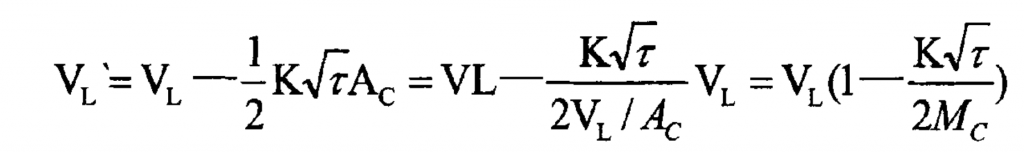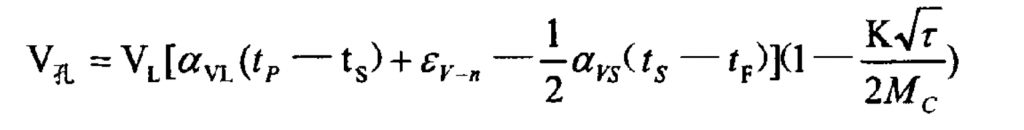After mold filling, the volume VL ‘of molten metal in the casting is equal to the cavity volume VL minus the amount solidified after pouring
Metal volume, i.e.:
Where:
MC – modulus of casting, MC = VC / AC = VL / AC;
AC – heat dissipation surface area of casting.
Therefore, the pouring time shall be considered τ The formula affecting the volume of shrinkage casting defects is:
As can be seen from the formula:
(1) Improving liquid shrinkage coefficient of cast alloy α VL and solidification shrinkage ε V-N increases the shrinkage cavity volume; And improve its solid-state shrinkage coefficient α VL, the shrinkage casting defects are reduced;
(2) The mold has strong chilling ability (such as metal mold), increases (TS TF) and K value, and reduces shrinkage casting defects;
(3) Increase the pouring temperature, such as increasing the volume of shrinkage casting defects:
(4) Extend pouring time τ, Reduce the volume of shrinkage casting defects. When the casting time is equal to the casting solidification time, the shrinkage casting defect disappears:
(5) For general alloy castings, the larger the modulus is, the larger the defect volume of shrinkage casting is (except for gray iron, nodular iron and vermicular iron with graphite as cast).
For alloy castings with a certain crystallization temperature range, shrinkage casting defects will occupy a certain volume. The influence of the above factors on the total volume of shrinkage cavity and shrinkage porosity casting defects is applicable in principle.