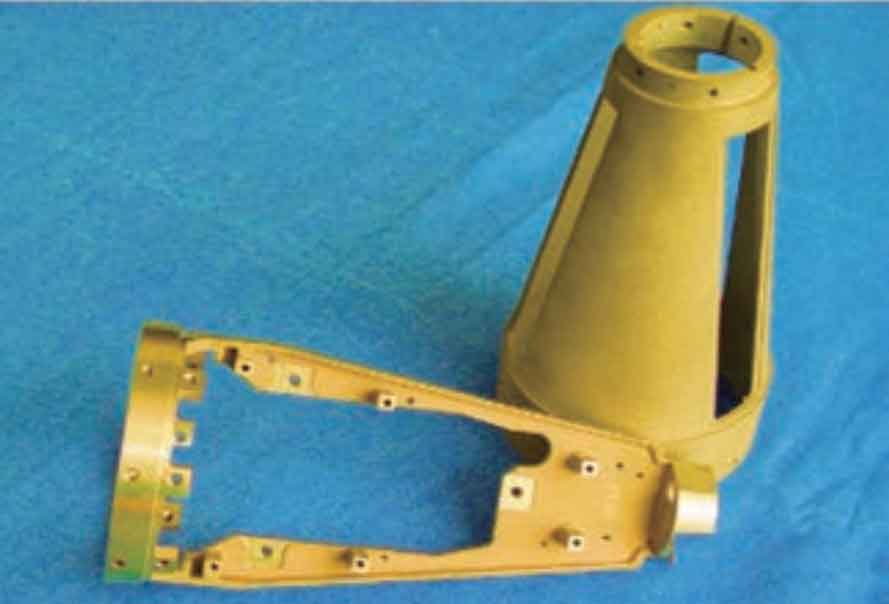
Aluminum alloy investment castings have been widely used in aerospace engines, airframe structures and airborne equipment. The mechanical properties can reach 350~500MPa, which is equivalent to the performance of medium-strength deformation aluminum alloy. The integrated forming manufacturing can replace some forging and riveting assemblies and sheet metal machining assemblies to achieve weight reduction in structural design, reduce manufacturing costs and shorten production cycle. A large number of aluminum alloy investment castings are used in the F – 16, F – 18, F – 22 and F – 35 fighter planes of the US military, and F357 aluminum alloy investment castings are also widely used in the hatch, flap, electronic instrument cabin shell and other components of the Hawkeye E – 2C early warning aircraft. Aluminum alloy investment castings are also widely used in the field of civil aircraft. Large aluminum alloy investment castings are used in the precision casting beam, cab electronic instrument framework, engine fuel pump shell, boarding door, etc. of Boeing’s 7X7 civil aircraft series, and in the cargo door frame beam, cab instrument framework, flap slide rail, etc. of Airbus’s civil aircraft series.

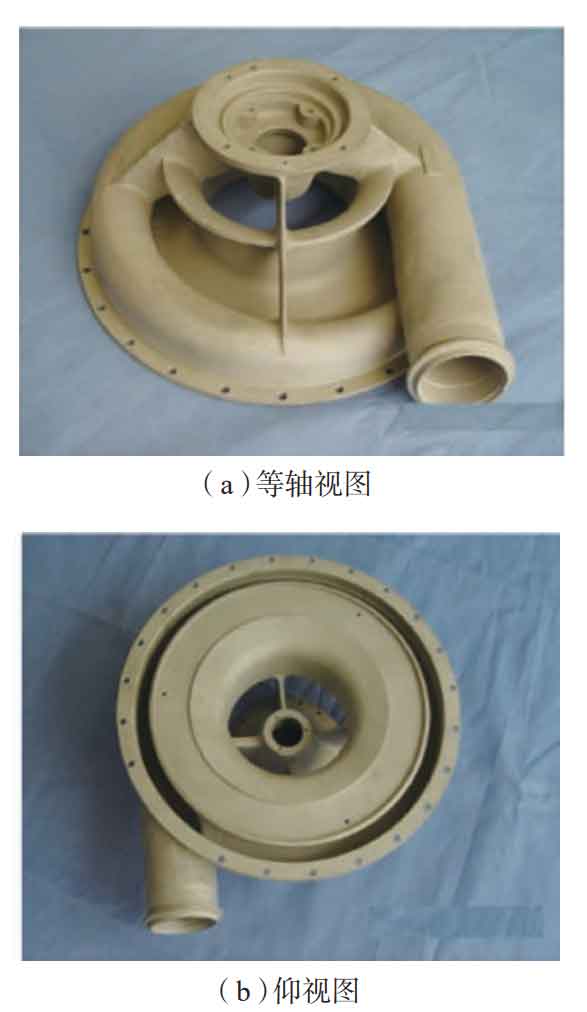
China’s aluminum alloy investment casting is mainly divided into ceramic shell and gypsum mold. At present, ceramic shell is still the mainstream manufacturing process of aluminum alloy investment casting in China. Figure 1 shows the volute aluminum alloy investment casting applied to Shenzhou spaceship series, which is made of ceramic shell, and the overall dimension is φ 320mm × 250mm, average wall thickness is 3mm. Figure 2 shows the aluminum alloy investment casting of the electronic shell of a missile fuze used by the navy, with the overall dimension of φ 98mm × 160mm, the average wall thickness is 5mm. The aluminum alloy gypsum mold investment casting is a new method developed internationally in the 1970s. In 1982, the original three mechanical departments organized the joint research on “aluminum alloy gypsum mold investment casting technology”, and initially completed the development of gypsum mixture. In the 1980s, China introduced gypsum mold investment casting production line from TEC, which promoted the industrial application of gypsum mold aluminum alloy investment casting technology in China.
