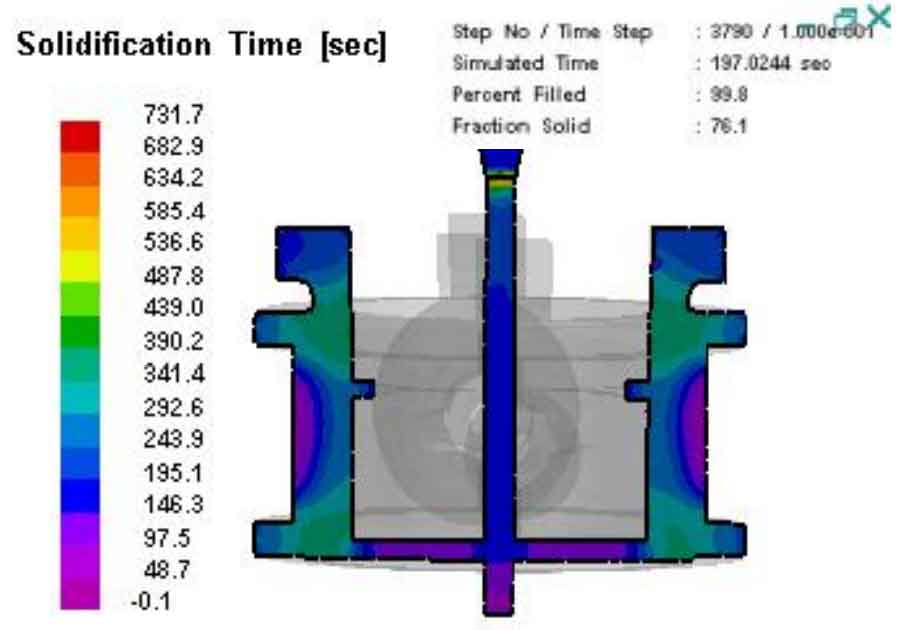
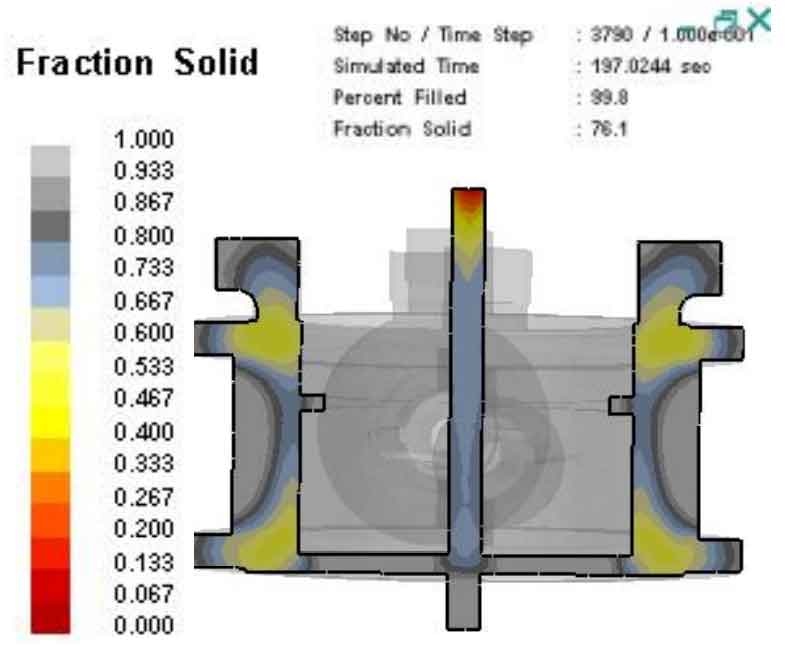
Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 are respectively solidification time nephogram and solid rate change diagram of ZY direction section plane of cast steel valve body EPC casting. The cross sections in Figures 1 and 2 are cut at the center in the ZY direction, and the time points are 197.0244s. By comparing and analyzing the two figures, it can be seen that the liquid metal temperature is the lowest and the solidification is the fastest at the runner and wall thickness; The second is the blue area in the figure, especially in the upper part of the riser. The temperature of the molten metal is slowly decreasing and begins to solidify from the outside to the inside; The place where the metal liquid temperature is higher is the connection between the riser root and the lost foam casting of the cast steel valve body, as well as the connection between the lower part of the lost foam casting of the cast steel valve body and the gate. At this time, the temperature is about 340 ℃, while other places of the lost foam casting of the cast steel valve body have tended to solidify, so that a hot spot area, i.e. isolated liquid phase area, is formed where the riser and gate are in contact, Neither the feeding of liquid metal from the outer gate nor the feeding of liquid metal in the riser can be obtained, so the shrinkage cavity and porosity defects shown in Fig. 3 occur near the gate and riser root.
It can be concluded from the above description that the original process design scheme made two mistakes: first, the metal liquid was introduced from the thick and large parts of cast steel valve body EPC casting. The consequence of artificially introducing high-temperature metal liquid in the thick and large parts is that the heat here is too high, which makes the heat in the original thick and large parts dissipate more slowly, so that it can not be supplemented by the surrounding liquid; Second, a concealed riser is placed at the thick part of the upper part of the valve body part, so that the temperature of the upper part of the riser is low due to the contact of molding sand and early solidification. According to the solid rate analysis in Figure 4, when the overall solidification of the valve body part reaches 60%, the upper part of the riser has tended to solidify, and the riser failed to play the role of feeding. Therefore, the position and size of the riser should be properly adjusted when the process improvement of cast steel valve body EPC casting is carried out.