Spheroidizing treatment and inoculation treatment are essential pre furnace treatment steps for raw molten iron of nodular cast iron. The purpose of spheroidizing treatment is to safely introduce spheroidizing elements into molten iron and promote the formation of spherical graphite crystals. Inoculation treatment is to obtain higher Eutectic Transformation Temperature and avoid white cast iron defects.
According to the material and performance requirements of nodular iron castings for hub support, Eken 5610 is selected as spheroidizing agent, with the addition amount of 1% and the weight of 4kg / package. For better spheroidizing effect, smash the spheroidizing agent into small pieces with the particle size controlled at 5 mm ~ 25mm. In order to make the spheroidizing alloy add molten iron more smoothly and ensure the high absorption rate of spheroidizing elements, many spheroidizing treatment methods have been developed, such as impulse method, pressure magnesium addition method, magnesium wire method, in mold spheroidizing treatment method and so on.
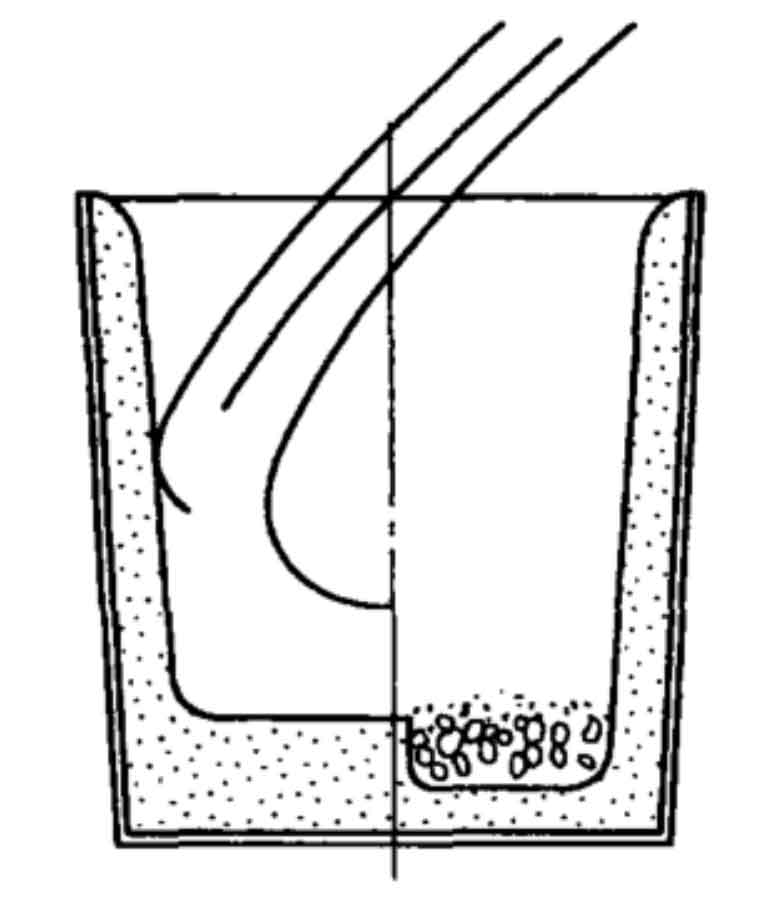
Considering the plant equipment and production efficiency, the most widely used flushing method in China (schematic diagram 1) is adopted for spheroidizing treatment, that is, an open cylindrical molten iron ladle is adopted, and the spheroidizing agent is placed in the pit on one side of the ladle bottom. In order to avoid the self ignition of spheroidizing agent caused by too high heat in molten iron ladle, the spheroidizing agent is added to the groove and then covered with 0.5% dry iron filings covering agent for compaction. When the water is discharged after smelting, it is necessary to avoid flushing the molten iron directly onto the spheroidized alloy, so as to ensure that the molten iron is completely immersed in the bottom of the ladle and then the spheroidization reaction occurs, so as to reduce the intensity of the reaction and improve the recovery rate of magnesium. The whole spheroidizing process lasts 40 ~ 100 s to ensure full spheroidization.