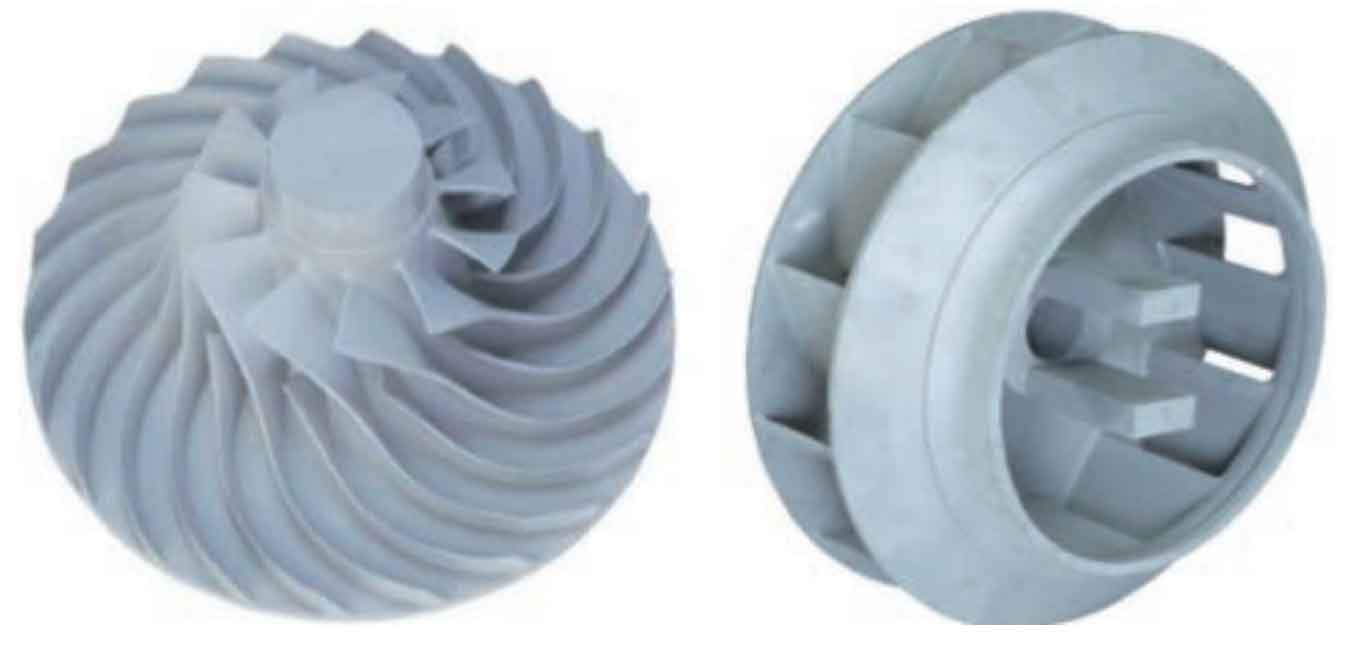

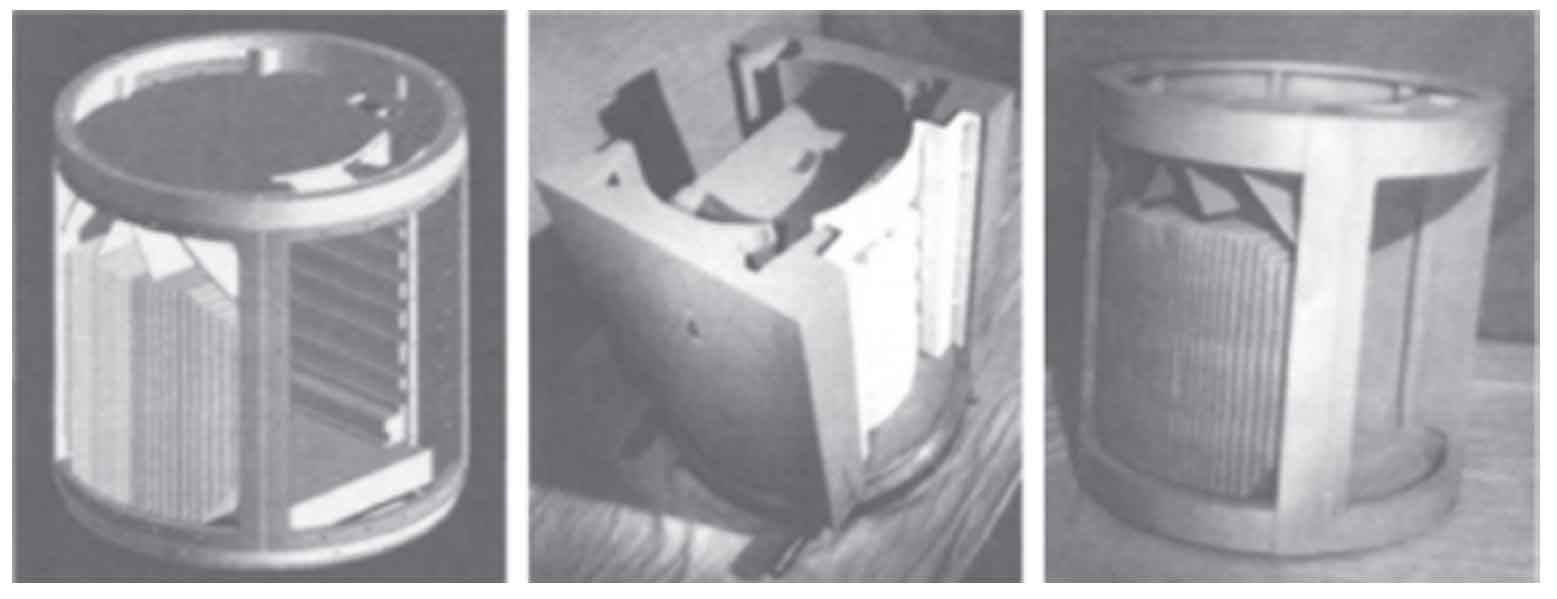
In the 1990s, China introduced the gypsum type SOPHIA process from the United States, and completed the digestion and absorption of gypsum mixture formula and overall manufacturing process. Based on this, the Pingyuan Optoelectronic Factory is the support unit for the industrial mass production of aluminum alloy gypsum type investment casting in China, which can carry out the gypsum type investment casting of large size and high-precision aluminum alloy components for aerospace. Xiong Yancai of the Beijing Institute of Aeronautical Materials successfully completed the one-time complete forming of the aluminum alloy impeller casting of a certain type of engine with a blade thickness of only 1.5mm and no allowance for the runner and blade by investment casting and metal mold composite casting; The impeller casting for a certain GE gas turbine was successfully cast by investment casting and resin sand composite casting, and the integral shape of the impeller tip with a wall thickness of 1.2 mm was achieved, as shown in Figure 3. Figure 4 is the structural diagram of investment precision casting of a certain type of electronic instrument shell, with a diameter of 390mm, a height of 440mm, a length of 275mm, a width of 3mm, and a spacing of 6mm on both sides of the heat sink, which is uniformly distributed along the outer side of the shell, with a total number of 26. It is a typical complex aluminum alloy precision part with integrated structure and function. In order to achieve the overall structure forming and ensure the internal metallurgical quality, Xiong Yancai uses the composite mold of resin sand mold and investment precision shell mold, It not only ensures the integral forming of the casting, but also ensures the internal metallurgical quality of the casting.