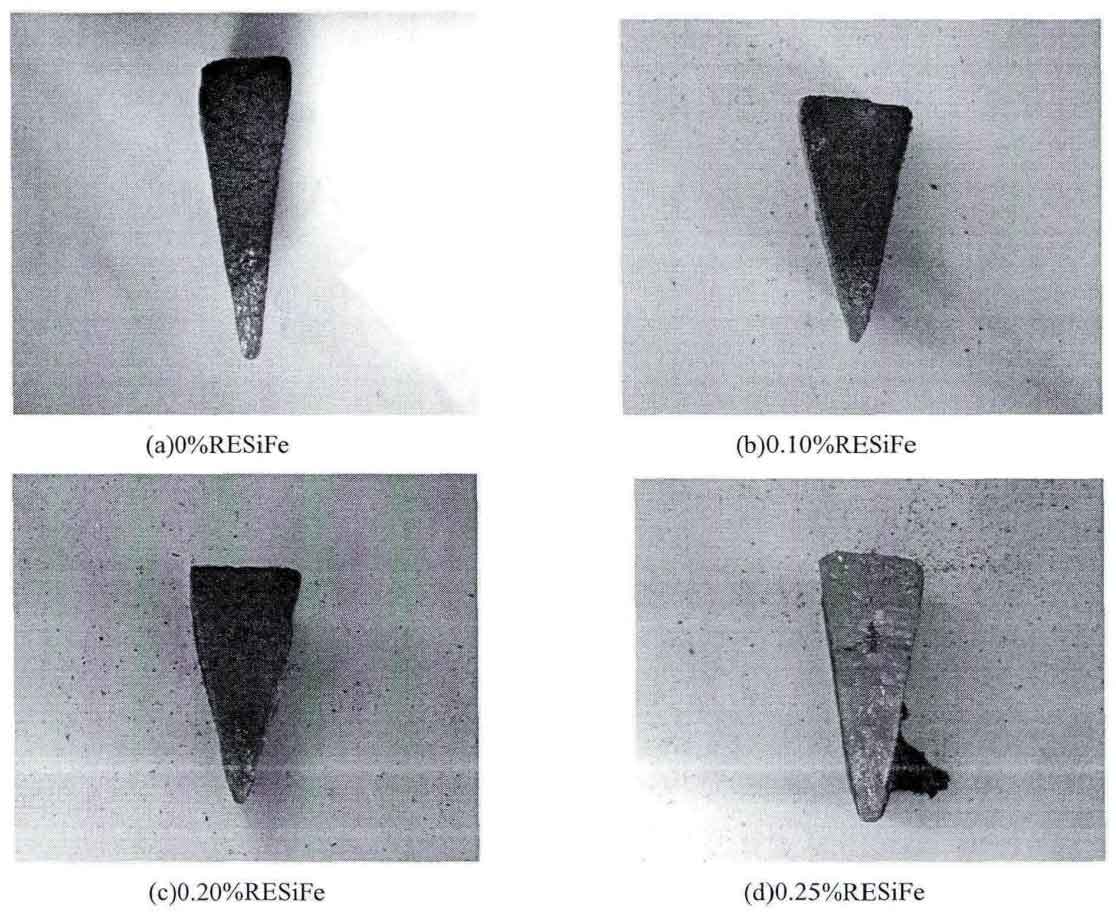
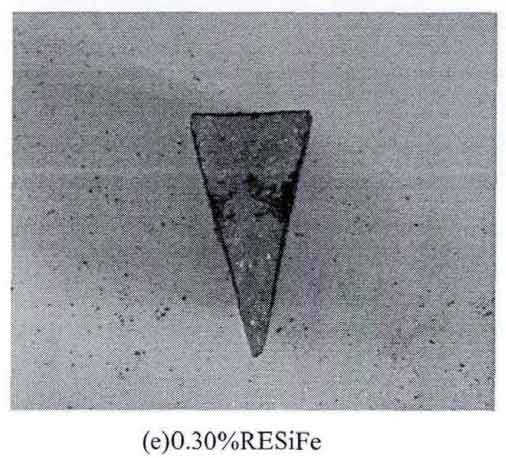
Change trend of white mouth width of triangular test piece: 5.5mm; 4.6mm ; 3.8mm; All white mouth; All white mouth (black spots in the heart), as shown in the table.
| Furnace No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Rare earth /% | 0 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.25 | 0.3 |
| White mouth width / mm | 5.5 | 4.6 | 3.8 | white | white |
It can be seen from the table and figure that when the addition amount of rare earth ferrosilicon alloy is within a certain range, it can play an obvious inoculation role, promote graphitization and reduce the tendency of white cast iron, but when the addition amount is too large, it will promote the white cast iron with low carbon equivalent. When the content of rare earth is between 0-0.2%, it has good inoculation effect, and the sample has less white mouth; However, when the addition of rare earth exceeds 0.2%, the white tendency of gray cast iron begins to increase significantly, and even reaches complete white, and the modification effect changes suddenly.
Rare earth has a significant dual effect on the white tendency of gray cast iron. When rare earth (0.1% – 0.2%) is less added to low carbon equivalent gray cast iron, the white tendency of gray cast iron is significantly weakened, but when rare earth is added too much, it will increase the white tendency of gray cast iron. This is because when rare earth is added less, rare earth reacts with oxygen, sulfur and other elements in molten iron to form rare earth oxides and rare earth sulfides, which have high flame points, Suspended in molten iron, as the external core of graphite, it promotes the nucleation and crystallization of graphite, which hinders the formation of white cast iron; At the same time, rare earth can increase the binding force between iron and carbon atoms. When the rare earth reaches a certain amount (> 0.2%), this influence is more obvious. At this time, rare earth promotes the formation of cementite, inhibits the precipitation of graphite and promotes the formation of white mouth.