In order to obtain more uniform microstructure and properties of sections with different thicknesses of complex castings, the molten iron after spheroidizing treatment needs to be inoculated. The inoculation process is to add a small amount of alloy material to the molten iron to achieve more stable Eutectic Transformation, increase the number of graphite balls in the casting, improve the supercooling tendency of molten iron and eliminate the white mouth tendency caused by spheroidizing elements. In order to maximize the inoculation effect and meet the specific technical requirements of different castings, many inoculants with different functions and brands have been developed in the market. Combined with the technical requirements of hub support casting, Eken calcium barium inoculant is selected in production.
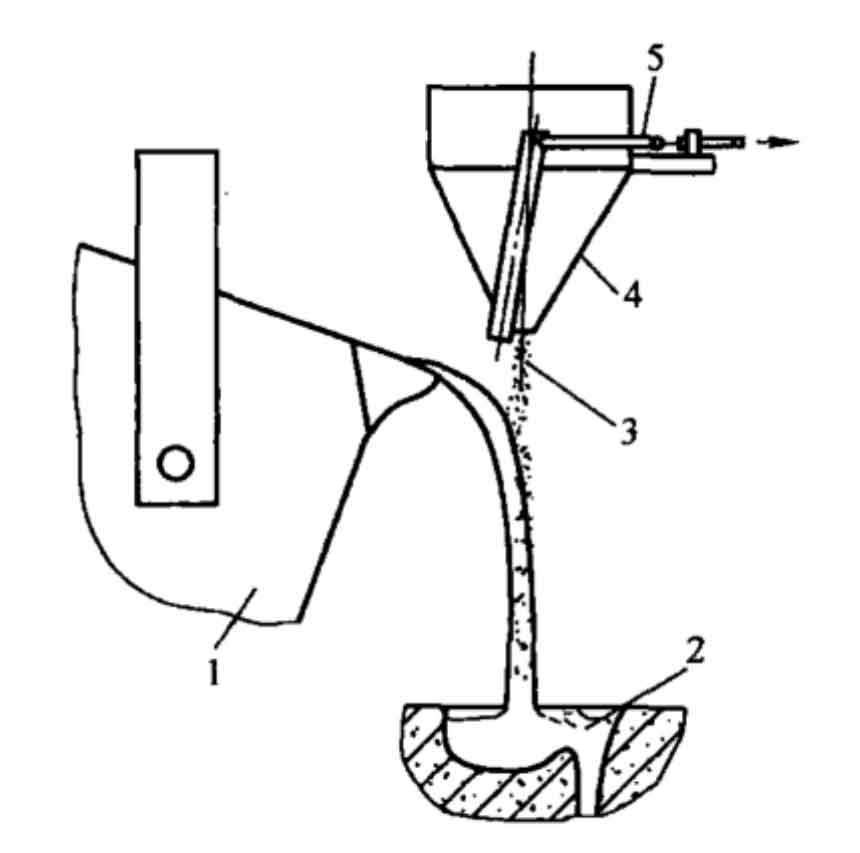
This inoculant can enhance the graphite core and improve the spheroidization grade. It is easier to dissolve and absorb than ordinary inoculants, and has strong anti recession ability, which can make the casting obtain more uniform structure. In order to prevent the molten iron from staying in the ladle for too long after inoculation treatment, the method of secondary flow inoculation is adopted (the primary inoculation is carried out during smelting, and the amount of inoculant is 0.4%), that is, the inoculant is added while the molten iron is poured into the mold, so that the inoculation time is closer to the solidification time, so as to ensure that the molten iron is in more full and uniform contact with the inoculant, and the inoculation effect is good. Fig. 2 is a schematic diagram of common flow inoculation. The addition amount of flow inoculant is 0.1%, the addition rate is 4.5 g / s, and the particle size is 0.2 mm ~ 0.7 mm.
After the pre furnace treatment steps are completed, the scum on the surface of molten iron shall be removed as soon as possible. In order to better monitor the treatment effect of molten iron, the test block method is used for sampling before pouring to check the composition and spheroidization rate after the furnace. Pouring can be carried out only when the temperature measured by the temperature measuring gun drops to 1415 ℃ ~ 1425 ℃.