1 Material of cold iron
The commonly used cold iron materials in our company include,
1) The material of cast iron cold iron is generally HT200.
2) Steel cold iron material is generally made of carbon steel, such as Q235, with a melting point of 1400-1500 ℃.
3) There are two types of graphite cold iron. Measured by volume density: 1.52-1.6g/cm (general 3-way), 1.8-2.1g/cm3 (high-purity graphite);
4) Other chilling materials. include
a. Chromium iron ore sand, using furan resin as the binder;
b. Steel sand (steel wire cut shot with a certain particle size), using water glass
Glass is used as a binder and a certain proportion of dispersant is added.
2 Pretreatment of chilled iron
Pre treatment includes surface treatment and setting anti detachment measures.
2.1 Surface treatment
When using cold iron, it is necessary to ensure that the surface is clean and dry. According to the different materials, pre-treatment is carried out separately.
2.1.1 Cast iron cold iron
There are two methods of manual grinding and shot blasting for cast iron cold iron, as shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1 Surface Pretreatment of Cast Iron Cold Iron
Among them, the efficiency of manual polishing is relatively low, and the working environment of workers is poor, so it is not recommended to use it. It is recommended to prioritize shot blasting treatment.
2.1.2 Graphite cold iron
Control the frequency of use and timely recycling, so that the working surface is intact and can continue to be used.
2.1.3 Surface treatment of chilled iron in the mold
1) Apply one coat of composite paint or graphite paint on the surface of the cold iron, without accumulating paint;
2) Diesel blowtorch baking is generally used before box closing;
3) After closing the box, insert the hot air duct of the hot air fan into the mold for overall baking;
2.2 Measures to prevent detachment of cold iron during use
Adopt appropriate anti detachment measures for different materials and shapes of cold iron.
2.2.1 Cast iron cold iron
Generally, a handle is cast on the non working surface of cast iron cold iron as an anti detachment device, as shown in Figure 2.
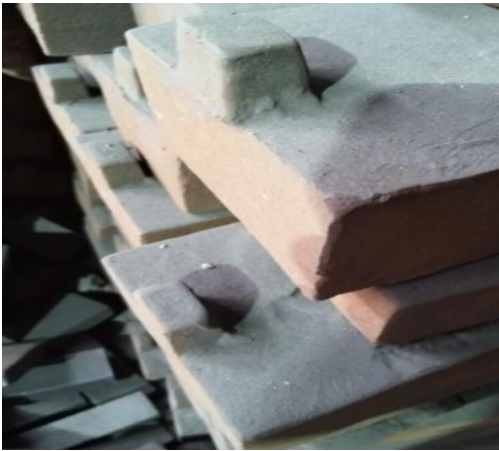

Figure 2 Anti detachment device for cast iron cold iron
2.2.2 Steel chill
Generally, the handle is welded on the non working surface of the steel cold iron as an anti detachment device, as shown in Figure 3.

