After a series of air hole measures are verified to have no effect, re-examine the defect characteristics. After dissecting the bodies of several defective castings, it was found that the holes were not smooth, there were local unevenness and shrinkage casting defects.
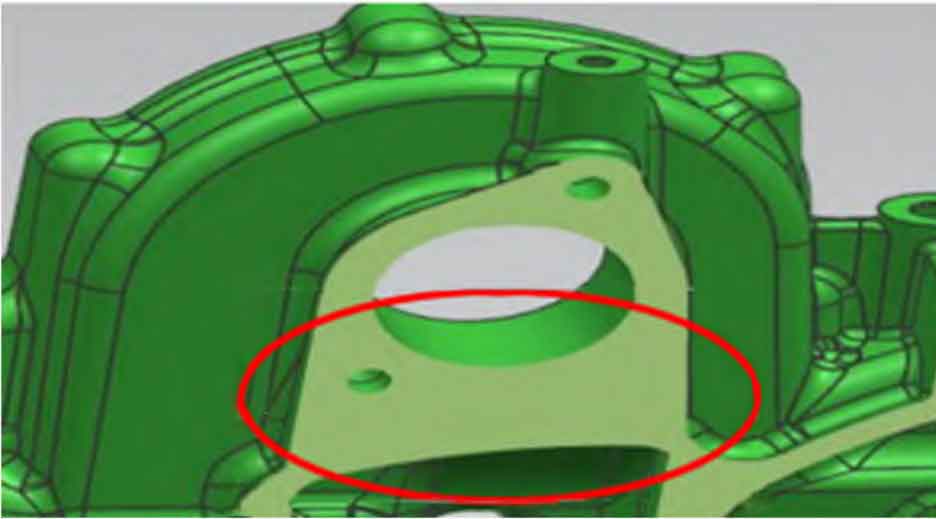
According to the three-dimensional diagram of the casting, the flange at the highest point is a circle of uniform thin wall with a wall thickness of about 5 mm, but there is a 65 mm piece below the water pump hole × 45 mm × 33 mm large solid hot spot (as shown in the figure), in addition, it is surrounded by a thin wall of about 5 mm, and there is no effective feeding channel during the final solidification. Only the molten iron above it can be used for feeding, which causes shrinkage casting defects at the highest point above, and causes the internal pressure of the molten iron at this position to decrease before solidification. The sand-coated iron mold process itself is difficult to exhaust. One of the main principles to prevent gas is to rely on the internal pressure of molten iron to be greater than the gas escape resistance, so that the gas is discharged towards the parting surface and the mold wall, and the casting does not produce pores; However, if the internal pressure of molten iron is not enough before solidification, the gas will be easily immersed, and finally the casting defects of gas shrinkage cavity will be produced.
