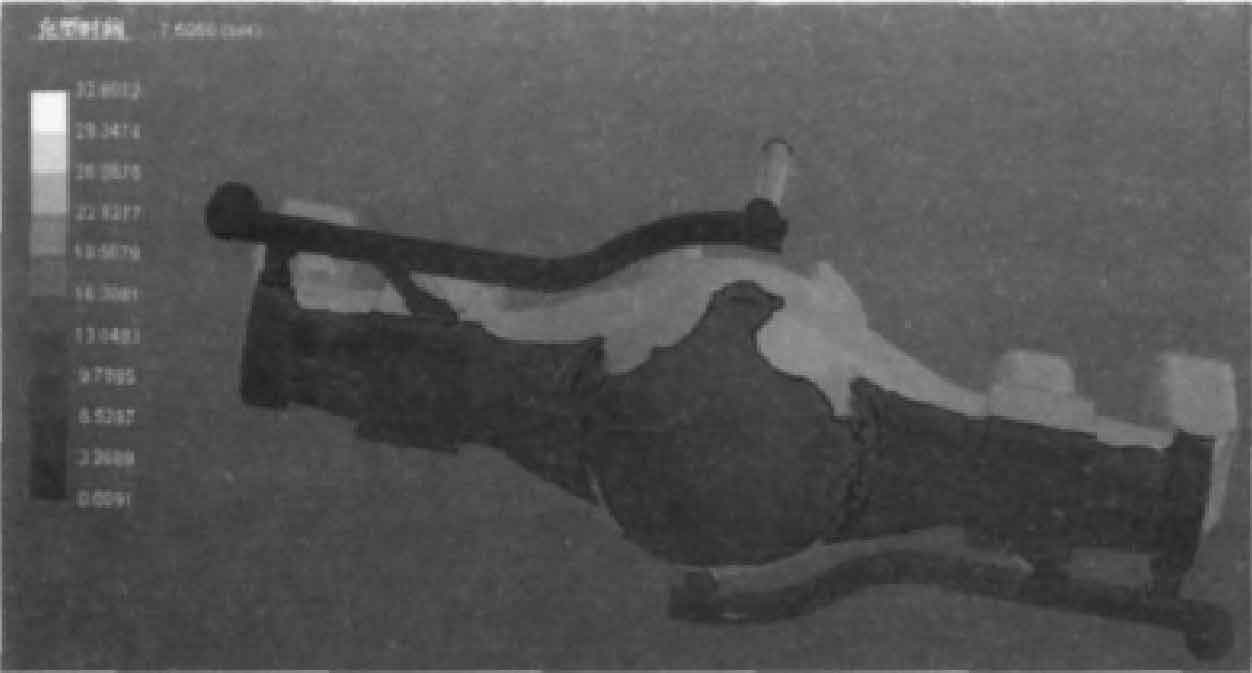
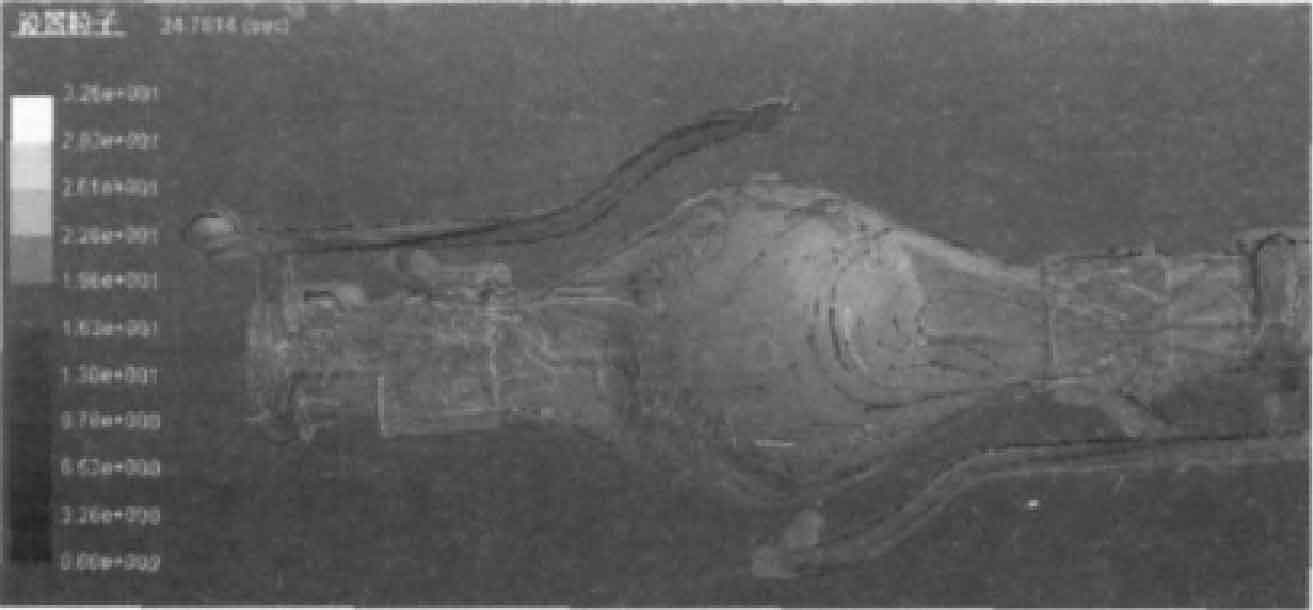
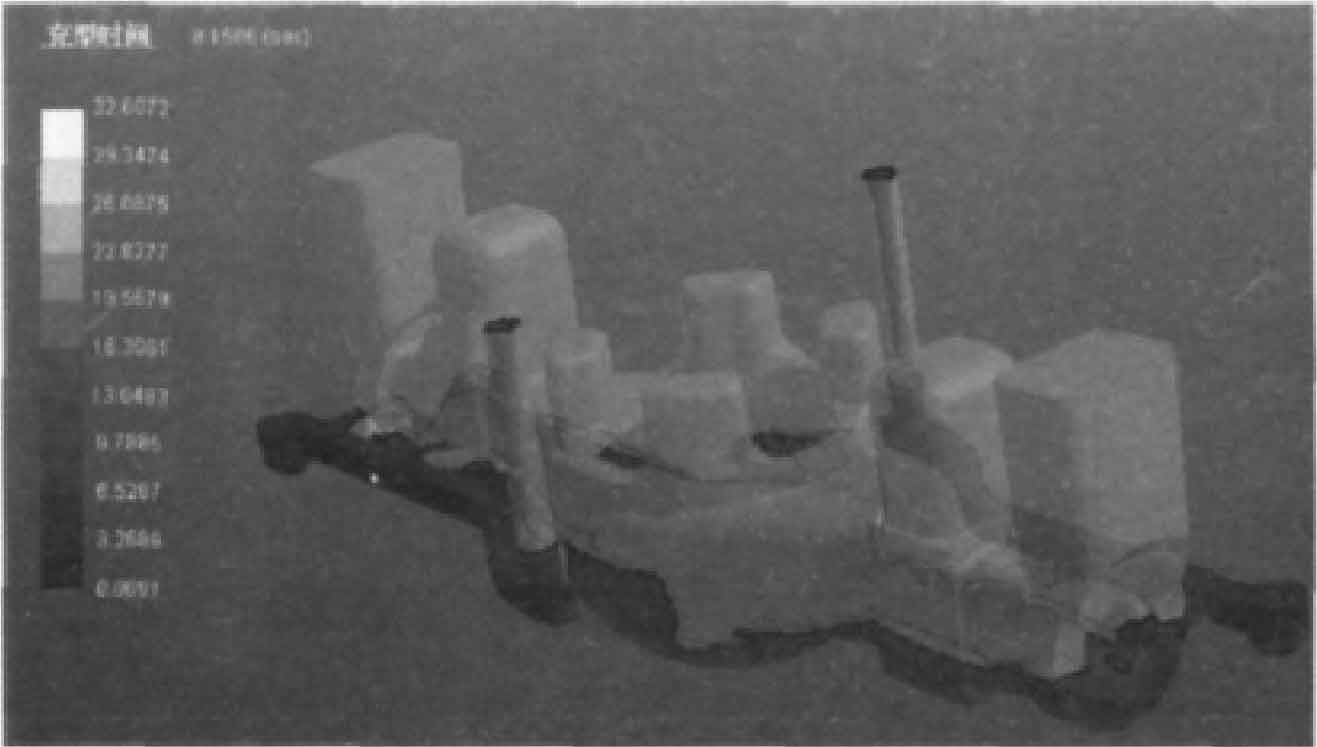
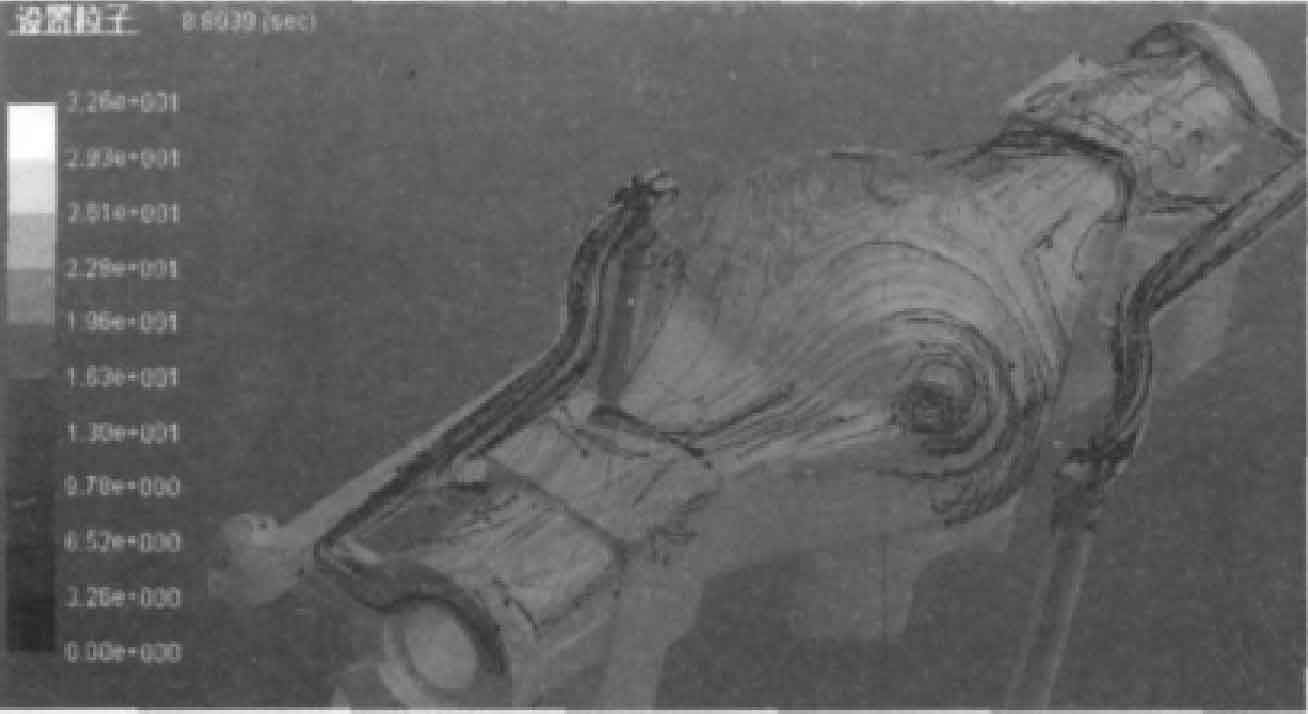
(1) Mold filling simulation analysis. Figure 1 and Figure 2 are the simulation diagrams of sand casting at 7.5 s and 8 s respectively. Fig. 3 and Fig. 4 are particle tracking diagrams of sand casting filling for 8 s and 24 s respectively.
It can be seen from Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 that liquid metal enters from both ends of the mold and collides at the intersection in the middle of the mold. The mold filling is unstable, the scouring force on the mold is large, and it is easy to produce oxidation inclusions. It can be seen from particle tracking figures 3 and 4 that during the liquid metal filling process, vortices appear on both sides and near the axial direction of the “pot bottom” of the sand casting of the rear axle housing. There is a size gradient at the bottom edge, where the molten metal has a large impact on the mold, which is easy to make the inclusions enter the sand casting with the vortex. The middle bottom wall of sand casting is thin. If the exhaust is not smooth, there may be air wrapping defects, which will destroy the continuity and compactness of sand casting matrix.
