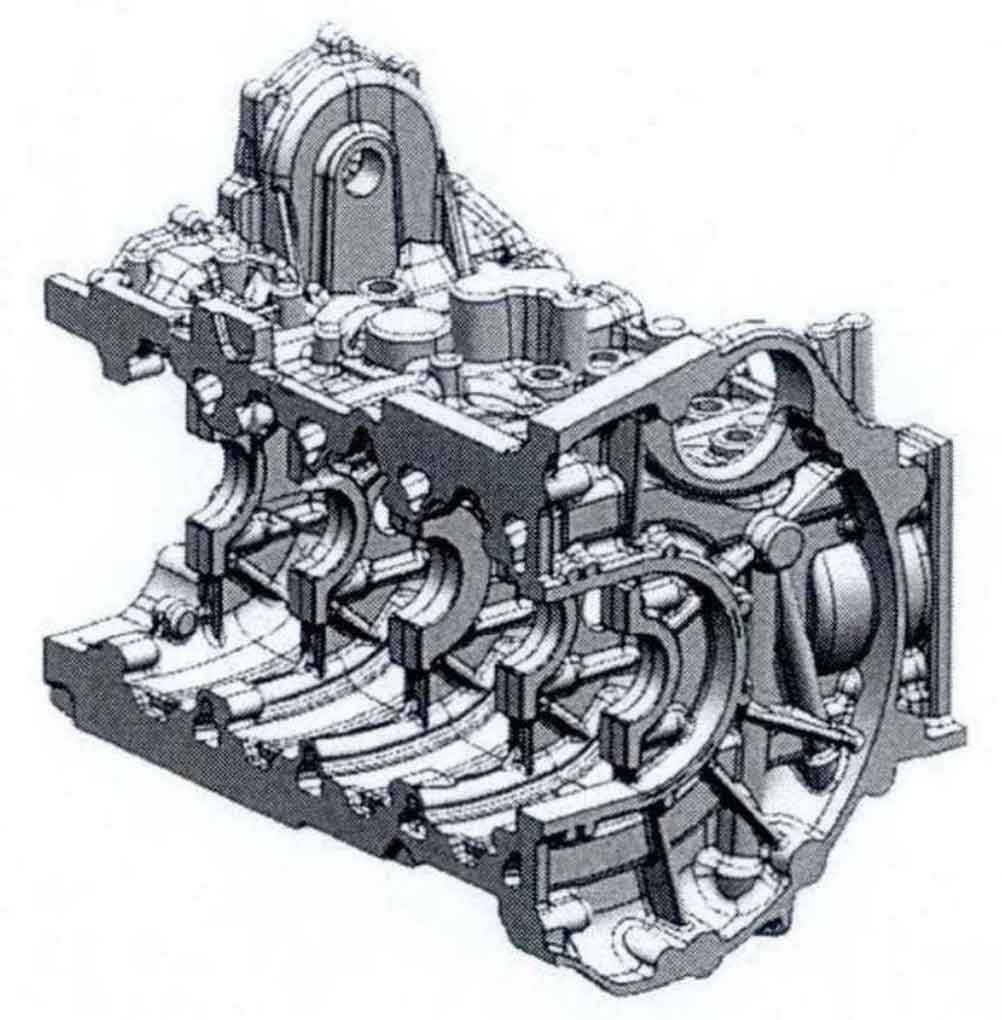
Figure 1 shows the model and production flow chart of a high-strength gray cast iron engine cylinder block. The main processes include raw material ratio, baking process, molding, core making process, pouring process and post-treatment process:
(1) Ingredients; The ingredients are divided into raw materials and auxiliary materials. According to the weight percentage, the raw materials for casting production mainly include scrap steel, pig iron and furnace return materials. The insufficient carbon is supplemented by the addition of carburizing agent. The auxiliary materials include ferrosilicon, ferromanganese, ferrochromium, pure tin, etc; Composition requirements of main raw materials and auxiliary materials in gray cast iron.