Figure 3 Anti detachment device for steel cold iron
2.2.3 Graphite cold iron
Generally, grooves are machined on the non working surface of graphite cold iron as anti detachment devices, as shown in Figure 4.
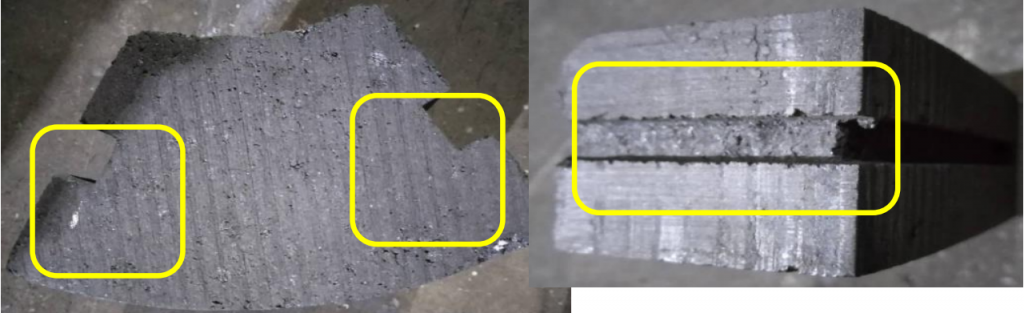
Figure 4 Anti detachment device for graphite cold iron
3 Example of using cold iron
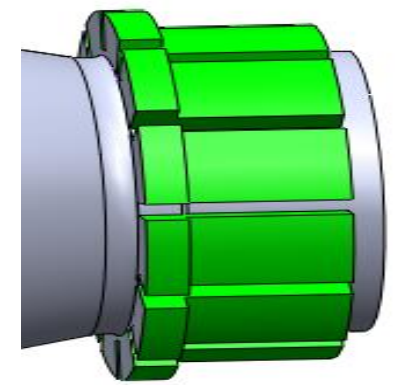
3.1 Stepped graphite cold iron
The casting in Figure 5 has a stepped structure, which is prone to shrinkage cavities Shrinkage defects. Using stepped cold iron to solve the problem of porosity in the stepped structure of castings.The three-dimensional diagram of the castings in Figure 5 using stepped cold iron is shown in Figure 6.
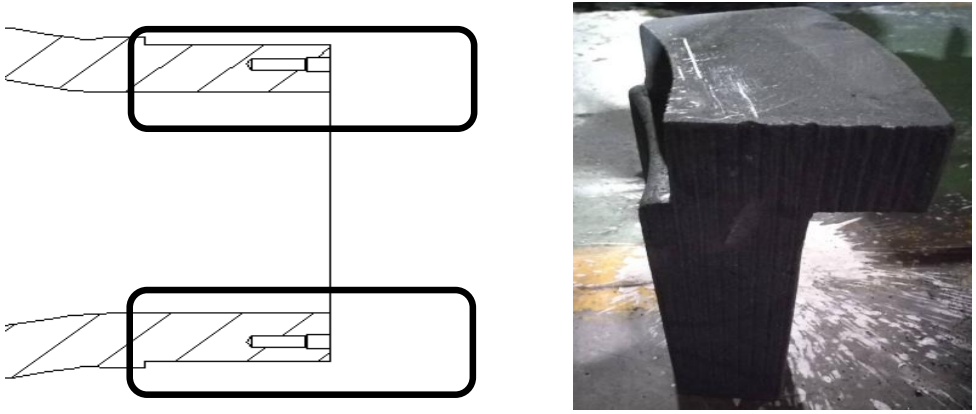
Figure 5 Selection of stepped cold iron
3.2 Selection of Different Materials of Cold Iron
For different situations, priority should be given to selecting cast iron and graphite cold iron respectively
3.2.1 Preferential use of cast iron cold iron
The casting in Figure 7 has a thicker flange in the middle and a thinner upper and lower wall thickness. Figures a) and b) show the casting CAE results of graphite cold iron and cast iron cold iron, respectively.

Figure 7 Simulation Results of Preferential Selection of Cast Iron Cold Iron
From Figure 7, it can be seen that Figure a) shows that when a circle of graphite cold iron is placed on the middle flange, there is an isolated solidification area at the flange position. Figure b) shows that there is no isolated solidification zone at the flange position when a circle of iron cold iron is set on the middle flange for quenching. Therefore, the use of cast iron cold iron for this piece has a better effect.
3.2.2 Preferential use of graphite cast iron
The casting in Figure 8 has a thinner wall thickness on the cylinder and a thicker wall thickness at the connection between the cylinder and the disc. Figures a) and b) show the casting CAE results of using cast iron chill and graphite chill, respectively.
From Figure 8, it can be seen that the wall thickness of the cylinder is thinner, and the wall thickness at the connection between the cylinder and the disc is thicker. Figure a) shows that when a circle of iron cold iron is placed at the connection between the cylinder and the disk, an isolated area appears. Figure b) shows that when a circle of graphite cold iron is placed at the connection between the cylinder and the disk, the isolated area disappears. Therefore, the use of graphite cold iron for this piece has a better effect.
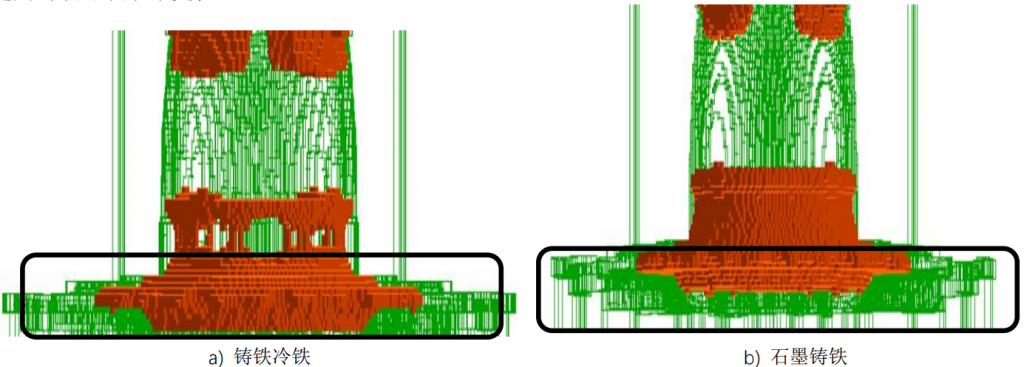
Figure 8 Simulation Results of Preferential Selection of Graphite Cold Iron
4 Conclusion
Practice has proven that using suitable materials and shapes of chilled iron can prioritize the prevention of shrinkage and porosity defects in ductile iron. Cold iron should be pre treated and equipped with anti detachment devices before use.