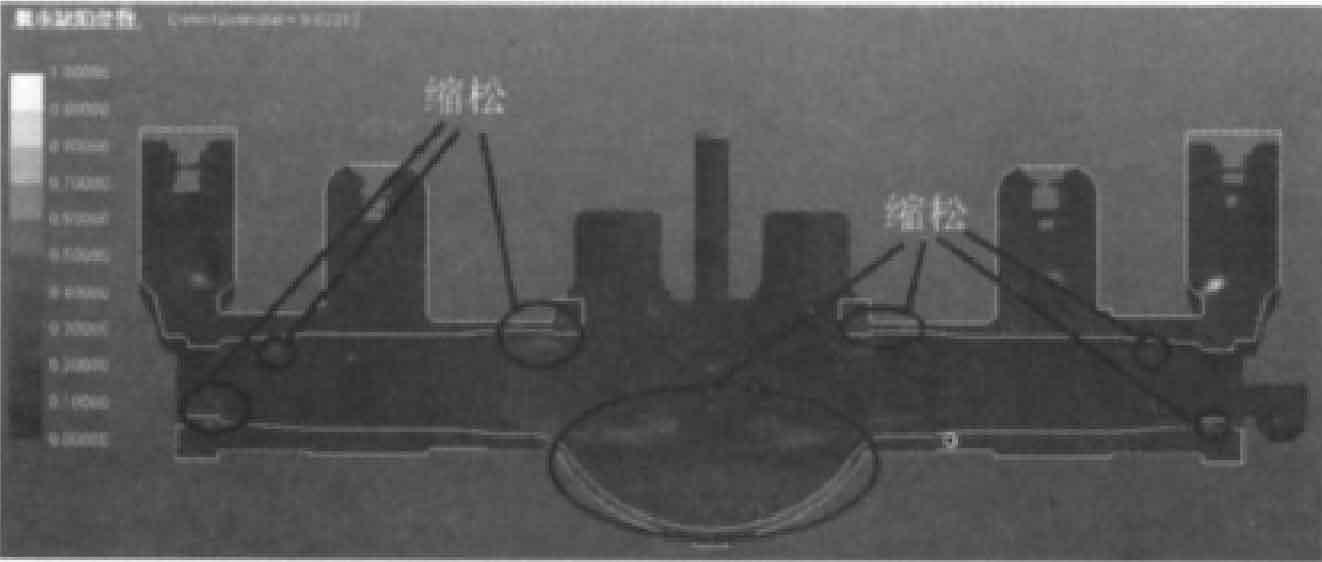
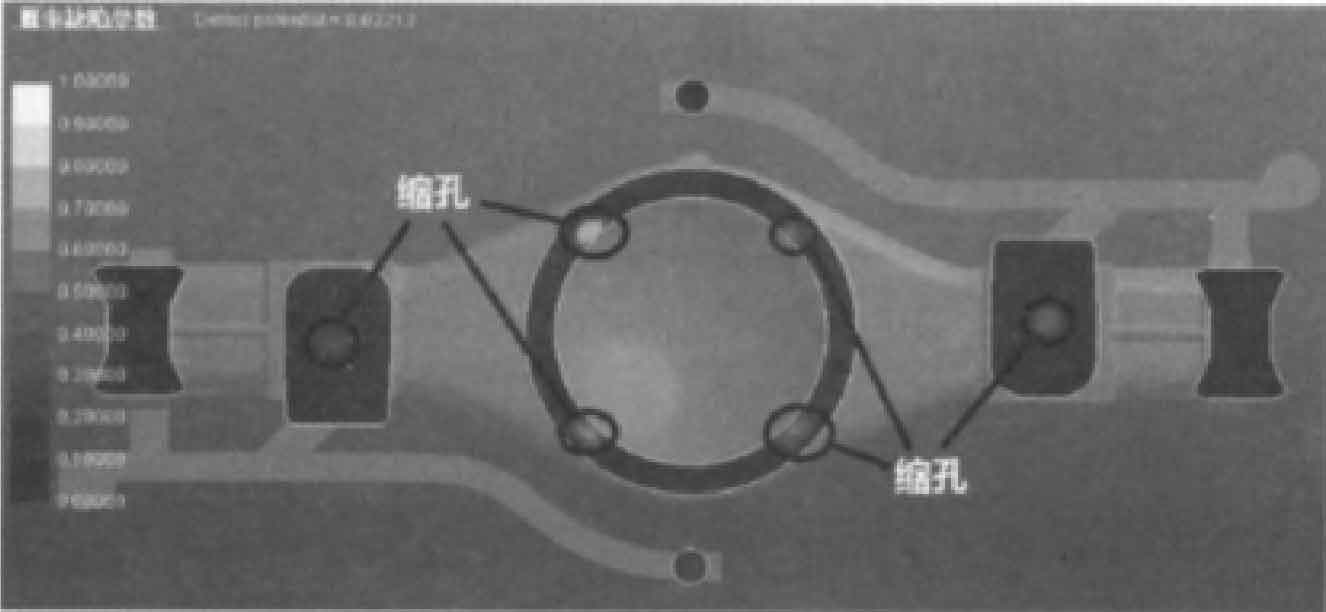
(2) Simulation analysis of solidification process. Fig. 5 is the defect probability parameter diagram of the sand casting of the rear axle housing, showing the location and size distribution of shrinkage porosity and shrinkage cavity that may occur in the sand casting respectively.
