Abstract: This paper focuses on the research of rapid casting methods for small parts of tractors, aiming to meet the short cycle and low-cost demands of small-batch manufacturing. The study incorporates the rapid casting process, mold design, and rapid molding techniques. The results indicate that the qualified blanks can be rapidly produced through moldless precision forming machines and subtractive manufacturing technology, resulting in cost savings and a shortened manufacturing cycle.
1. Introduction
The internal and external lifting arms, separator manipulators, transmission levers, and brake housings of tractors are classified as small parts. During product structure design, process adjustments, and new product trials, there is a demand for small-batch manufacturing. Traditional casting methods with patterns cannot meet these requirements due to long lead times and high costs. Therefore, there is a need to develop a rapid, efficient, and low-cost casting method to fulfill the small-batch manufacturing needs of tractor small parts.
The table below summarizes the comparison between traditional casting methods and the proposed rapid casting method:
| Casting Method | Lead Time | Cost | Flexibility | Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Casting | 2-3 Months | >3000 Yuan | Low | Low |
| Rapid Casting | Significantly Shorter | Significantly Lower | High | High |
2. Research Methodology
2.1 Equipment and Methods
The research employs moldless digital precision forming machines for milling and shaping water glass sand and resin sand molds and cores. A 500kg medium-frequency melting furnace is used for metal melting, and a manual molding line is utilized for assembly, molding, and pouring. Spectral analyzers, microscopes, and performance testing equipment are used for pre-pouring composition control and performance testing.
2.2 Rapid Casting Process Flow
The rapid casting process for tractor parts. The process integrates CAD design, subtractive manufacturing, and sand casting methods.
2.3 Casting Process Design
To ensure production efficiency and process yield for small-batch castings, a one-pouring-system-connecting-multiple-castings design approach is adopted. The casting process and parting scheme design follow these methods:
- 3D Modeling: Use 3D modeling software for casting modeling to facilitate CAD design of processes and parting.
- Pouring System Design: Determine the number of castings per box, as well as the size and quantity of the pouring system and risers based on component size, structure, and sand block size.
- CAE Simulation: Use casting simulation software to predict casting defects and optimize the casting process.
Table: Key Steps in Casting Process Design
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | 3D Modeling of Casting |
| 2 | Pouring System Design |
| 3 | CAE Simulation |
2.4 Parting Design, Sand Block Forming, and Machining
2.4.1 Parting Design
After completing the casting process design, the casting mold is reversely sought, and parting design is carried out. The principle of “few partings and few assemblies” is followed, typically divided into upper and lower molds and internal cores.
2.4.2 Sand Block Forming
The moldless precision forming machine uses milling to complete the processing and shaping of molds and cores. Sand blocks of different sizes and shapes are manually created for small-batch manufacturing of tractor small parts.
Table: Sand Block Forming Methods
| Material | Method Description | Strength | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Glass Sand | Mixed with silica sand and water glass, low cost, suitable for low-strength molds | Moderate | Upper and lower molds with no thin-wall structure |
| Phenolic Resin Sand | Mixed with specific binders and hardeners, high strength | High | Cores with high strength requirements |
2.4.3 Machining and Shaping
The sand blocks are processed into the required molds and cores using a moldless precision forming machine.
2.5 Core Assembly, Pouring, and Clean-up
After processing and shaping, the molds and cores are assembled, poured, and cleaned. The specific methods are as follows:
- Assembly and Measurement: Measure and further modify the molds and cores.
- Pre-assembly: Use mud strips to check wall thickness.
- Painting and Drying: Apply and dry paint on the molds and cores.
- Boxing and Backfilling: Use sand boxes, fill with back sand, and add risers as needed.
- Pouring and Cooling: Pour the molten alloy and let the castings cool.
- Clean-up: Remove the sand boxes, gates, and risers. Clean and shot-peen the castings.
3. Experimental Results
3.1 Water Glass Sand Casting Test
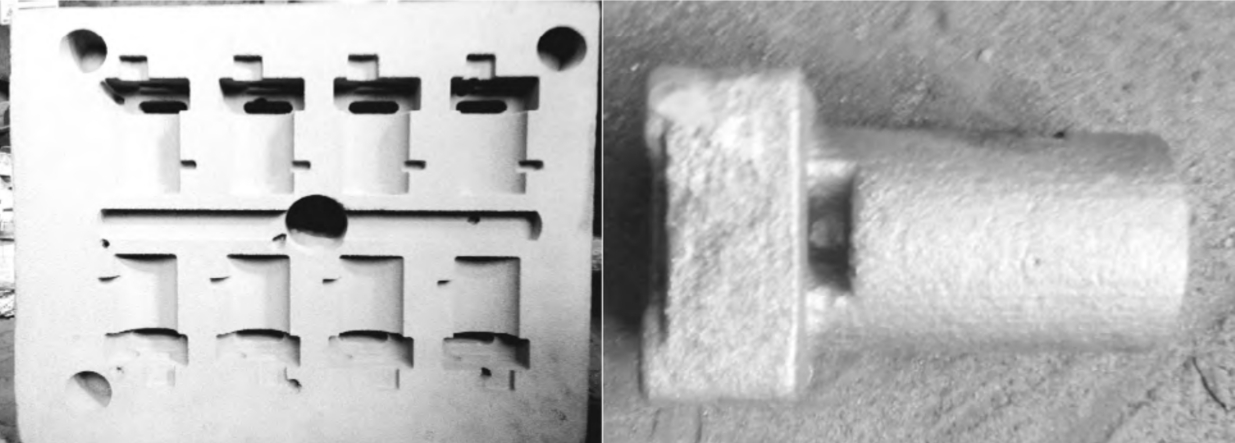
The water glass sand casting test of a tractor brake arm. The casting dimensions are 160mm × 60mm × 60mm, with a single piece weighing 0.85kg. Using traditional casting methods, the process takes at least 30 days and costs 3880 yuan. With digital moldless casting technology, the process takes only 2 days and costs 950 yuan, resulting in a 93% reduction in time and a 75% cost savings.
3.2 Phenolic Resin Sand Casting Test
The phenolic resin sand casting test of a tractor distributor housing. The casting dimensions are 90mm × 90mm × 130mm, with a single piece weighing 4.7kg. Using traditional casting methods, the process takes at least 30 days and costs 5080 yuan. With digital moldless casting technology, the process takes only 4 days and costs 1400 yuan, resulting in a 86.7% reduction in time and a 72.2% cost savings.
4. Conclusion
- The integration of CAD, CAE, and moldless forming technology eliminates the mold development and manufacturing stage, reducing the manufacturing cycle by over 85% and costs by over 70%.
- Using moldless digital precision forming machines and numerical control cutting technology, the rapid casting of tractor small parts achieves dimensional accuracy within 0.5mm, surface roughness Ra 25μm, and dimensional tolerance CT10.
- The optimal conditions for water glass sand and phenolic resin sand blocks in terms of strength and machinability are: water glass addition of 5%-6%, phenolic resin addition of 1% for each type, and hardener addition of 1%-6% of CPI-1600.
This research demonstrates the feasibility and advantages of rapid casting methods for small parts of tractors, offering a promising solution for small-batch manufacturing.