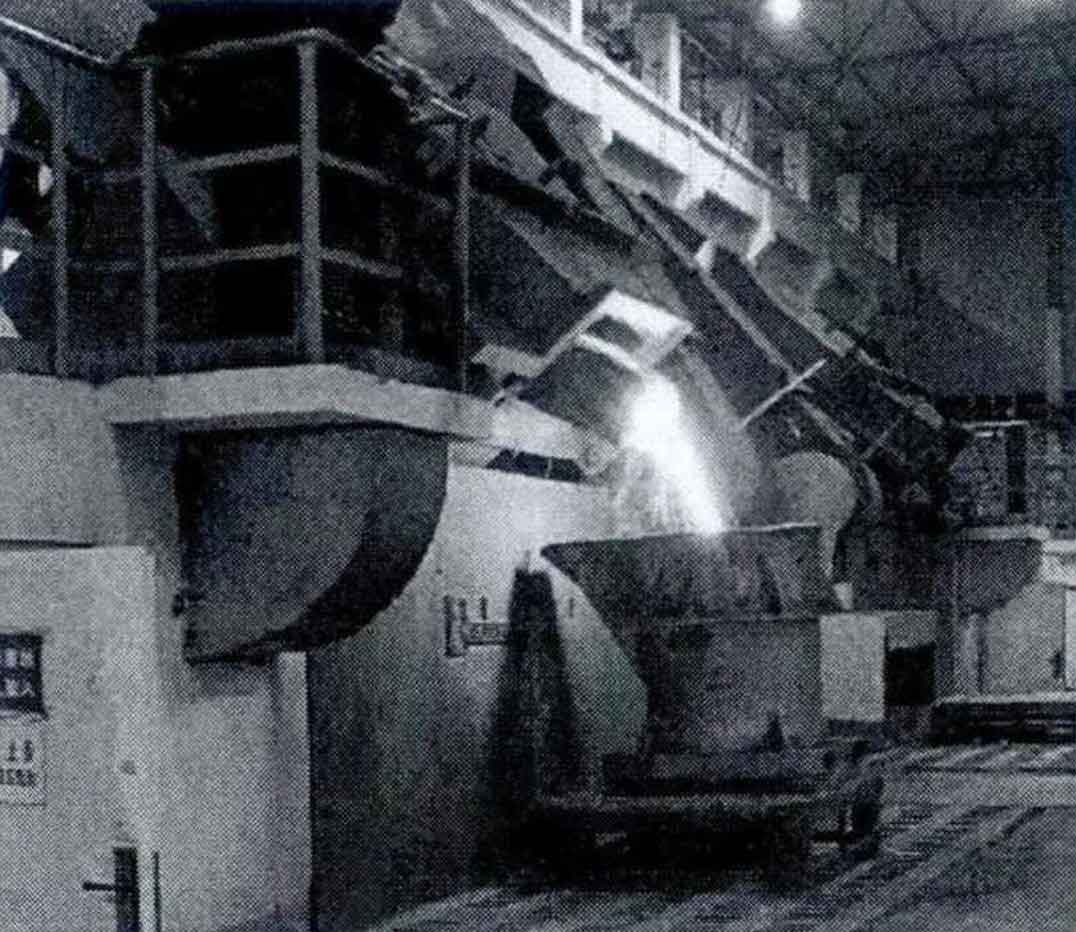
(2) Branding; The melting of gray cast iron liquid adopts 6000kW, 8t / h medium frequency induction furnace (Fig. 2), the outlet temperature of molten iron is controlled at 1510 ± 30 ° C, the content of molten iron C is detected by thermal analyzer, and the content of other alloy elements is detected by direct reading spectrometer. The composition control of molten iron is shown in Table 1, and its carbon equivalent CE is 3.90-4.03, near the eutectic point of Fe GR phase diagram, in order to ensure that the molten iron has good mold filling ability and graphitization ability. Make triangular test block to detect the white width of gray cast iron. When the white width is ≤ 4mm, it indicates that the molten iron quality is qualified.
(3) Modeling and core making: the upper and lower box sand mold adopts static pressure molding line modeling, the main core and water jacket core adopt cold core box method, and the oil duct is pulled by hot core box method; After dip coating and drying, the prepared sand core is combined by core assembling machine; During the drying process, the temperature needs to be strictly controlled to prevent excessive moisture in the sand mold and the increase of gas generation, so as to produce pore defects in gray cast iron. After drying, the sand mold also needs to polish the burr to avoid more sand holes, slag holes and other defects in the later stage.
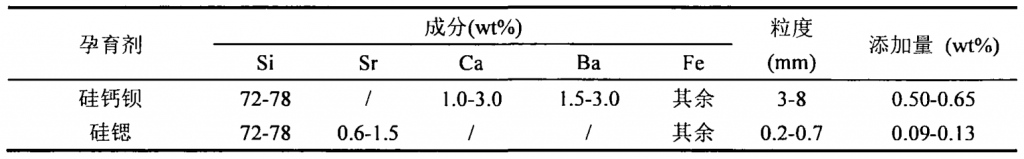
(4) Pouring and inoculation; The molten iron with qualified melting is transferred to the insulation pouring furnace through the pouring ladle, Transfer the primary inoculant (silicon calcium barium inoculant shall be placed at the bottom of the ladle for one inoculation. Before pouring, the thermal analyzer shall be used to measure and analyze the C content and solidification curve in the molten iron, and the direct reading spectrometer shall be used to measure the composition of other elements to ensure that the composition of molten iron before box injection meets the requirements. At the same time, the white width of gray cast iron shall still be detected, and the pouring temperature shall be controlled at 1435 ± 1 5°C 。 Secondary flow inoculation (silicon strontium inoculant) shall be carried out during injection in the holding furnace box. The amount of inoculant added in the two times is calculated according to the proportion of hot metal water output, and its specifications are shown in Table 2. The secondary inoculation treatment is used to delay the decline of inoculant and give full play to the inoculation effect of inoculant.
(5) Cooling and cleaning: the gray cast iron after box injection is unpacked after 2H and enters the sand dropping system to obtain the gray cast iron with a small amount of molding sand on the surface. After rough polishing and fine polishing, the sand on the surface is removed, then the pouring riser is removed, and the burrs and excess parts are polished to obtain the gray cast iron.