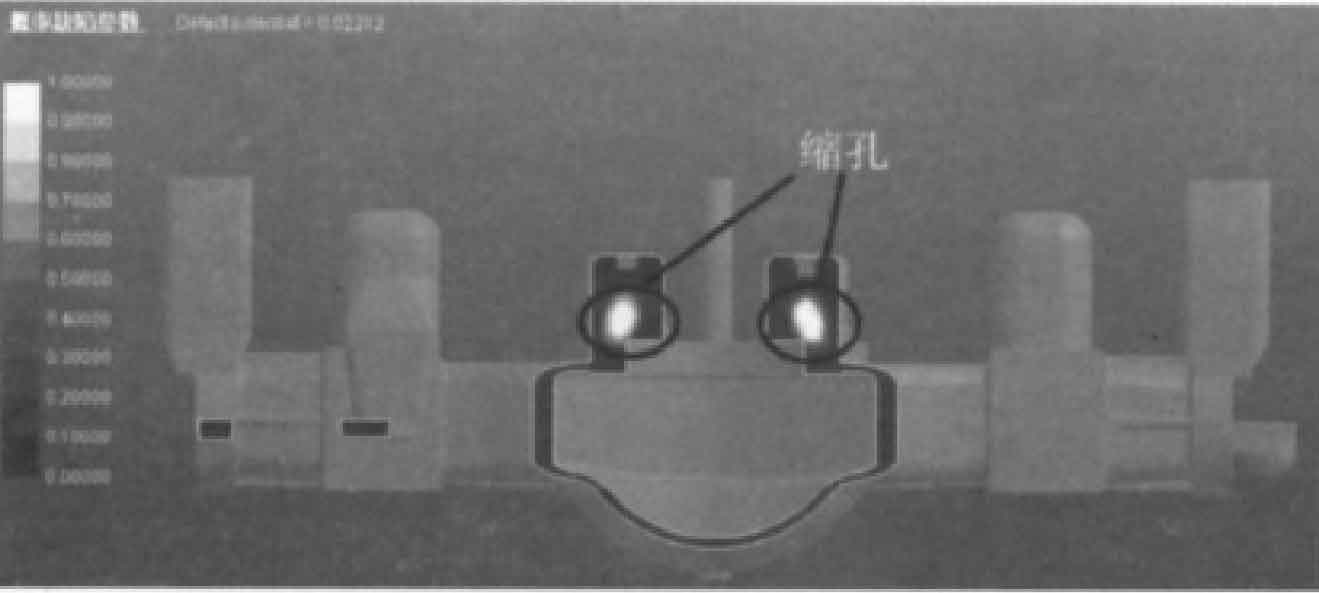
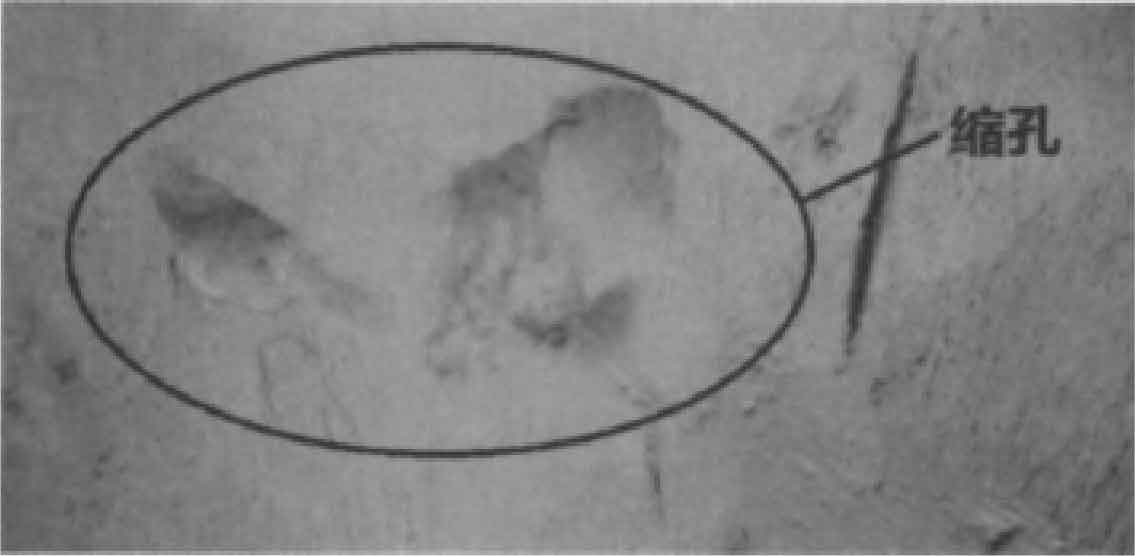
It can be seen from Figure 5 that the shrinkage porosity probability of sand casting near the middle step and bottom reaches 0.6. The middle step of sand casting is the last solidification part, and some shrinkage cavities appear in the step of sand casting, as shown in Fig. 5B and 5C; The simulation results are consistent with the shrinkage cavity position of sand castings in actual production, as shown in Figure 6. There is a large shrinkage cavity around the ring boss in the middle of the sand casting of the rear axle housing, and the feeding of the boss by the four risers is not enough, which indicates that the size of the riser is too small and needs to be increased in the middle. The hot spot radius at both ends of sand casting is large, so it is necessary to place cold iron to realize sequential solidification. At the same time, the gating system should be improved to enhance the exhaust capacity.
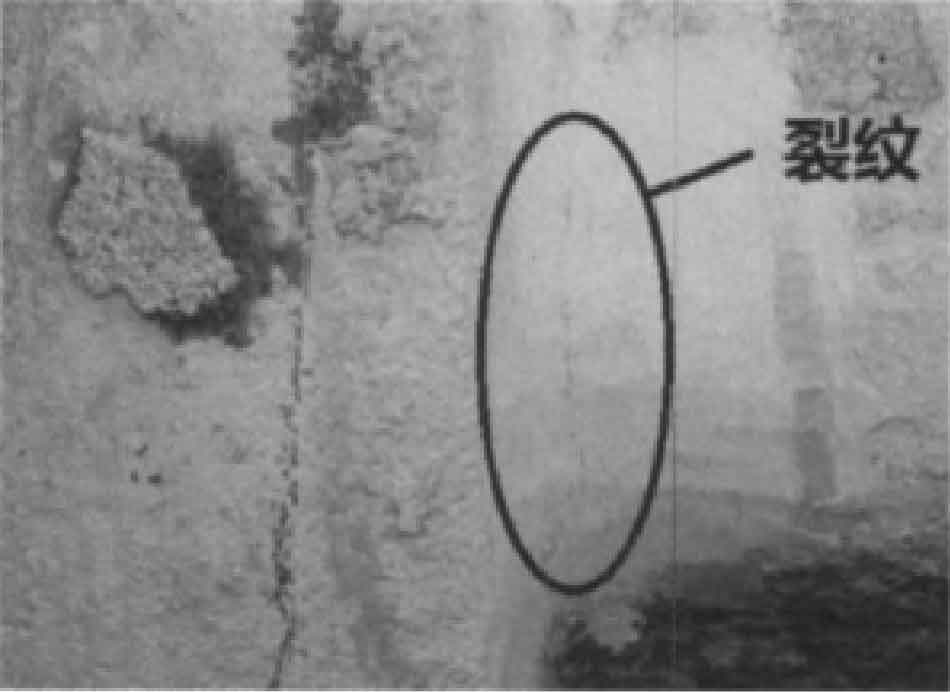
Due to the large shrinkage and linear shrinkage of steel castings, shrinkage cavity, shrinkage porosity and crack defects are easy to occur. During the solidification process of sand casting, the fillet radius at the hot joints at both ends of the rear axle housing is too small, the transition design between thin wall and thick wall is unreasonable, the internal and external cooling speed is quite different, resulting in large tensile stress and cracks, as shown in Figure 7.